E-pismo dla elektryków i elektroników
AUTOMATYKA, ELEKTRYKA, ZAKŁÓCENIA
Vol. 14 Nr 4 (54) 2023
Research into the Causes of Undesired Synchronisation Between the Motor Speed and the PWM Modulation Frequency in a PM BLDC Drive
Badania przyczyn niepożądanej synchronizacji prędkości obrotowej silnika z częstotliwością modulacji PWM w układzie napędowym PM BLDC
Andrzej TUTAJ; Tomasz DRABEK; Pawel PIATEK; Pawel KOCWA; Jerzy BARANOWSK
Abstract
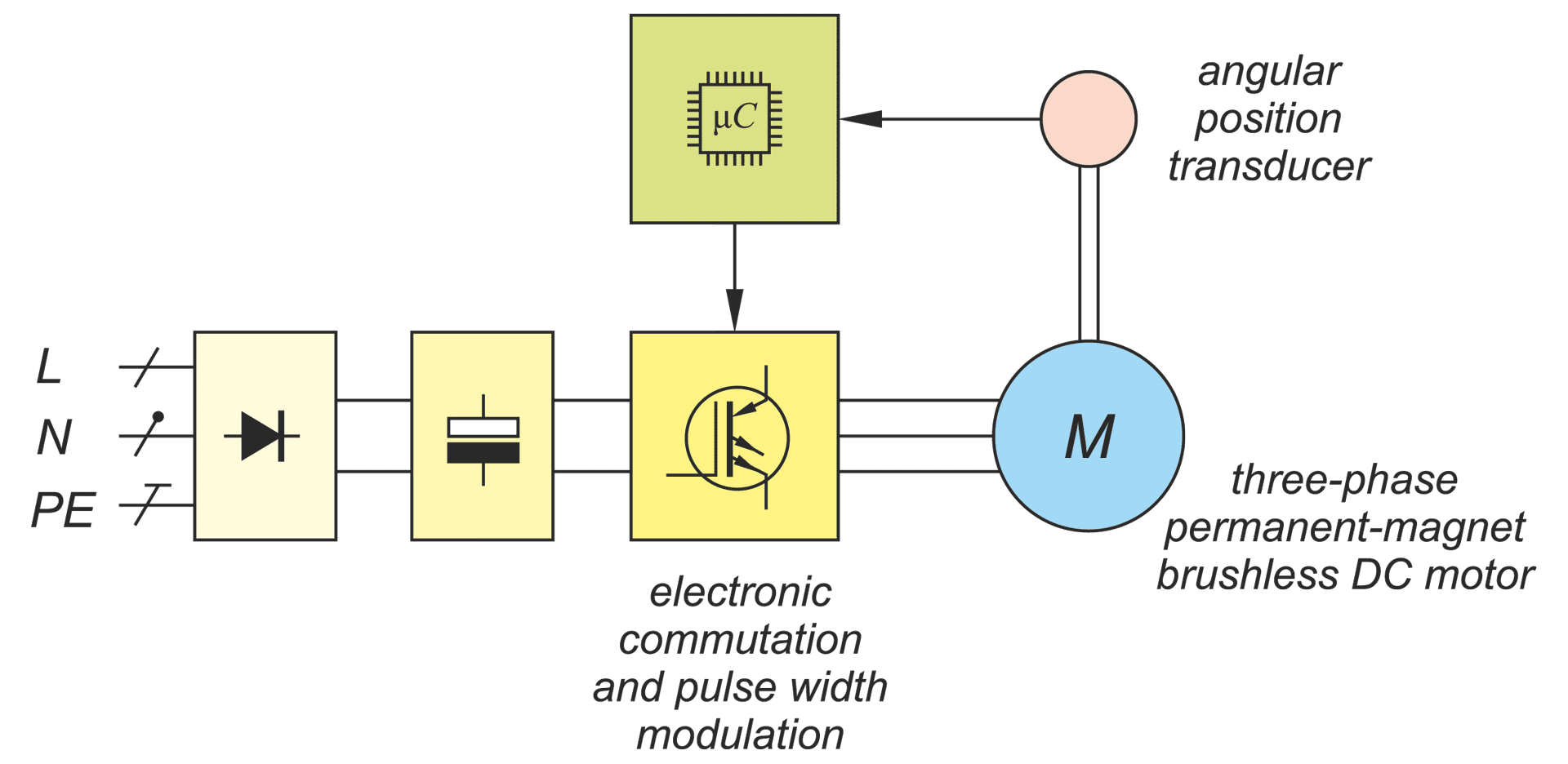
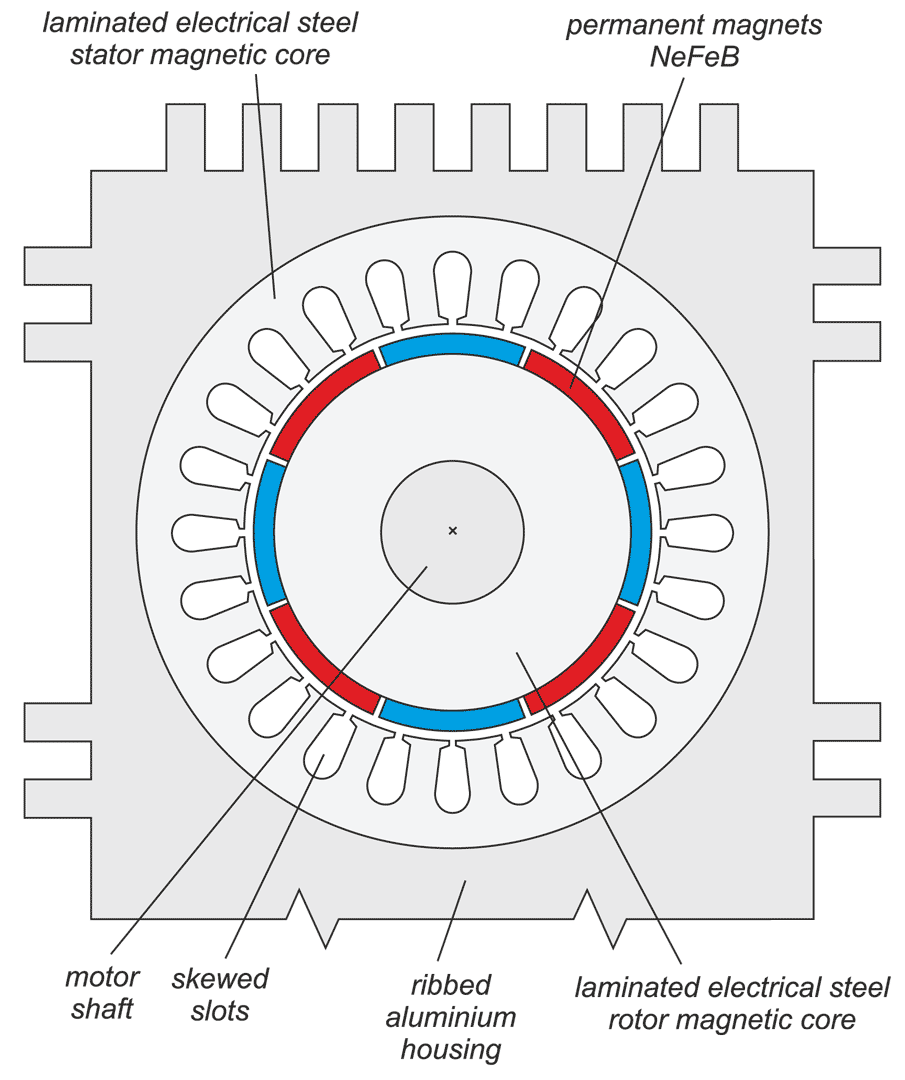
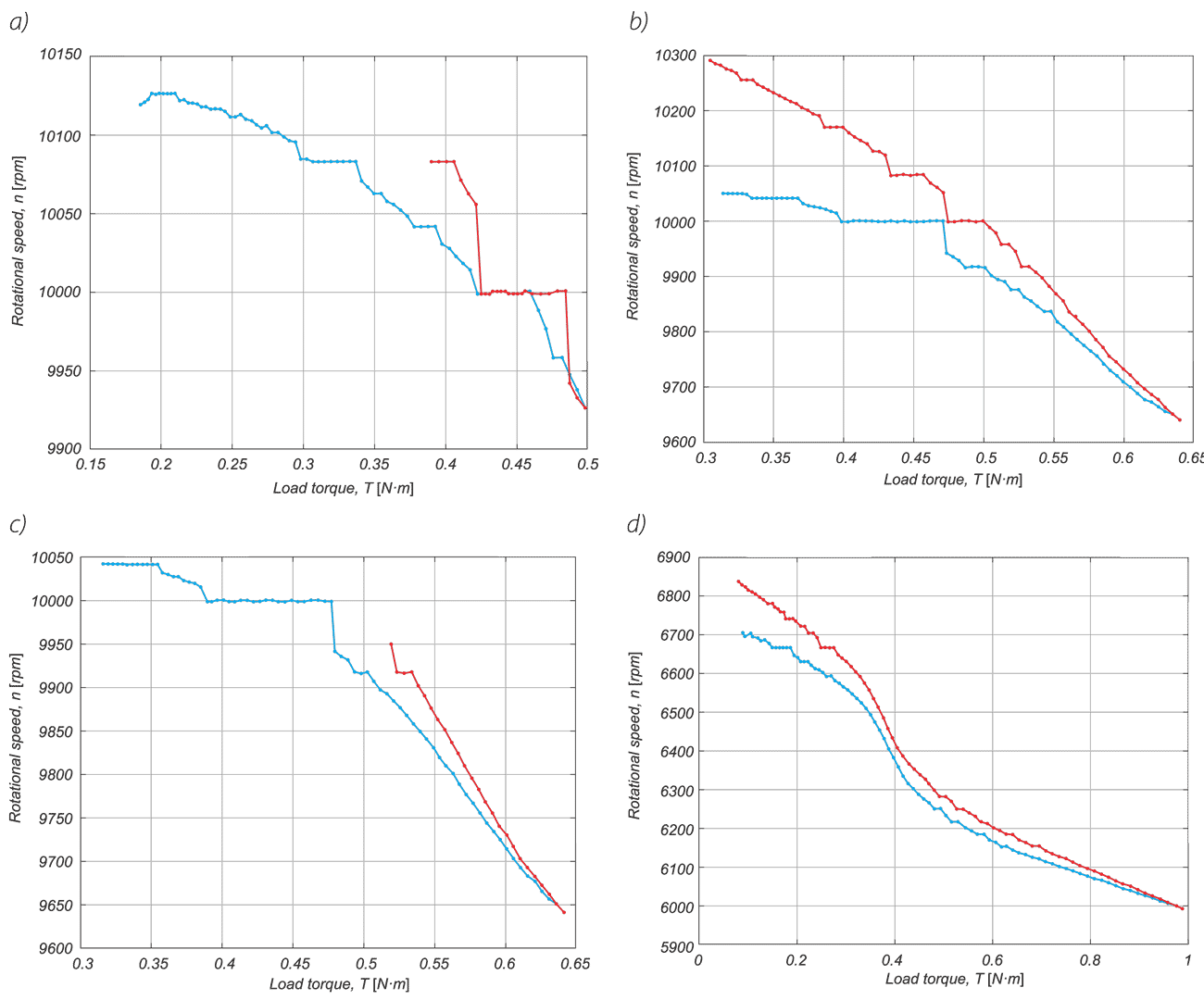
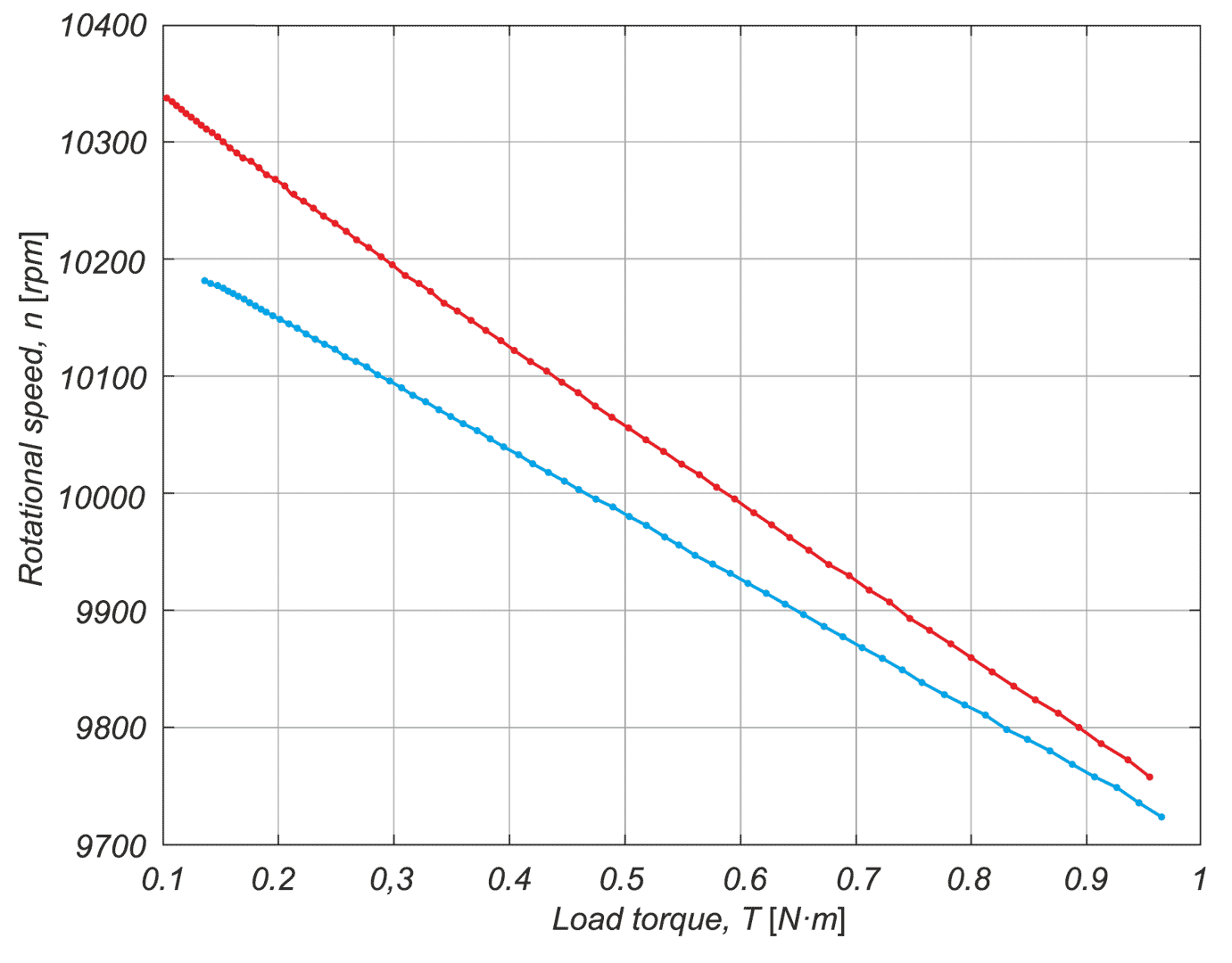
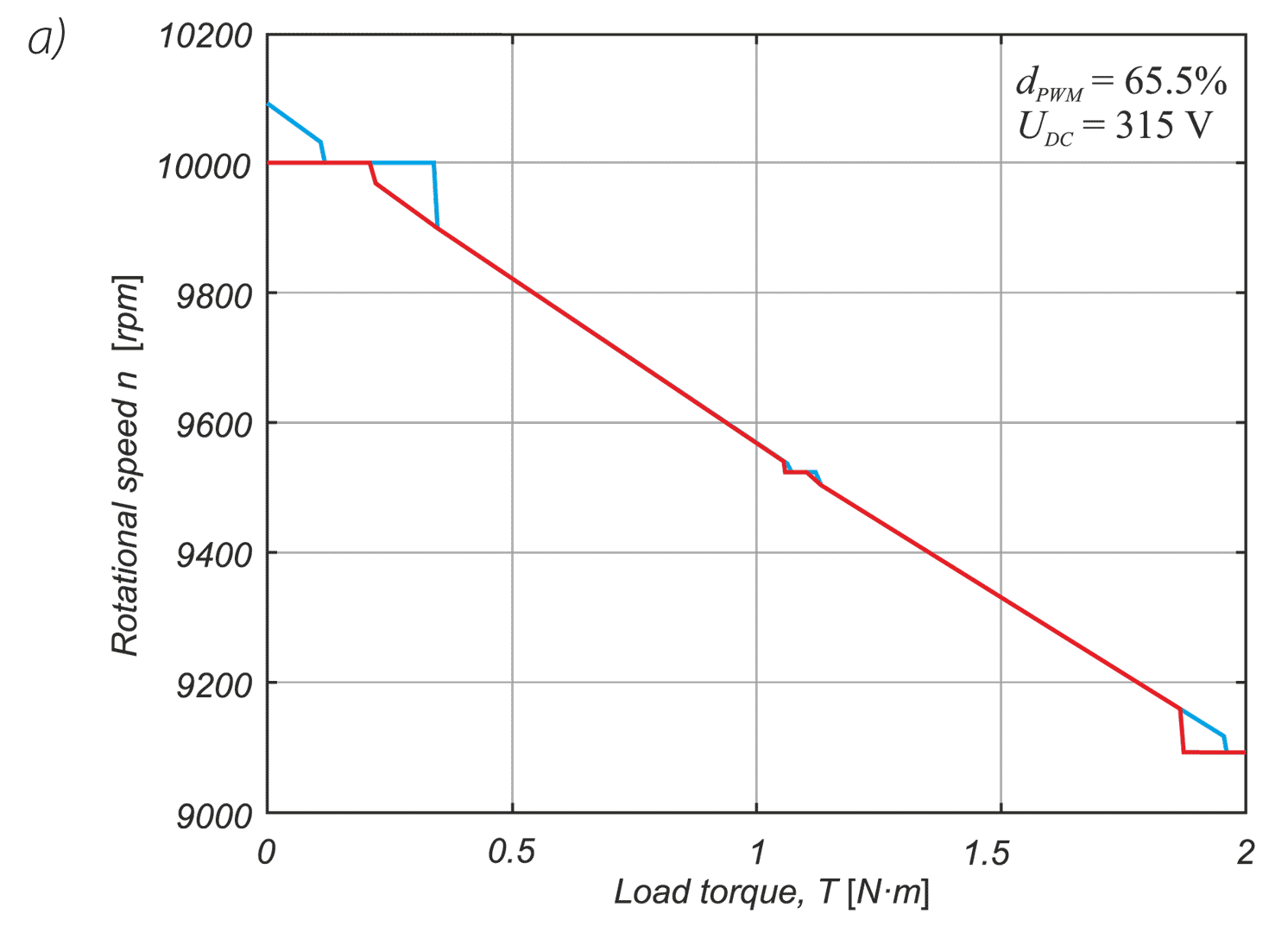
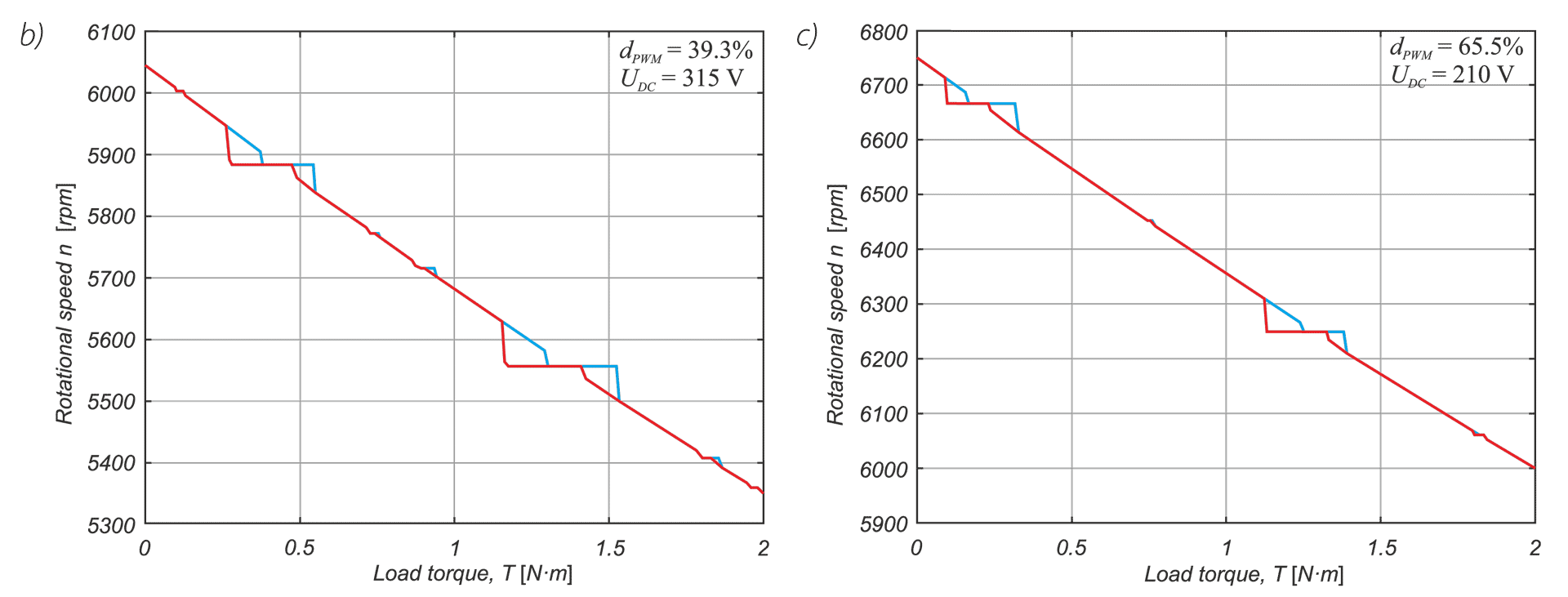
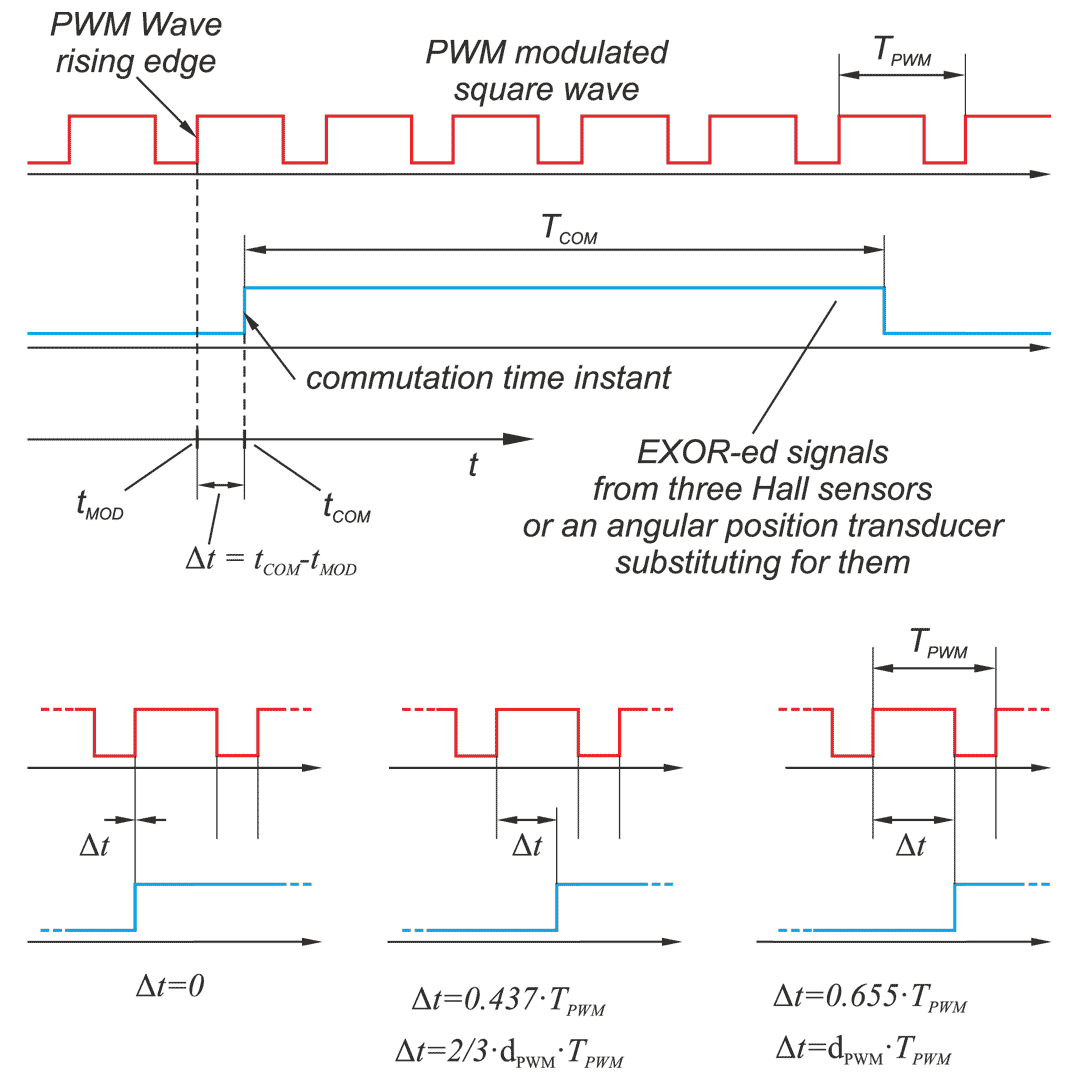
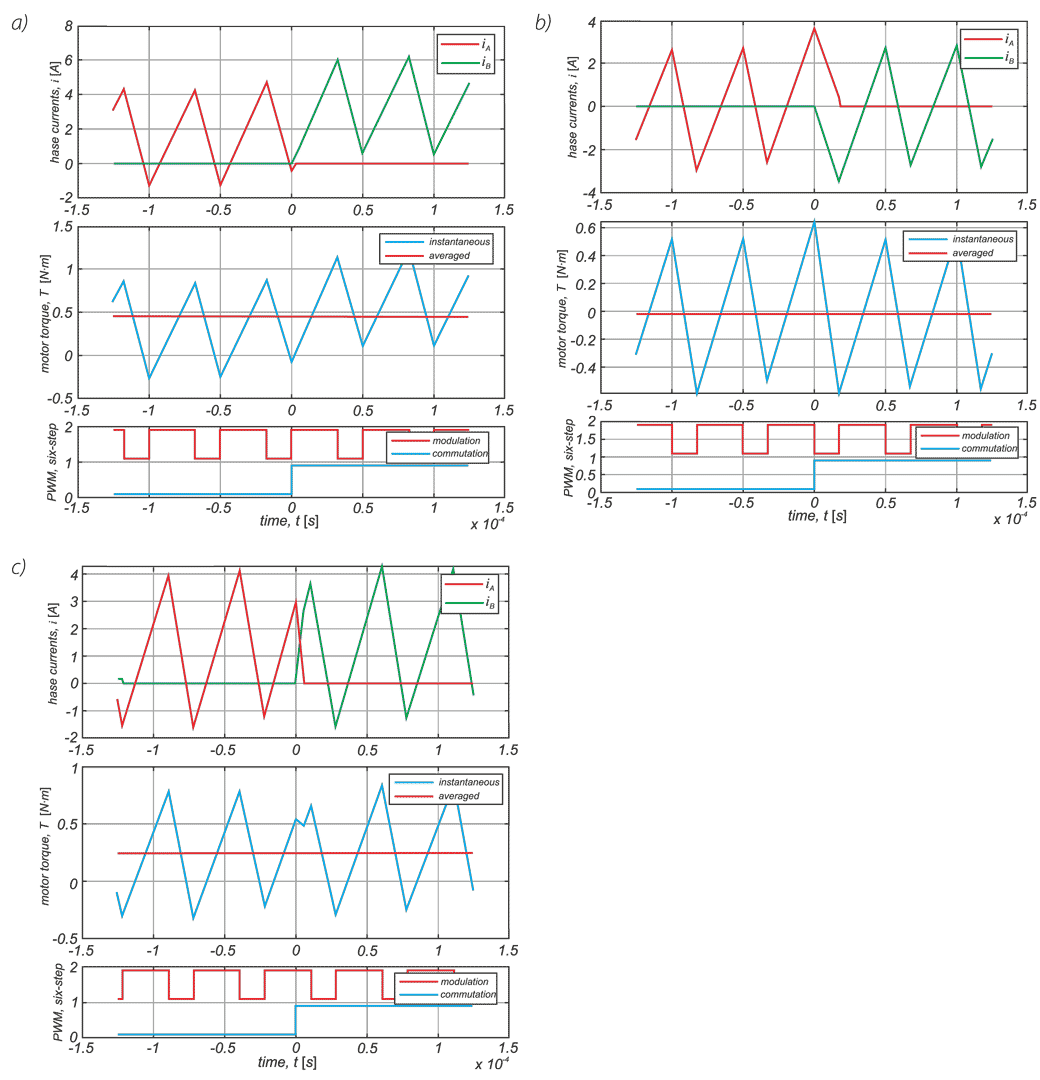
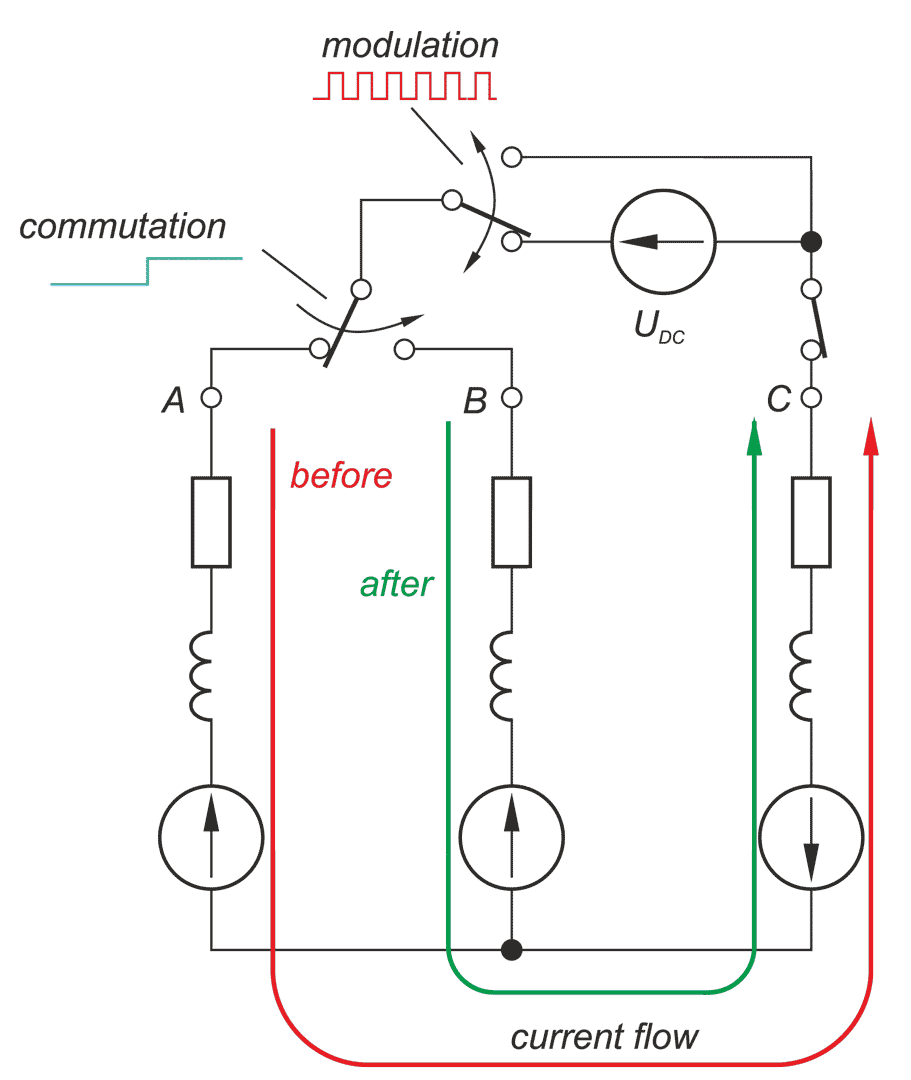
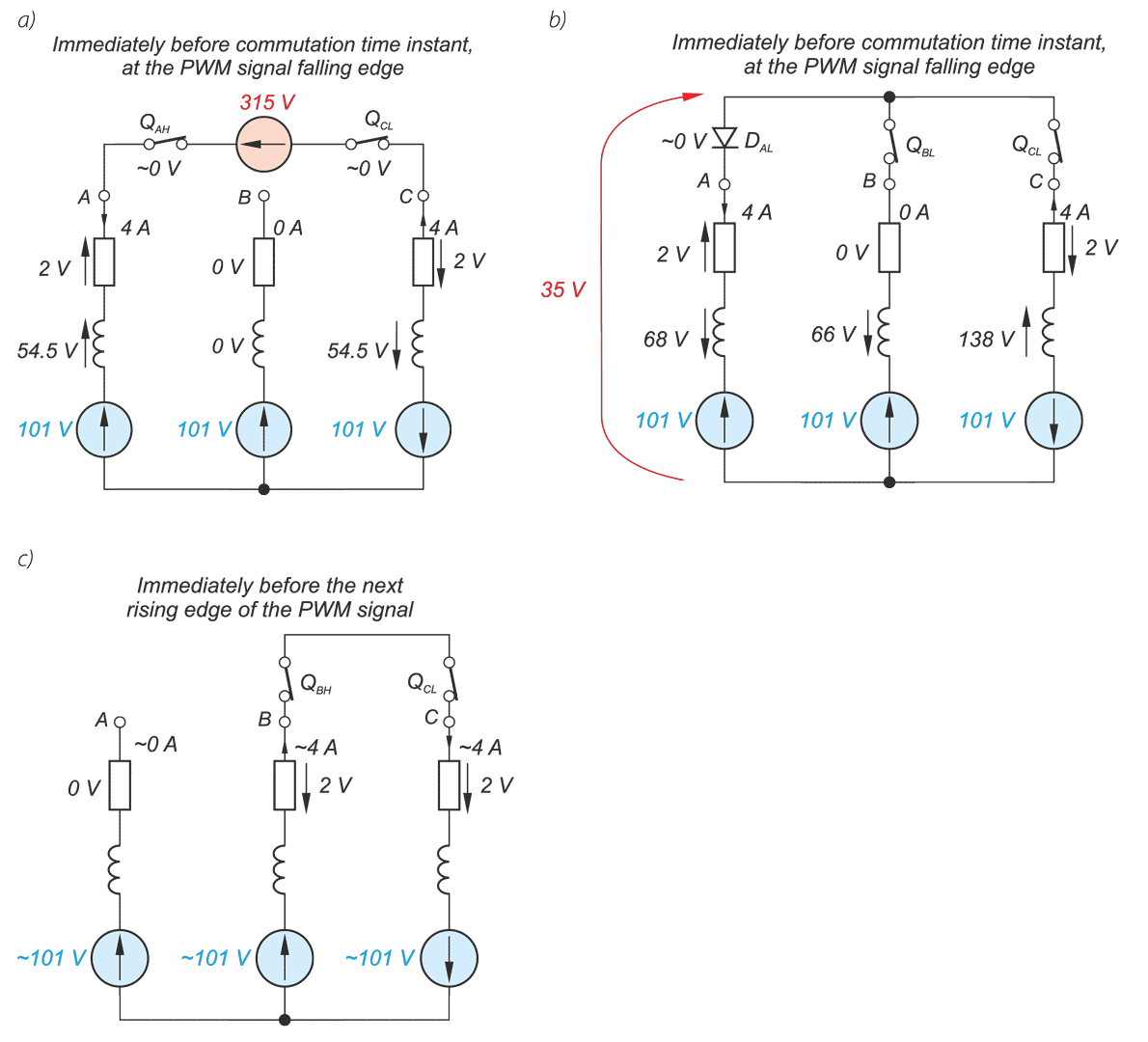
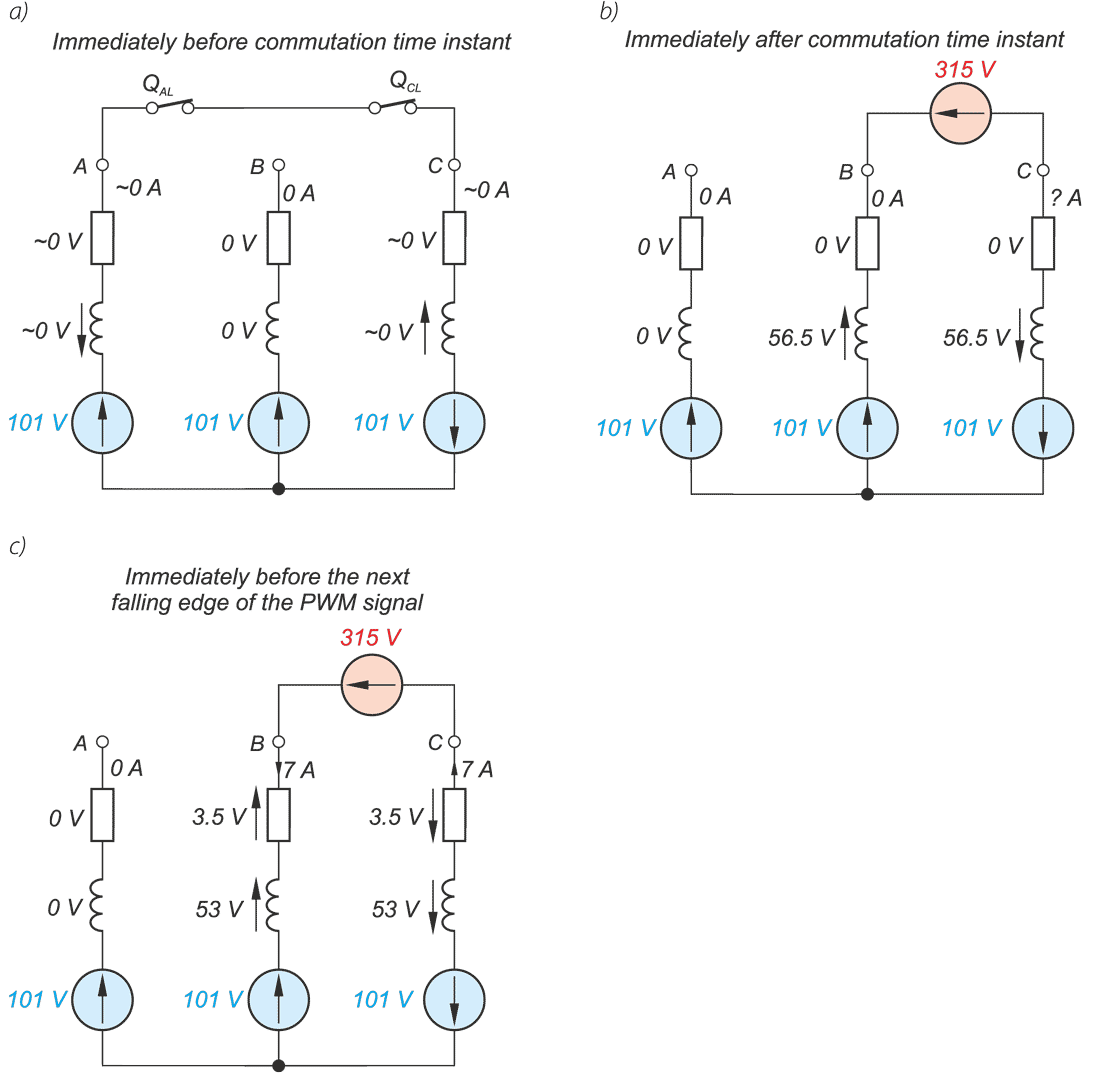
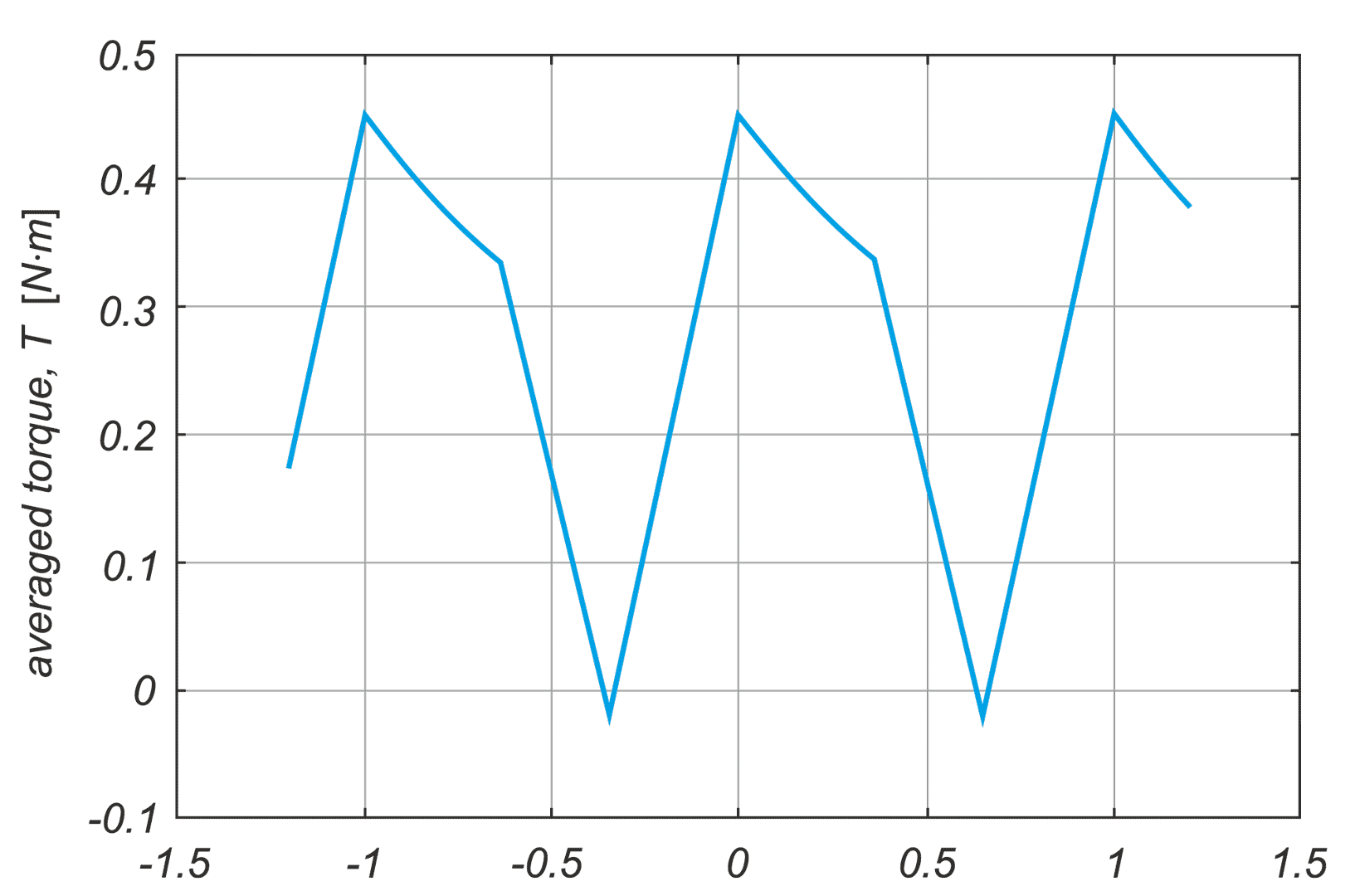
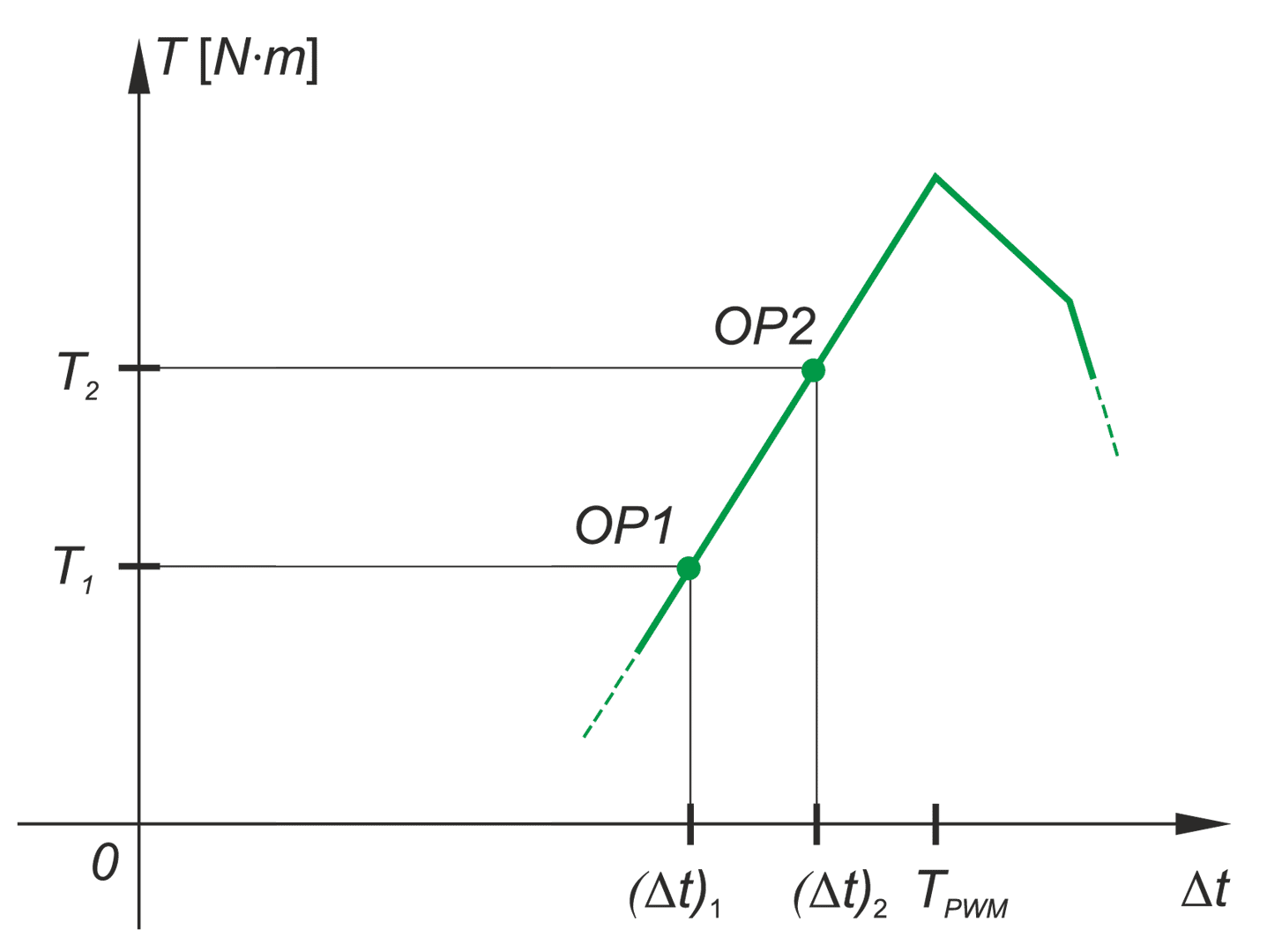
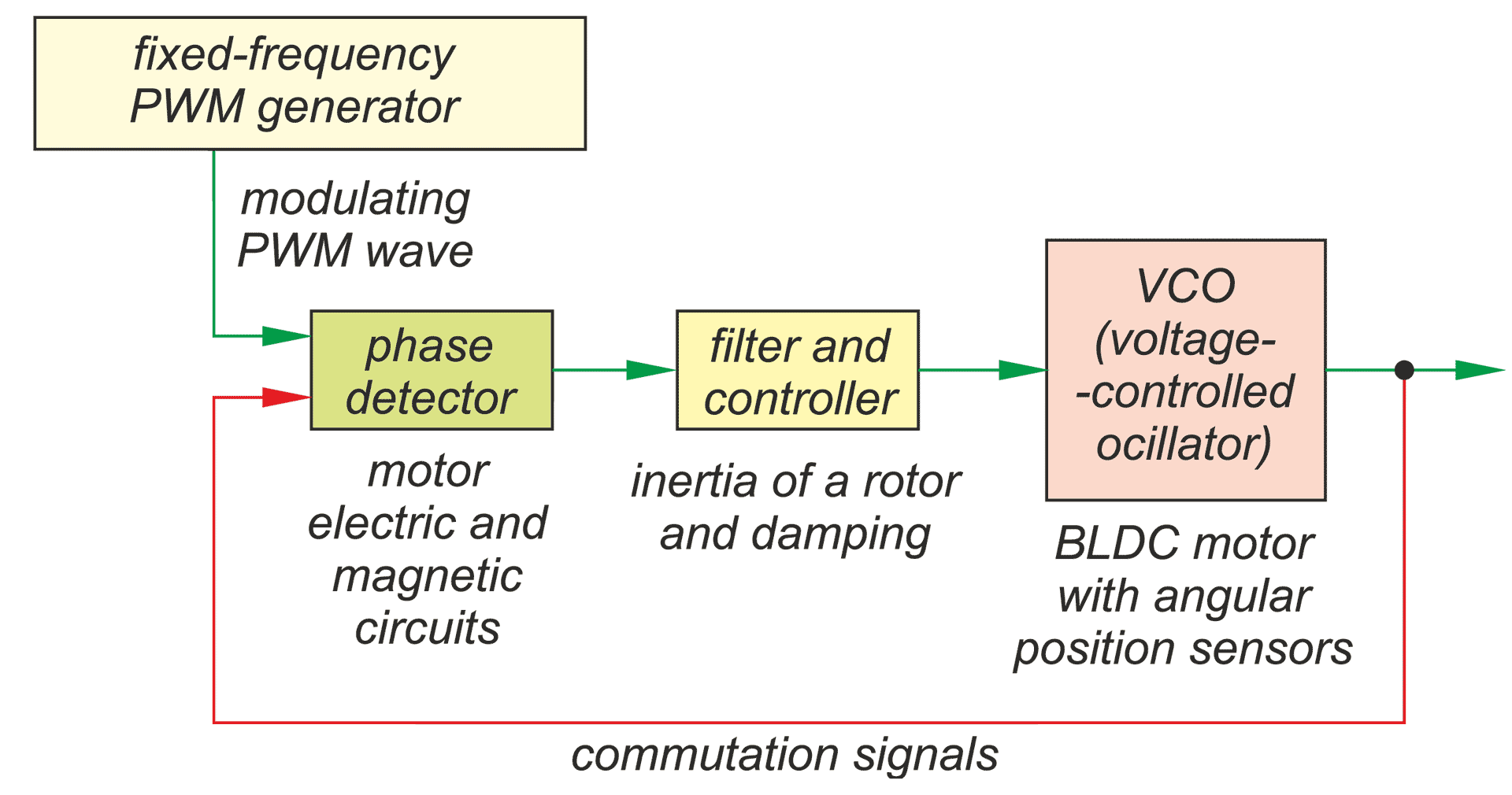
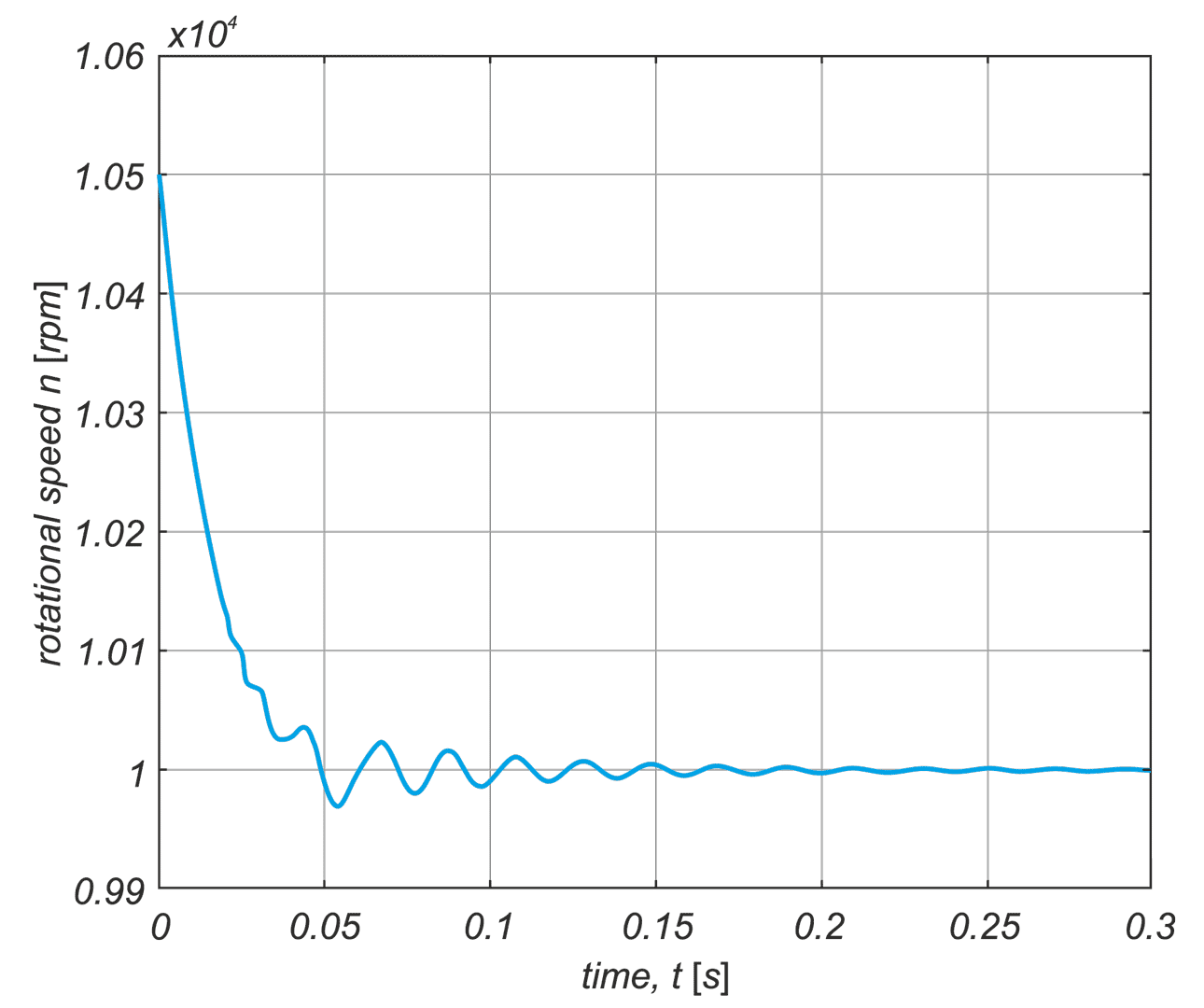
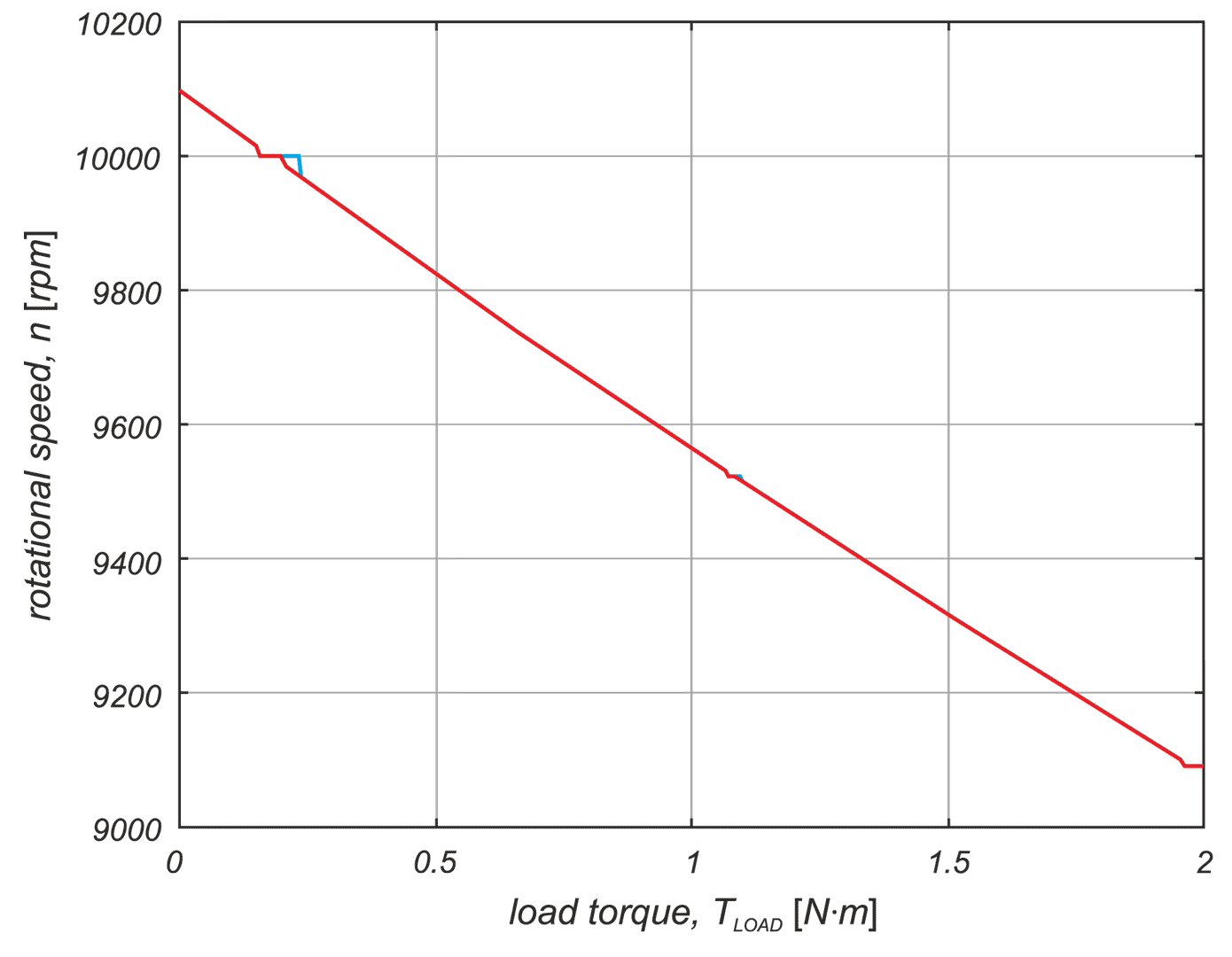
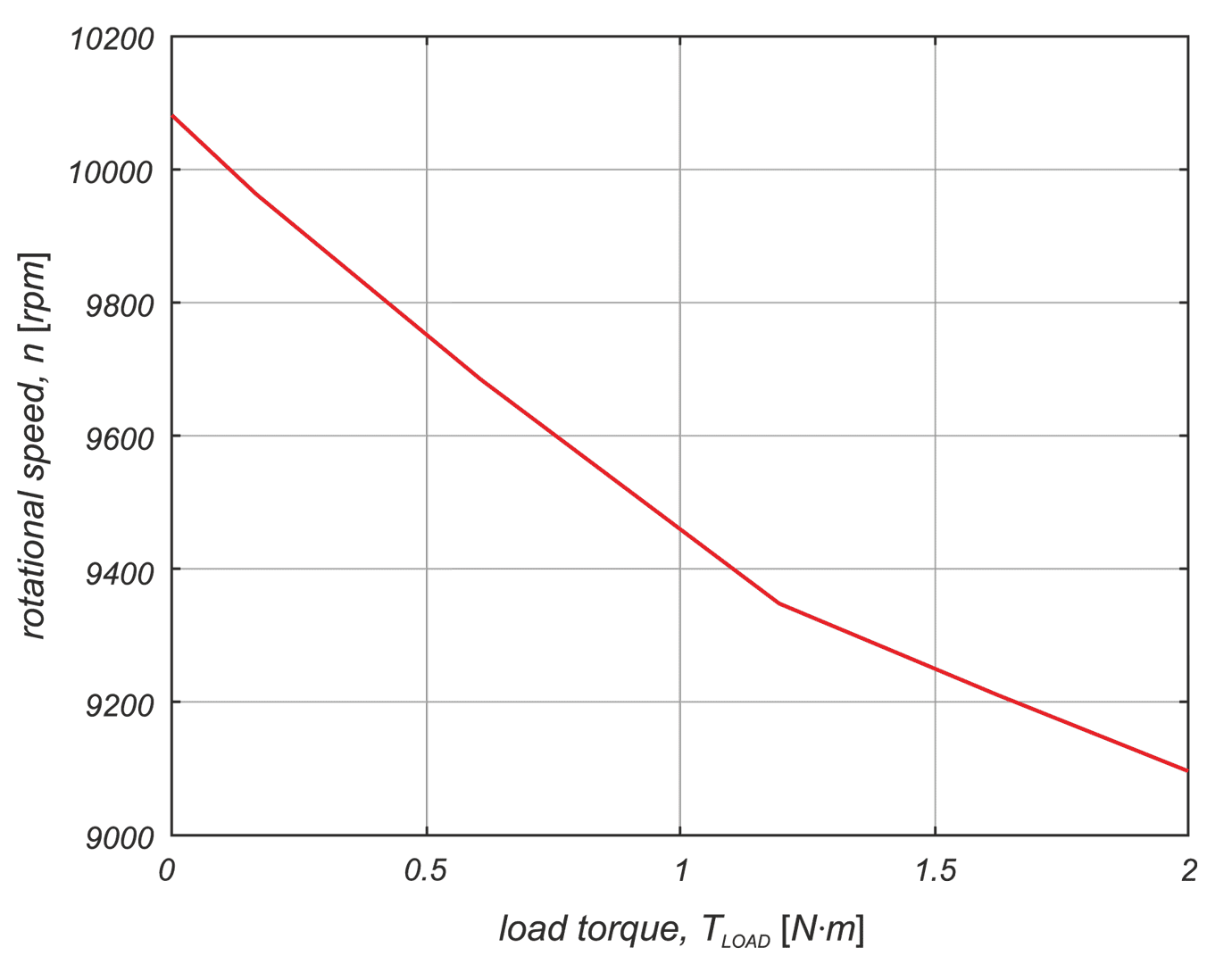
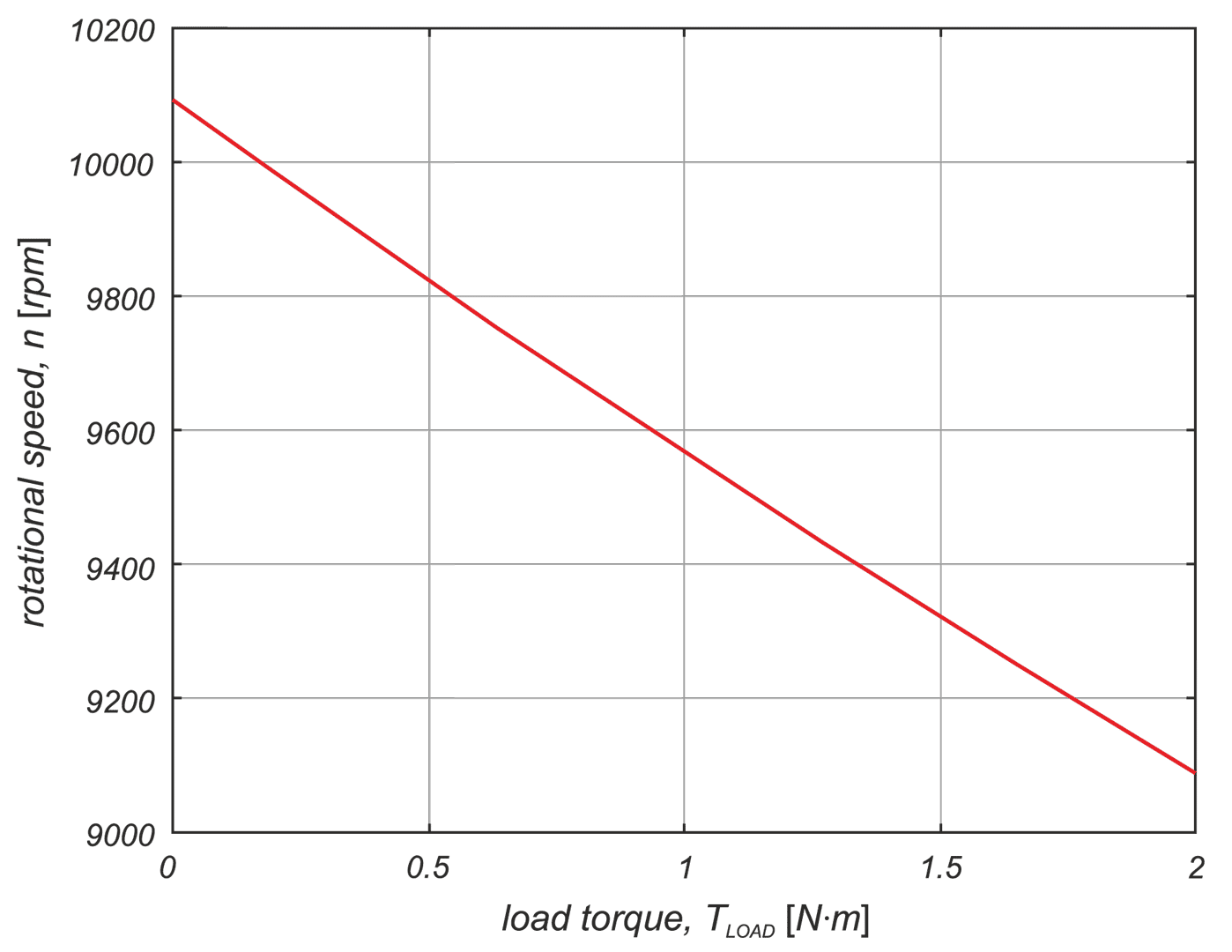
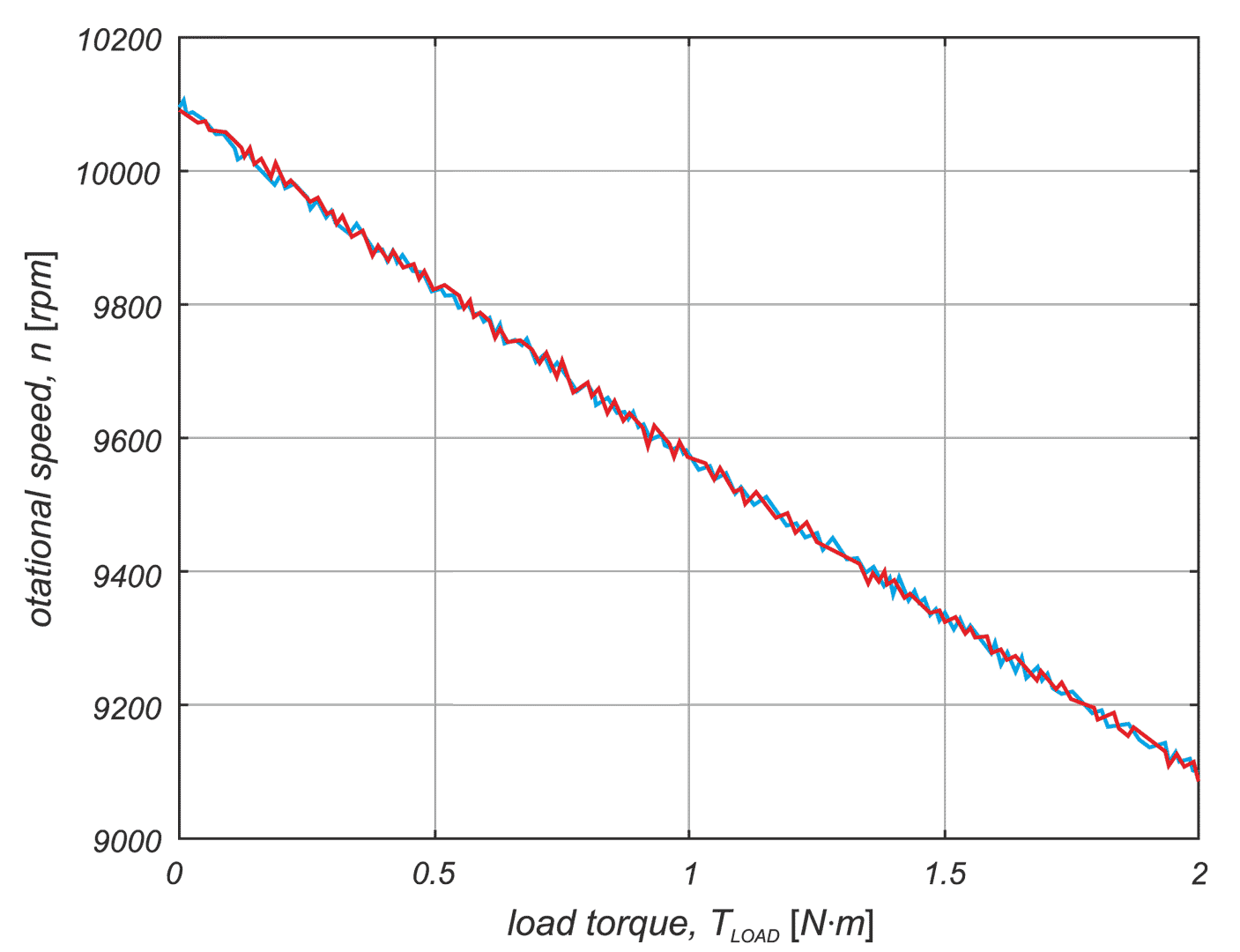
In a drive system comprising a high- speed PM BLDC motor and an inverter implementing motor phases commutation and phase voltages PWM modulation, a spontaneous synchronisation between the PWM modulation frequency and the motor rotational speed may occur. The drive behaves like an unintended phase locked loop. The effect distorts mechanical characteristic of the drive by introducing flat segments where the rotational speed remains constant despite changing load torque. It makes the speed - torque relationship discontinuous, nonlinear, and non unique. The phenomenon is closely related to the problem of phase current and motor torque ripples. The paper presents experimental results recorded with a laboratory test bench for drives for electric power tools where the phenomenon of the parasitic speed locking has been observed. A root cause of this effect is discussed, and the mechanism of unwanted synchronisation is investigated. Several mitigation techniques are proposed and verified with computer simulations.
Streszczenie
W układzie napędowym składającym się z wysokoobrotowego silnika PM BLDC i falownika realizującego komutację faz silnika i modulację napięcia fazowego PWM może wystąpić spontaniczna synchronizacja częstotliwości modulacji PWM z prędkością obrotową silnika. Efekt ten zniekształca charakterystykę mechaniczną napędu poprzez wprowadzenie płaskich segmentów, w których prędkość obrotowa pozostaje stała pomimo zmieniającego się momentu obciążenia. W pracy przedstawiono wyniki doświadczeń zarejestrowane na laboratoryjnym stanowisku badawczym dla napędów elektronarzędzi, na którym zaobserwowano zjawisko pasożytniczej synchronizacji prędkości. Przeanalizowano i omówiono przyczyny tego zjawiska. Zaproponowano kilka technik łagodzenia jego skutków i zweryfikowano je za pomocą symulacji komputerowych.
Keywords
PM BLDC, parasitic phase locked loop, speed-frequency synchronisation
Słowa kluczowe
PM BLDC, pasożytnicza pętla synchronizacji, synchronizacja prędkość
Rys. / Fig.
Bibliografia / Bilbiography
[1] A. Tutaj, T. Drabek, T. Dziwiński, J. Baranowski, and P. Piątek: „Unintended synchronisation between rotational speed and PWM frequency in a PM BLDC drive unit”, Proceedings of the conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics, 27-30 August 2018, Międzyzdroje, Poland (https://ieeexplore-1ieee-1org-1000047hr0065.wbg2.bg.agh.edu.pl/document/8486090).
[2] Joong-Ho Song, Ick Choy: “Commutation Torque Ripple Reduction in Brushless DC Motor Drives Using a Single DC Current Sensor”, IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 312-319, March 2004.
[3] I. O. K. Khudhair and T. Tűrker: „A Discrete Time Controller for the Reduction of Commutation Torque Ripple in BLDCM Drives,” IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), 14–17 March 2016, Taipei, Taiwan, pp. 122–127.
[4] S. J. Park, H. W. Park, M. H. Lee, and F. Harashima: “A New Approach for Minimum-Torque Ripple Maximum Efficiency Control of BLDC Motor”, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 109-114, February 2000.
[5] Dae-Kyong Kim, Kwang-Woon Lee, and Byung-Il Kwon: „Commutation Torque Ripple Reduction in a Position Sensorless Brushless DC Motor Drive”, IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 1762-1767, November 2006.
[6] G. Brando, A. Dannier, A. Del Pizzo: „An Effective Control Technique for Shaft-Torque Smoothing in DC-Brushless Drives with Arbitrary Shape of Air-Gap Magnetic Field”, IEEE Explorer, 978-1-4673-1372-8, 2012.
[7] Sung-An Kim, Geo-Seung Choi, Sang-Geon Lee, Yun-Hyun Cho: „A Novel Twelve-Step Sensor-less Control for Torque Ripple Reduction in Brushless DC Motor”, 2014 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, pp. 1062-1068, Oct. 22-25 2014.
[8] Hou Hongsheng and Liu Weiguo: „Instantaneous Torque Ripple Control in Brushless DC Motors Based on Conduction PWM Duty Ratio,”Proceedings of the 34th Chinese Control Conference, July 28–30, 2015, Hangzhou, China, pp. 4313–4318.
[9] Yue Liu, Jianhui Hu, Shili Dong: „A Torque Ripple Reduction Method of Small Inductance Brushless DC Motor Based on Three-level DCConverter”, 14th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), 19-21 June 2019, Electronic ISBN: 978-1-5386-9490-9,
DOI: 10.1109/ICIEA.2019.8834385.
[10] G. Sieklucki: „Pole placement method for DC motor torque controller,” Archives of Control Sciences, no. 19 (3), pp. 307–324, 2009.
[11] M. P. Ciurys, I. Dudzikowski, and M. Pawlak: „Laboratory tests of a PM BLDC motor drive,” Proceedings of the conference on Selected Problems of Electrical Engineering and Electronics (WZEE), 17 19 September 2015, Kielce, Poland.
[12] G. Buja, M. Bertoluzzo, and R. K. Keshri: „Torque Ripple Free Operation of PM BLDC Drives with Petal Wave Current Supply,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 62, no. 7, pp. 4034–4043, July 2015.
[13] K. Krykowski: „Silniki PM BLDC. Właściwości, sterowanie, aplikacje”, Publishing House BTC, Poland, 2015.
[14] A. Domoracki: „Influence of the electronic commutator control method on properties of a DC brushless motor”, Doctoral Thesis, Gliwice 2008.
[15] J. Baranowski, P. Piątek, T. Drabek, T. Dziwiński, Ł. Cyganik, E. Król and J. Ossa: „Electric Torque Tool with Brushless motor – challenges and opportunities,” Conference on Fundamentals of Electrotechnics and Circuit Theory (SPETO), 17–20 May 2017, Poland.
[16] B. Broel Plater, P. Dworak, and K. Jaroszewski: „Fractional order controller in a servo drive – Case of cogging moment,” 21st International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR), 29 August – 1 September 2016, Miedzyzdroje, Poland.
[17] Krishnatreya Bhattacharya, Subhendu Bikash Santra, Debashis Chatterjee, and Sanjeevikumar Padmanaban: „Torque Ripple and Loss Minimization of Trapezoidal Brushless DC Motor Drive by Harmonics Current Excitation Switching Technique”, IEEE International
Conference on Power Electronics, Smart Grid and Renewable Energy (PESGRE2020), 2-4 January 2020, Electronic ISBN:978-1-7281-4251-7, DOI: 10.1109/PESGRE45664.2020.9070523
[18] K. Kolano: „Improved Sensor Control Method for BLDC Motors,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 186158-186166, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2960580
[19] S.H. Kam, J.D. Seo and T.U. Jung: „A Study of Voltage Control Method for Torque Pulsation Factor Reduction for Home Applications Integrated BLDC Motor Drive,” 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines nad Systems (ICEMS), 25–28 October 2015,Pattaya City, Thailand, pp. 1448–1451.
[20] C. Concari, G. Franceschini and A. Toscani: „Vibrationless alignment algorithm for incremental encoder based BLDC drives,” Electric Power Systems Research, vol. 95, pp. 225–231, February 2013.
[21] Y. Zhou, D. Zhang, X. Chen, and Q. Lin: „Sensorless Direct Torque Control for Saliency Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motors”, IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 446-454, June 2016.
[22] Shao Yunbin, Yang Rongrong, Guo Jianwen, Fu Yongling: „Sliding Mode Speed Control for Brushless DC Motor Based on Sliding Mode Torque Observer”, Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, pp. 2466-2470,
August 2015.
[23] Sang-Yong Jung, Yong-Jae Kim, Jungmoon Jae, and Jaehong Kim: „Commutation Control for the Low-Commutation Torque Ripple in the Position Sensorless Drive of the Low-Voltage Brushless DC Motor”, IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 29, no. 11, pp. 5983-5994, November 2014.
[24] A. Ramya, V. Srinath, S. Samyuktha, R. Vimal, M. Balaji: „Commutation torque ripple reduction in brushless DC motor using modified SEPIC converter”, IEEE 11th International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems, 9-12 June 2015, Electronic ISBN: 978-1-4799-4402-6, DOI: 10.1109/PEDS.2015.7203486.
[25] Ł. Cyganik, E. Król, J. Baranowski, T. Drabek, T. Dziwiński, and P. Piątek: „The Design of the Brushless Electric Motor for Application in the Drive System of Electric Torque Wrench”, Maszyny Elektryczne − Zeszyty Problemowe, no. 2/2017 (114), pp. 141-145, 2017, Poland.
[26] K. Kolano: „Stanowisko do analizy wpływu błędów rozmieszczenia czujników położenia wału silnika BLDC na jego pracę”, Przegląd Elektrotechniczny, 2016, nr 8, t. 92, ss. 62–65, Warszawa, SIGMA-NOT, ISSN 0033-2097 (print), ISSN 2449-9544 (on-line)