E-pismo dla elektryków i elektroników
AUTOMATYKA, ELEKTRYKA, ZAKŁÓCENIA
Vol. 15, nr 1 (55) 2024
Generator do małej elektrowni wiatrowej
Generator for a Small Wind Power Plant
dr hab. inż. Zbigniew GORYCA; dr. inż. Artur PAKOSZ
Abstract
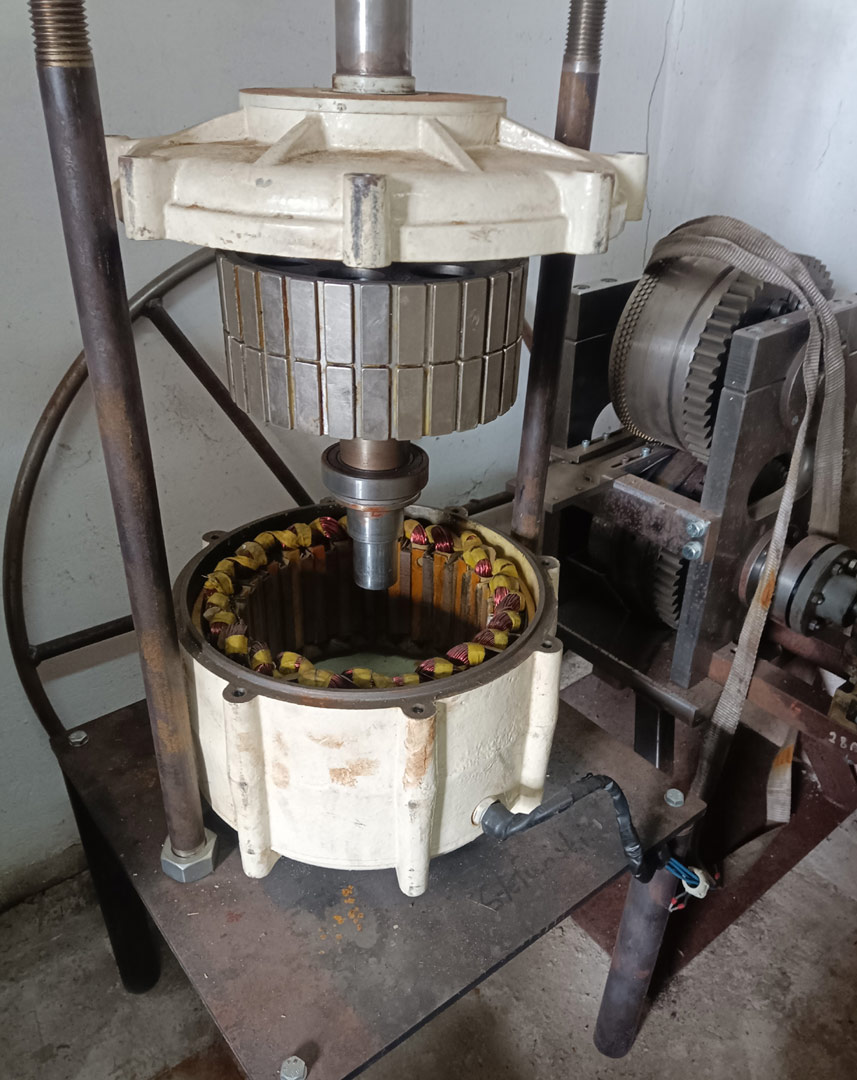
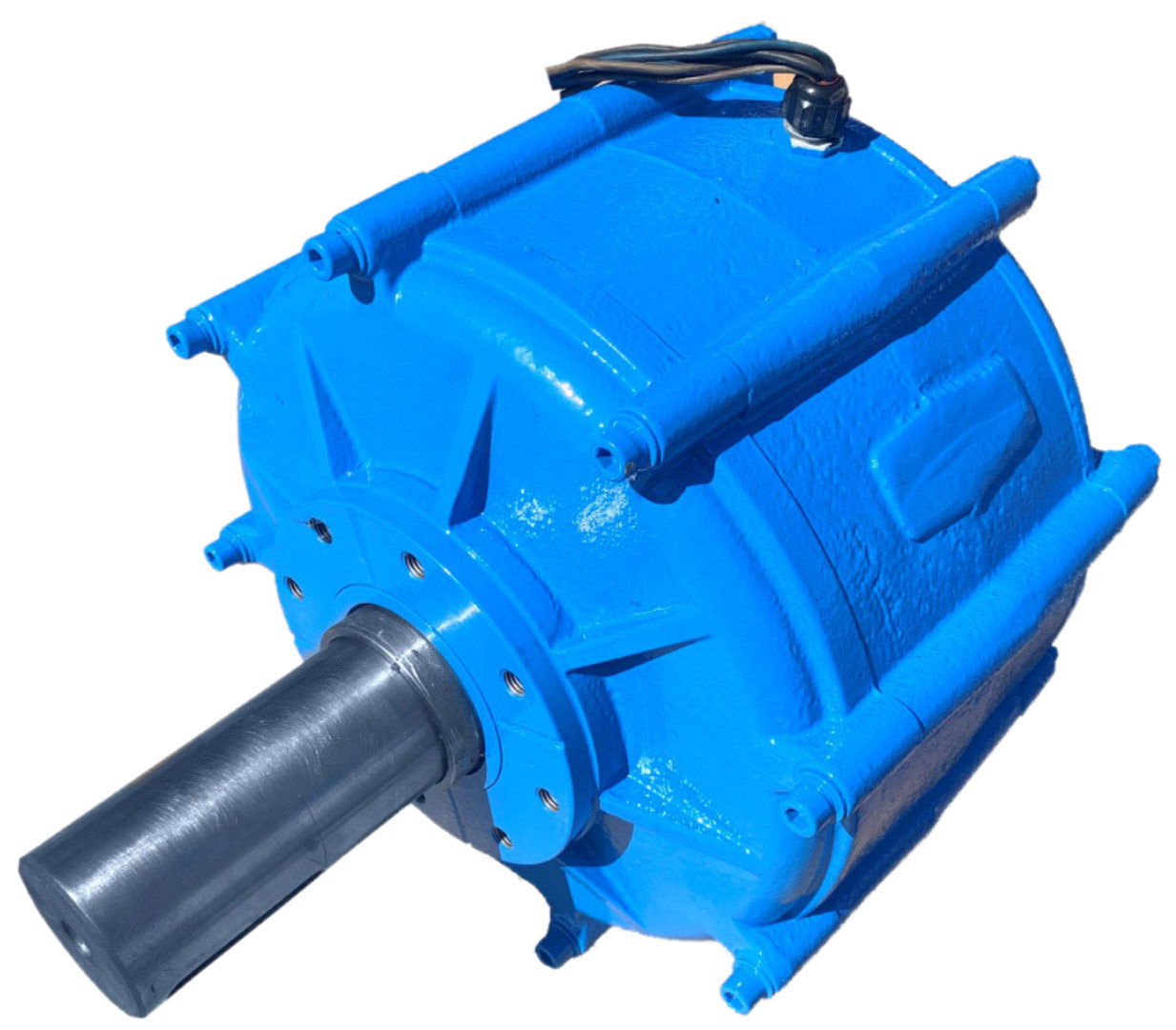
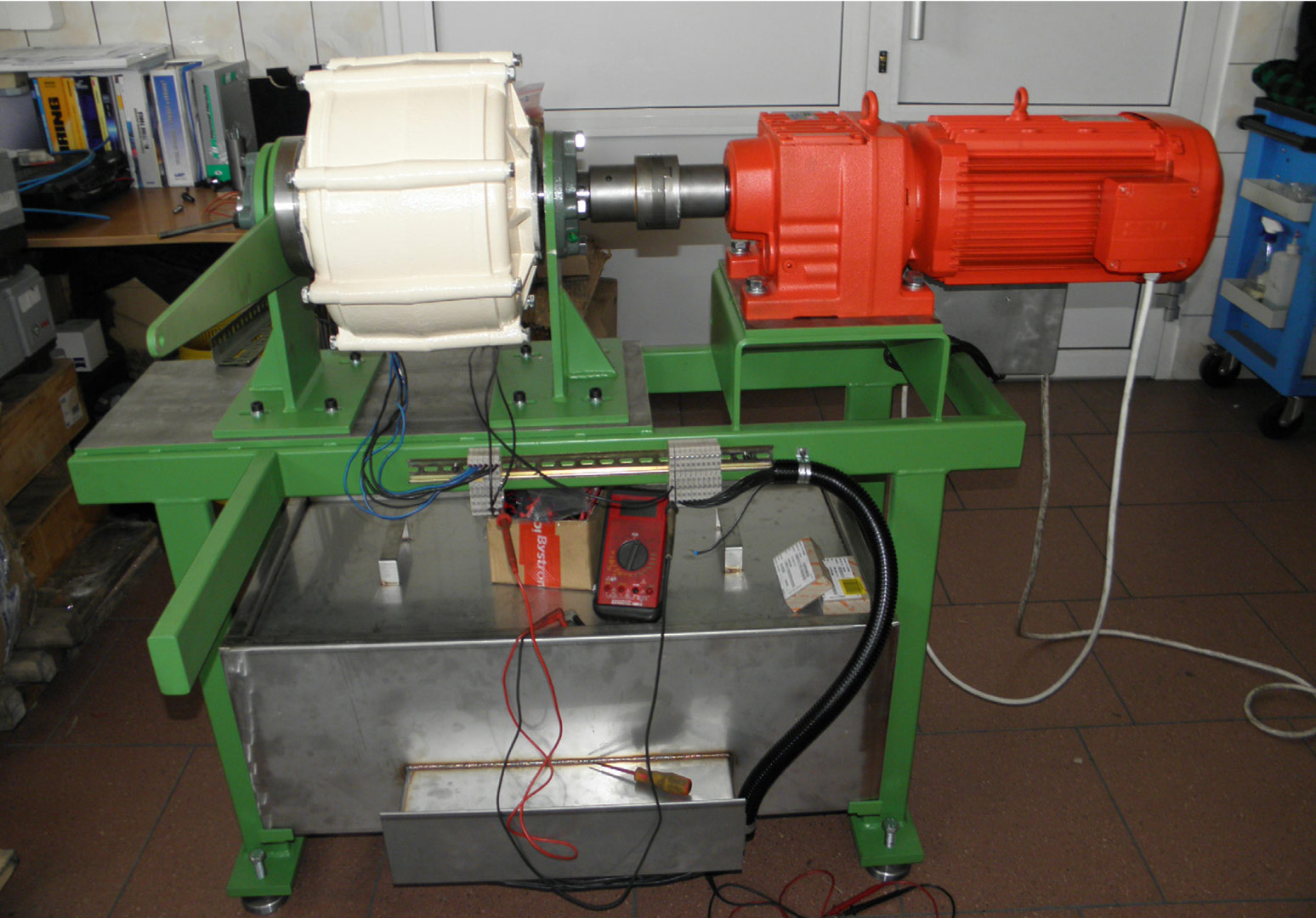
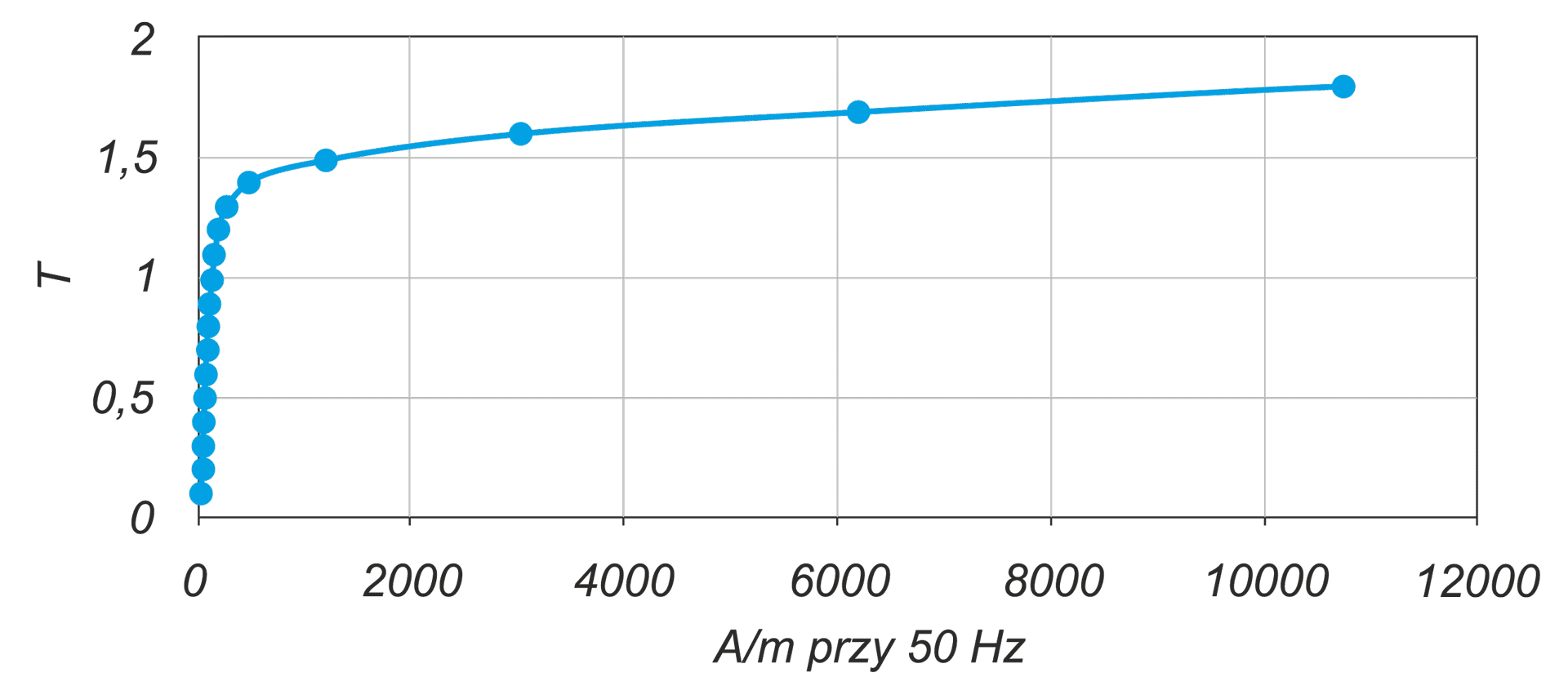
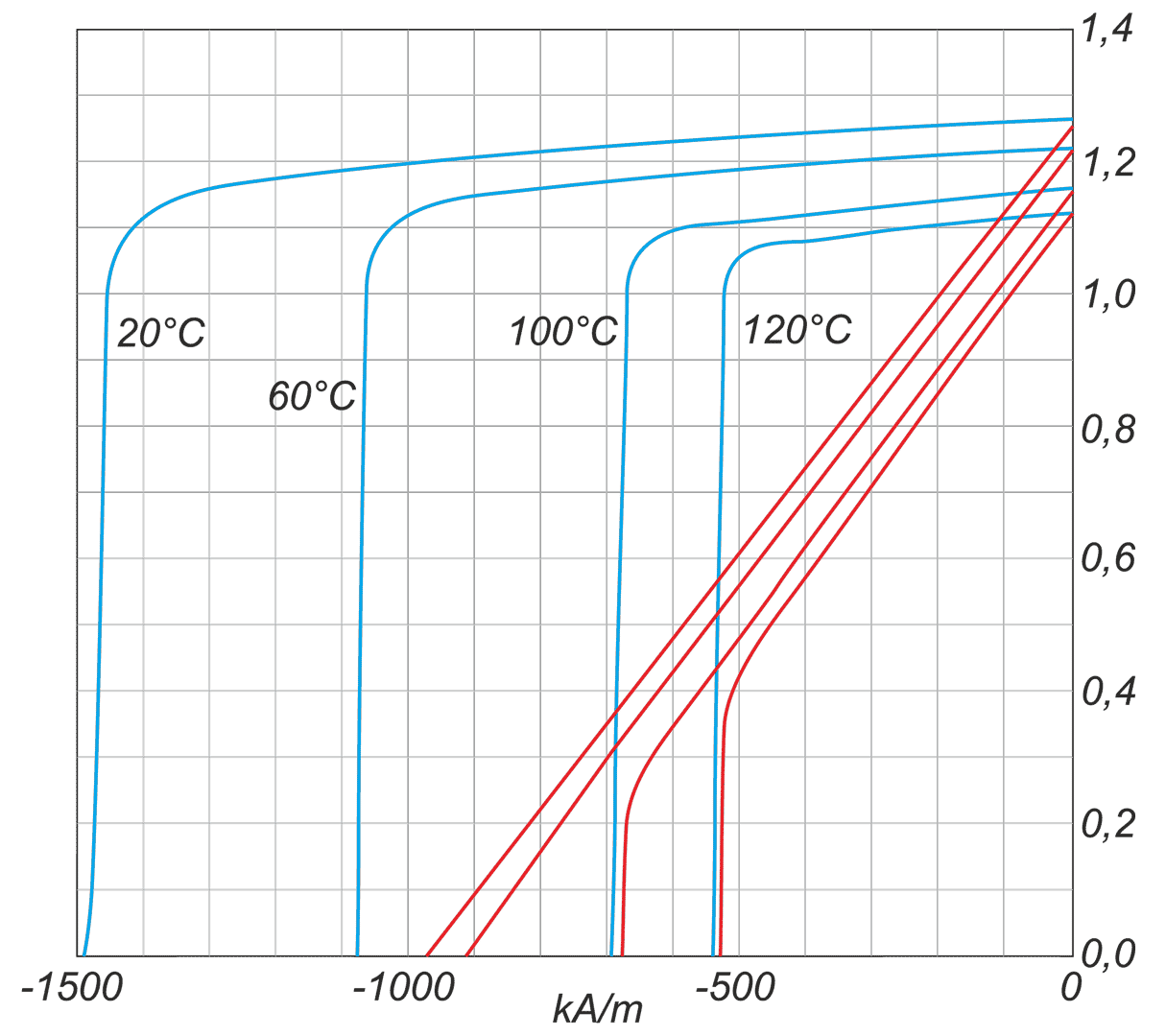
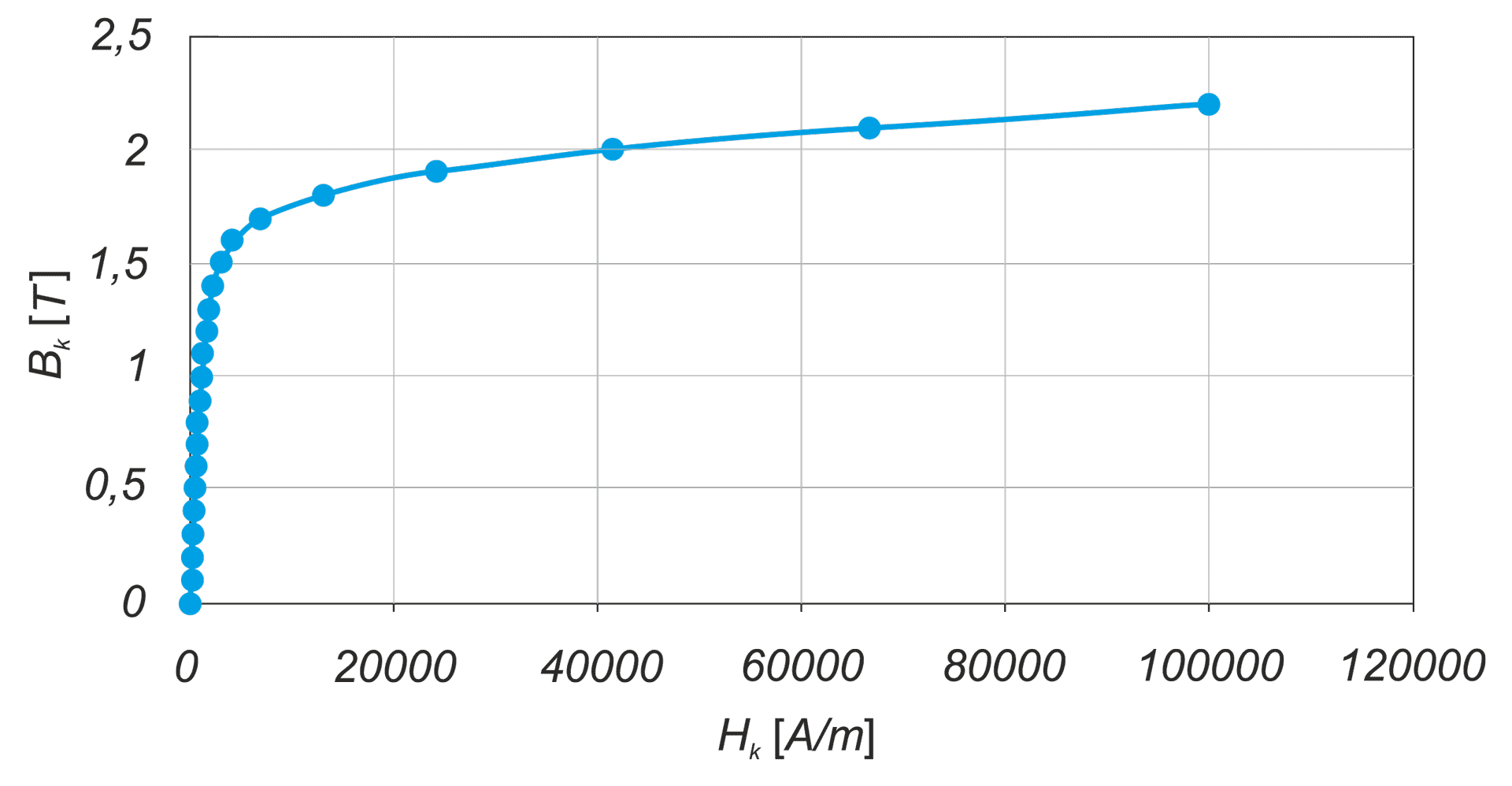
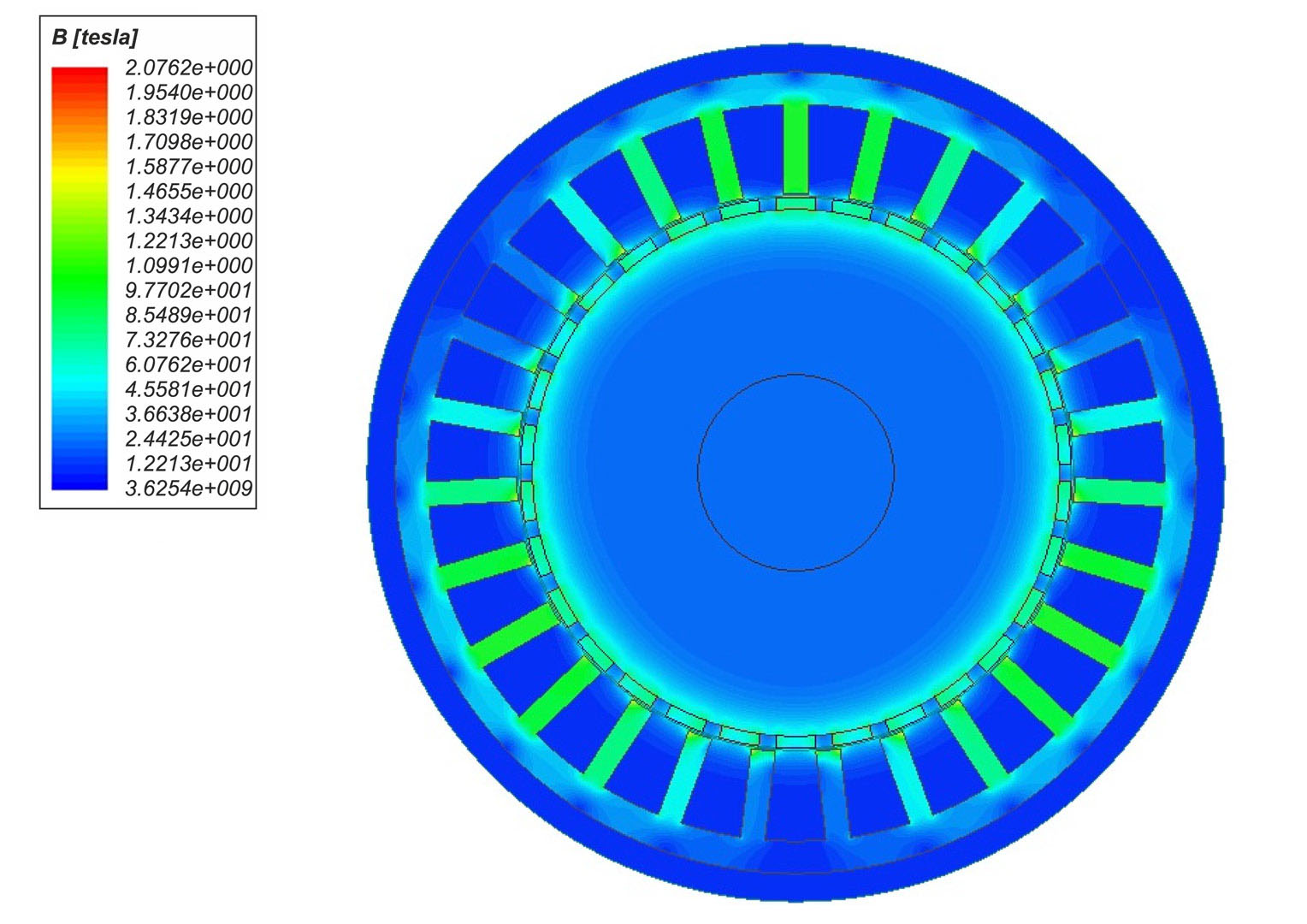
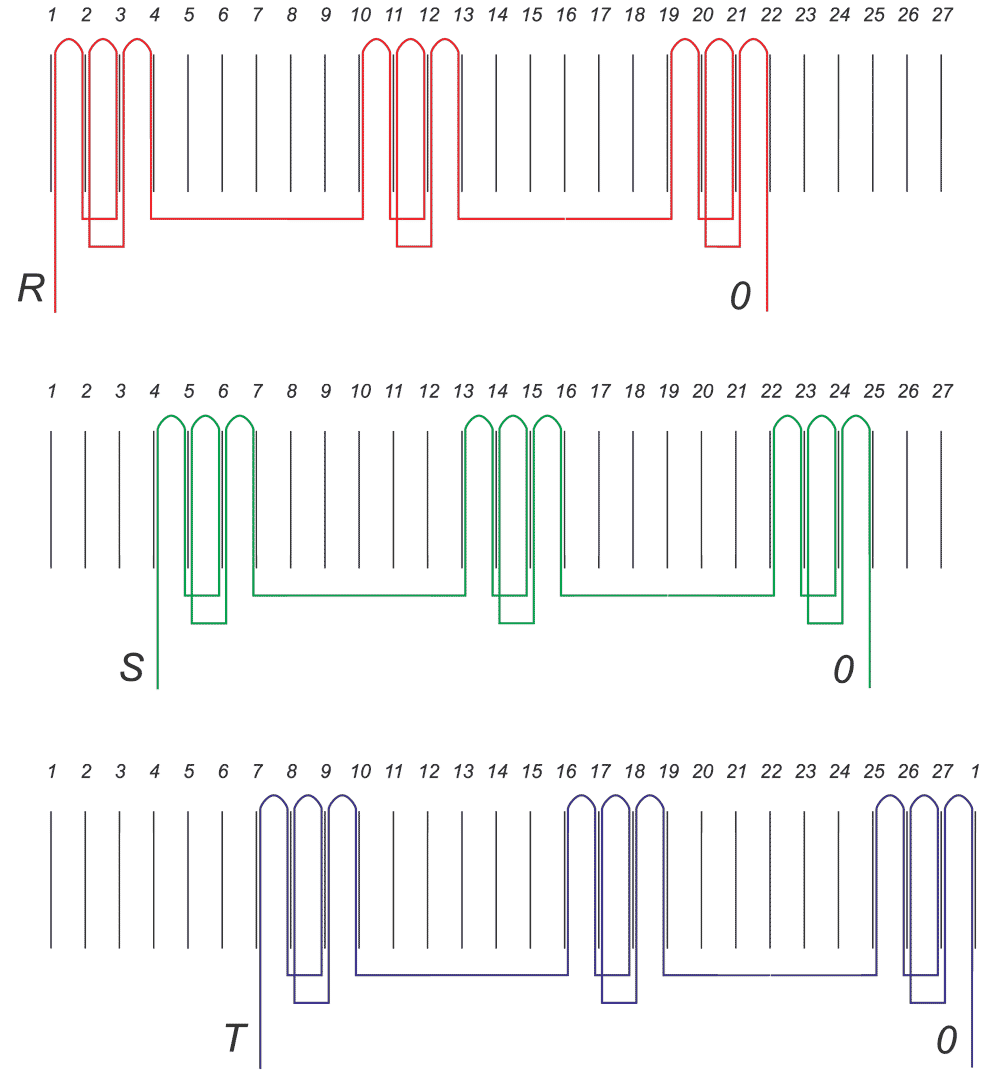
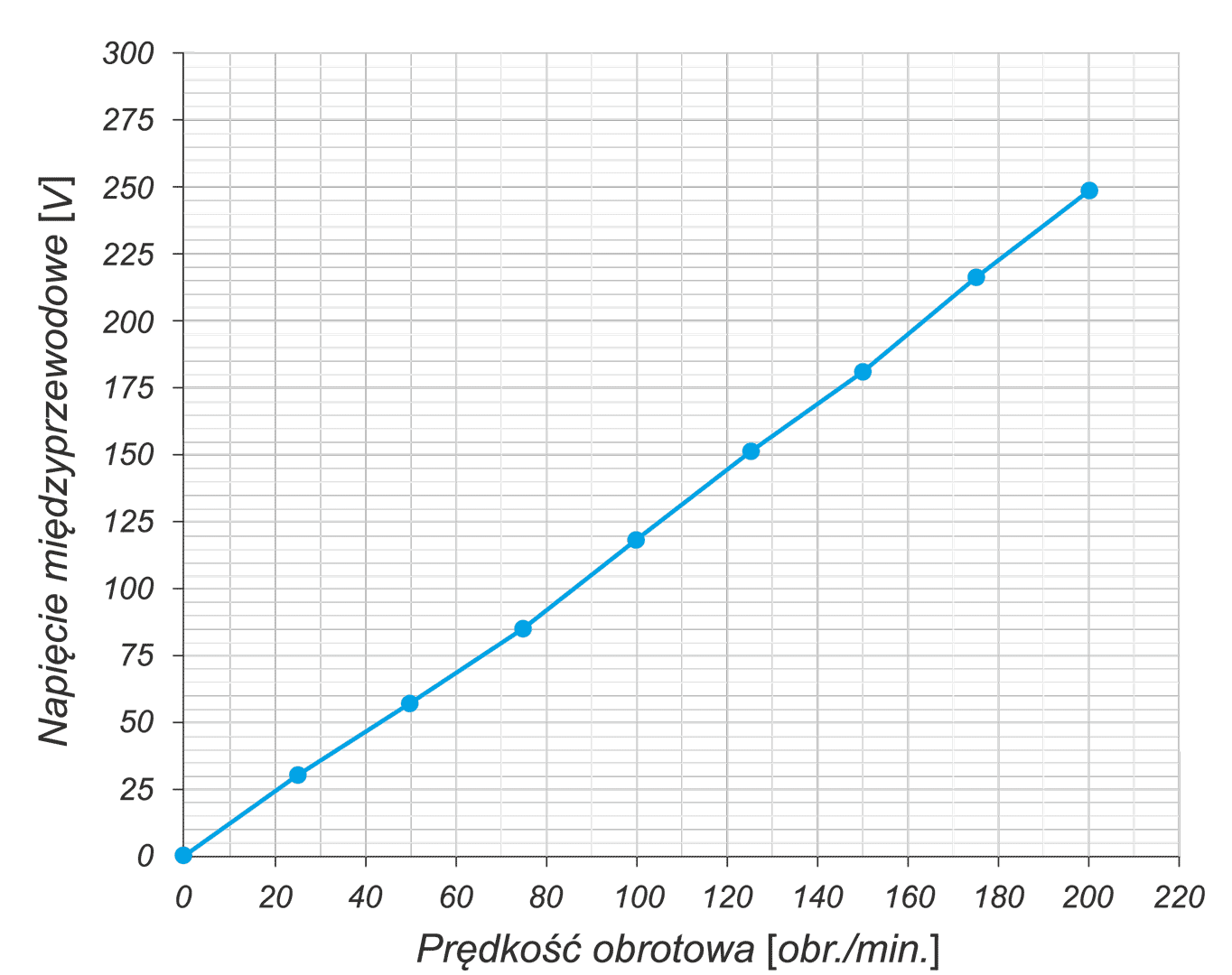
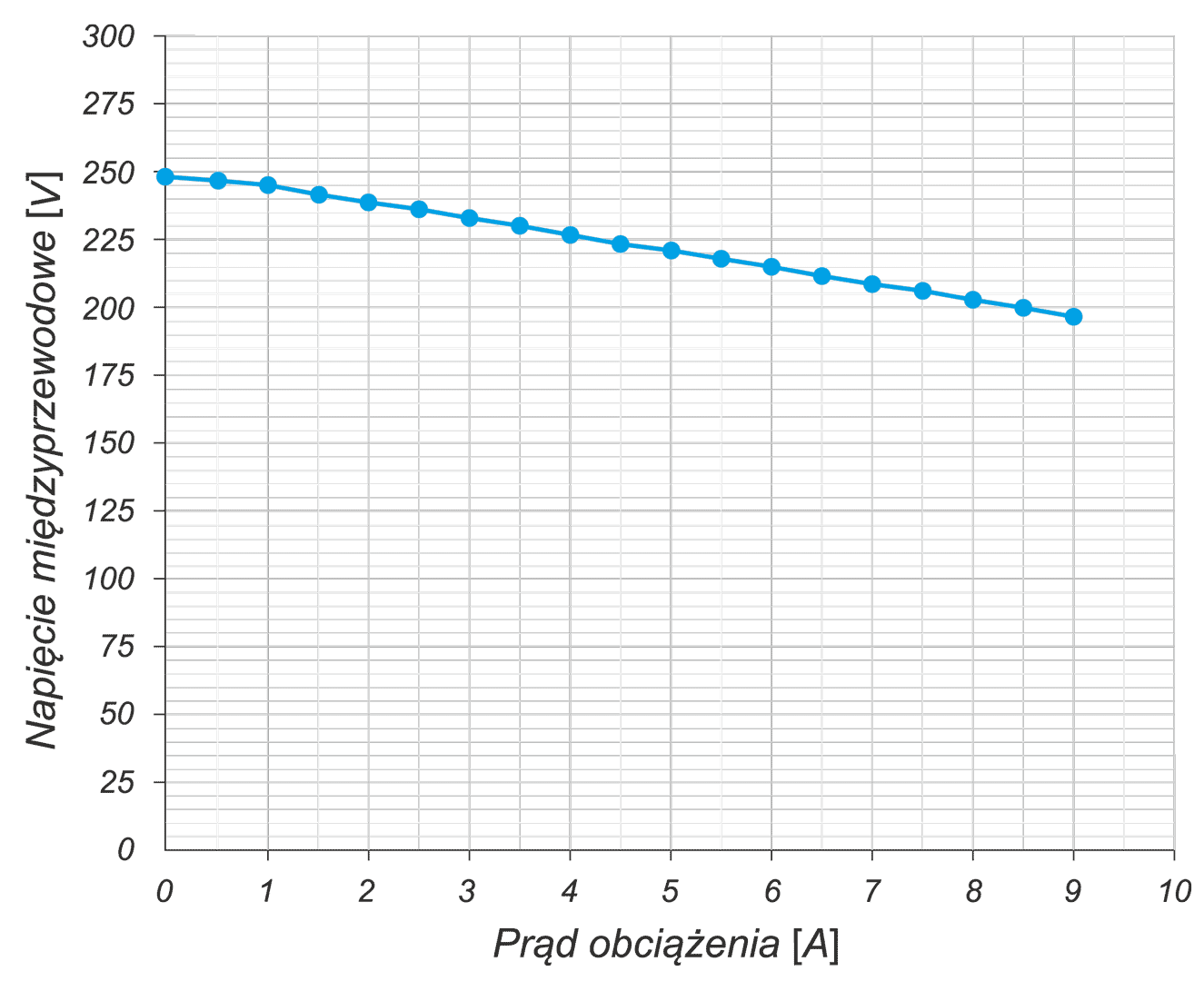
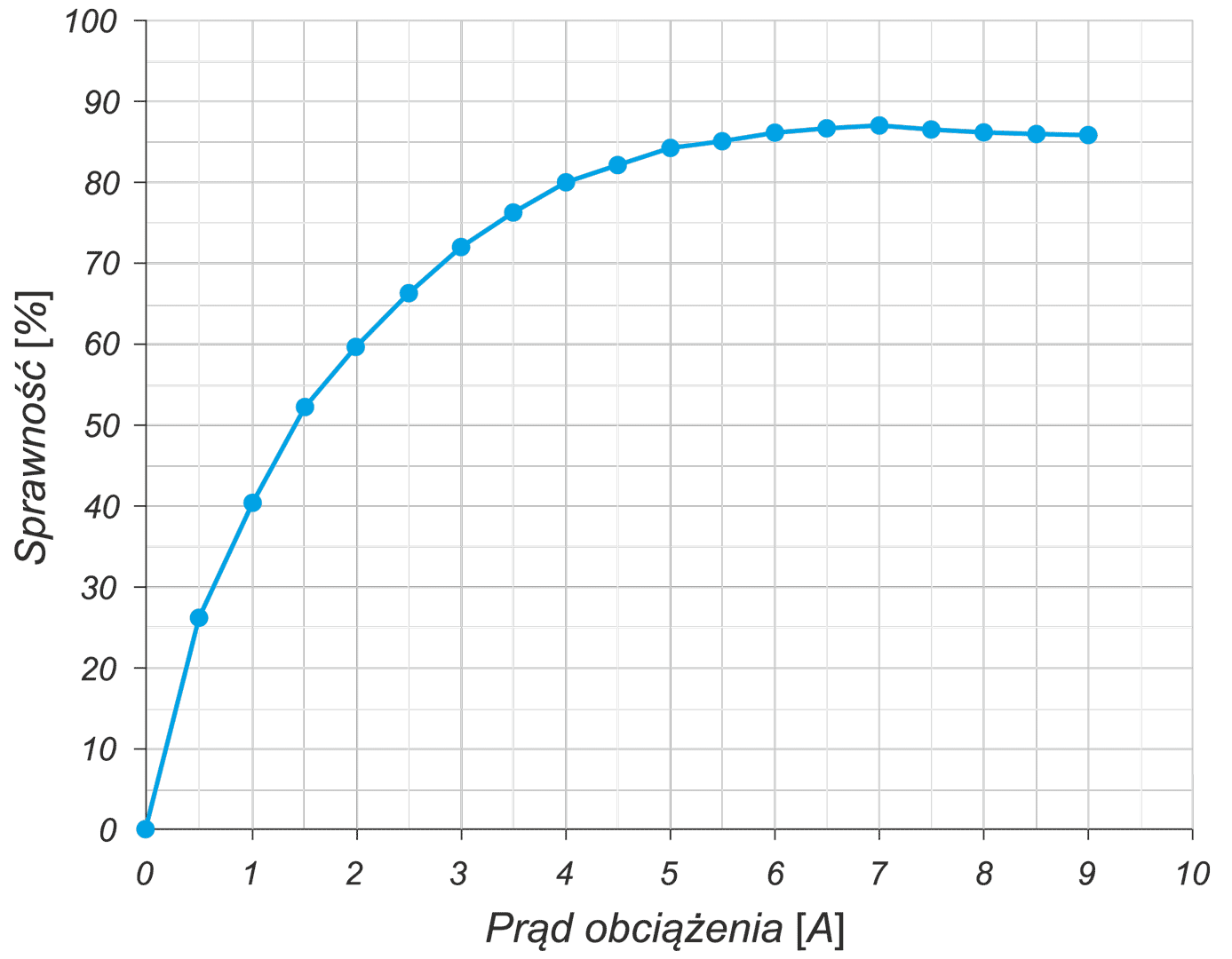
The article presents the design of permanent magnet generator dedicated for use in a transmisionless domestic wind power plant. During the design stage, the magnetising properties of stator /rotor iron have been considered in different magnetic field intensity ranges. The detailed calculations have been performed using FEMM4.2 software. A prototype generator was manufactured, and laboratory tests were conducted. Generator design and selected test results have been presented graphically in the article. This design stands out from numerous commercially available designs since it is characterized by low, non-standard rotational speed and low starting torque (allowing for wind power plant start-up at wind speeds below 2 m/s). The rigid construction of the generator makes it possible to attach the wind turbine directly to the generator shaft
Streszczenie
W artykule opisano konstrukcję generatora z magnesami trwałymi do bezprzekładniowej przydomowej elektrowni wiatrowej. Na etapie projektowania uwzględniono właściwości magnesujące stali wirnika i stojana w różnych zakresach natężenia pola. Szczegółowe obliczenia wykonano przy użyciu programu FEMM 4.2. Wykonano prototypowy generator i przeprowadzono badania laboratoryjne. Pokazane w artykule rysunki ilustrują budowę generatora oraz wybrane wyniki badań. Parametrem wyróżniającym tę konstrukcję na tle szerokiej gamy produkowanych generatorów jest niska, niestandardowa prędkość obrotowa i niski moment rozruchowy, który pozwala na rozruch elektrowni przy wietrze o prędkości poniżej 2 m/s. Sztywna konstrukcja generatora pozwala na założenie turbiny wiatrowej bezpośrednio na wale generatora
Keywords
electrical machine, electric micropower plant, cogging torque
Słowa kluczowe
maszyna elektryczna, mikroelektrownia, moment zaczepowy
Rys. / Fig.
Bibliografia / Bilbiography
[1] M. Degner, A. Munoz, F. Liang: “Evaluation of interior pm and surface pmsynchronous machines with distributed and concentrated windings.”, InIECON,pages 1189–1193, 2008.
[2] T. Glinka: „Maszyny elektryczne wzbudzane magnesami trwałymi.”, PWN 2018.
[3] Z. Goryca, K. Paduszyński, A. Pakosz: “Model of the multipolar engine with decreased cogging torque by asymmetrical distribution of the magnets.”, Open Physics, Tom: 16, Zeszyt: 1, s. 42-45, 2018.
[4] Z. Goryca, S. Różowicz, A. Różowicz, A. Pakosz, H. Wachta, M. Leśko: “Impact of Selected Methods of Cogging Torque Reduction in Multipolar Permanent-Magnet Machines.”, Energies Vol. 13, no 22, 2020, p. 6108, https://doi.org/10.3390/en13226108.
[5] S.M. Hwang, J.B. Eom, G.B. Hwang, W.B. Jeong, Y.H. Jung : “Cogging torque and acoustic noise reduction in permanent magnet motors by teeth pairing.”, IEEE Trans. Magn., vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 3144-3146, Sept. 2000.
[6] D. Ishak, Z.Q. Zhu, D. Howe: “High torque density permanent magnet brushless machines with similar slot and pole numbers.”, Journalnof Magnetism and Magnetic Materials vol.272-276, pp.1767-1769, 2004.
[7] C.S. Koh, J.S. Seol: “New cogging torque reduction method for brushless permanent-magnet motors.”, IEEE Trans. Magn., vol. 39, no. 6,pp. 3503-3506, Nov. 2003.
[8] F. Libert, J. Soulard: “Investigation on pole-slot combinations for permanent magnet machines with concentrated windings.”, Proc. Int. Conf. on Electrical Machines, (ICEM), 2004.
[9] K. Paduszyński, Z. Goryca, A. Pakosz: “The influence of asymmetrical distribution of rotor’s magnets on the cogging torque of the multipolar machine.”, 18th International Symposium on Electromagnetic Fields in Mechatronics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering (ISEF) 2017 Tom: 18, Zeszyt: 18.
[10] J. Steinbrink: “Analytical determination of the cogging torque in brushless motor excited by permanent magnets.”, in Proc. IEEE int. Electric Machine & Drives Conf., vol. 1, pp. 172-177, May 2007.
[11] Y. Yang, X. Wang, R. Zhang, C. Zhu, T. Ding: “Research of cogging torque reduction by different slot width pairing permanent magnet motors.”, in Proc. 8th int. Electric Machines and Systems Conf., vol. 1, pp. 367-370, Sept. 2005.
[12] Z.Q. Zhu, J.T. Chen, L.J. Wu, D. Howe: “Influence of stator asymmetry on cogging torque in permanent magnet machines.”, IEEE Trans. Magnetics vol.44, no.11, pp.3851-3854, 2008.
[13] L. Zhu, S.Z. Jiang, Z.Q. Zhu, C.C. Chan: “Analytical methods for minimizing cogging torque in permanent-magnet machines.”, IEEE Trans.Magn., vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 2023-2031, April 2009.
[14] http://www.eclipsemagnetics.com/media/wysiwyg/brochures/neodymium_grades_data.pdf
[15] Z. Goryca, M. Malinowski, A. Pakosz: „Wielobiegunowa prądnica do elektrowni wiatrowej o pionowej osi obrotu i małym momencie zaczepowym.”, Patent nr PL221114.
[16] M.S. Batory: „Optymalizacja generatora z magnesami trwałymi do małej elektrowni wiatrowej.”, Praca dyplomowa, Politechnika Warszawska, Wydział Elektryczny 2021.
[17] Z. Goryca, S. Różowicz, A. Różowicz: “Permanent Magnet Generator for a Gearless Backyard Wind Turbine.”, Energies, Vol. 15, no 10, 2022, p. 1-12.
[18] https://www.eclipsemagnetics.com/site/assets/files/2399/neodymium_grades_data.pdf