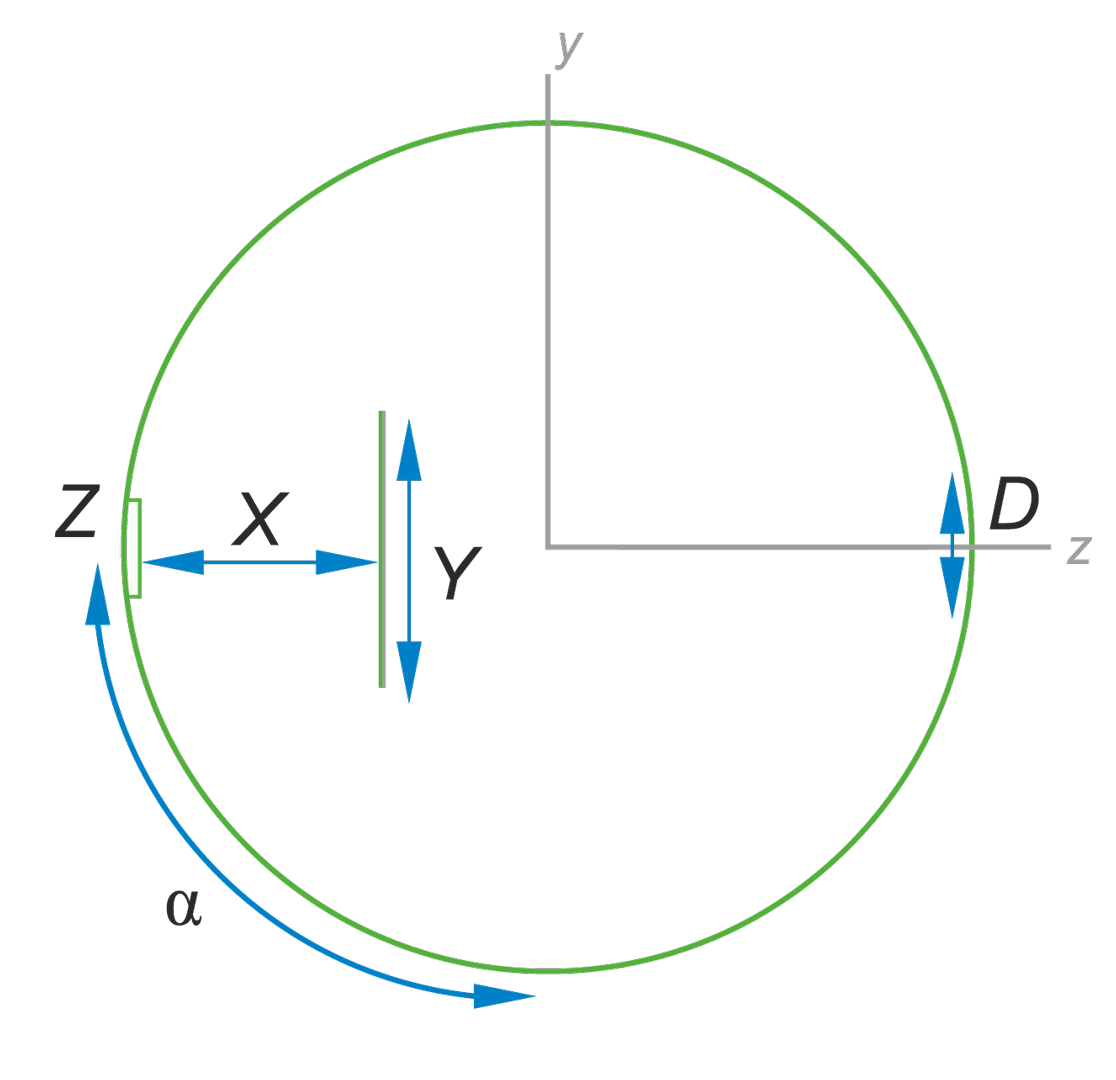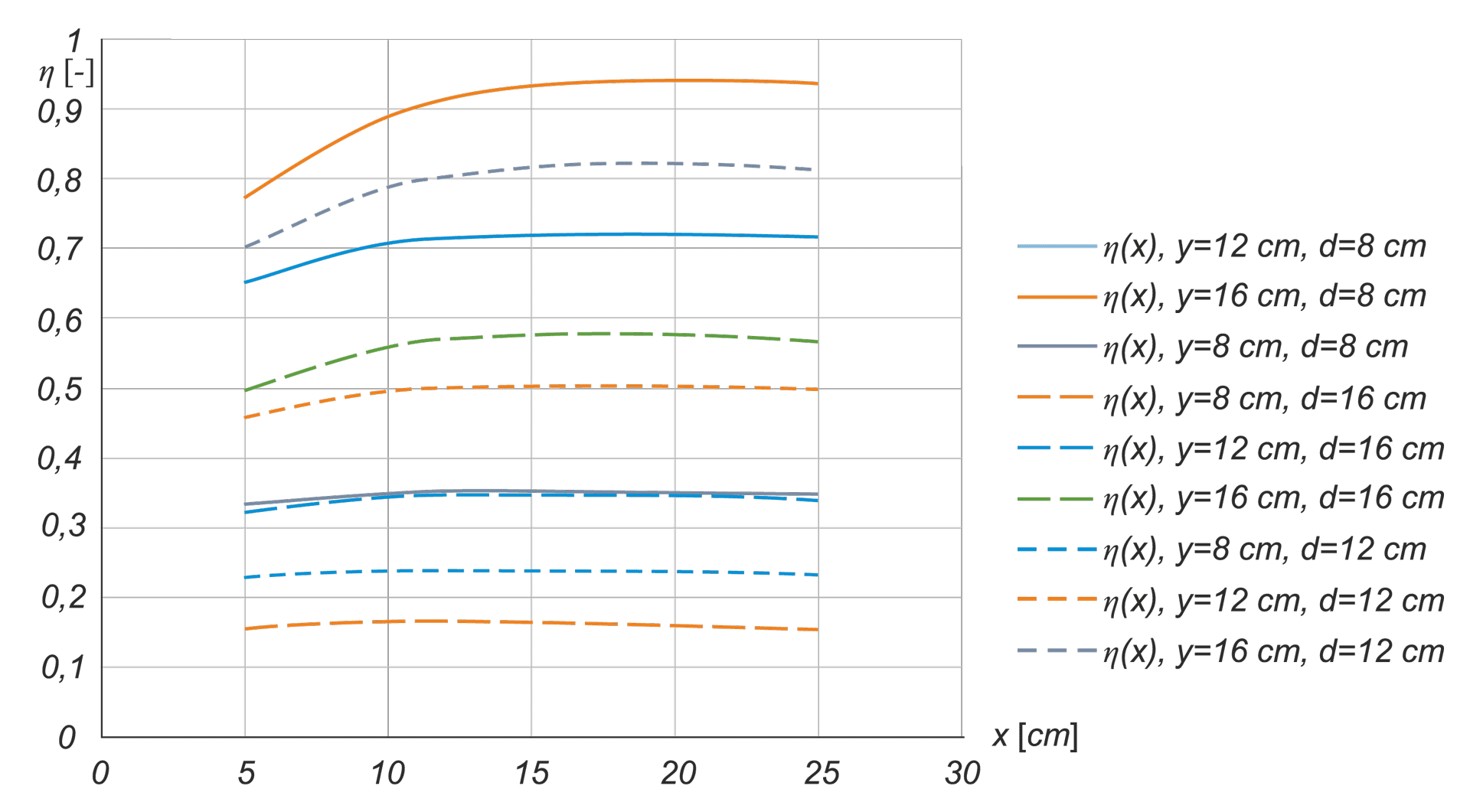E-pismo dla elektryków i elektroników
AUTOMATYKA, ELEKTRYKA, ZAKŁÓCENIA
Vol. 14, nr 2 (52) 2023
Koncepcja budowy stanowiska do wzorcowania matrycowych mierników luminancji
Concept of Construction a Station for Calibrating Matrix Luminance Meters
dr inż. Urszula BŁASZCZAK, dr inż. Marcin LEŚKO, dr inż. Henryk WACHTA, dr inż. Krzysztof BARAN, dr hab. inż. Maciej ZAJKOWSKI
Abstract
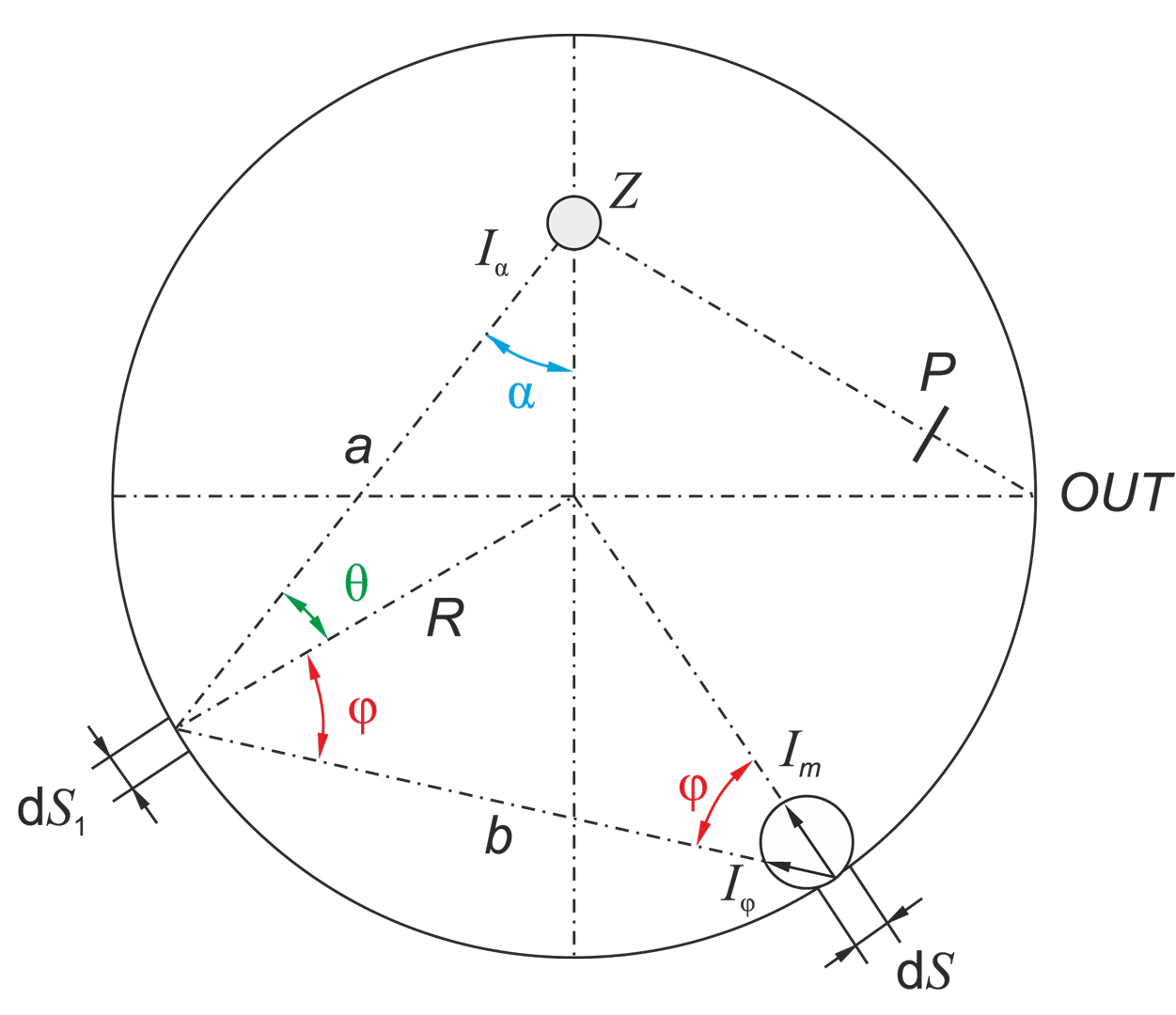
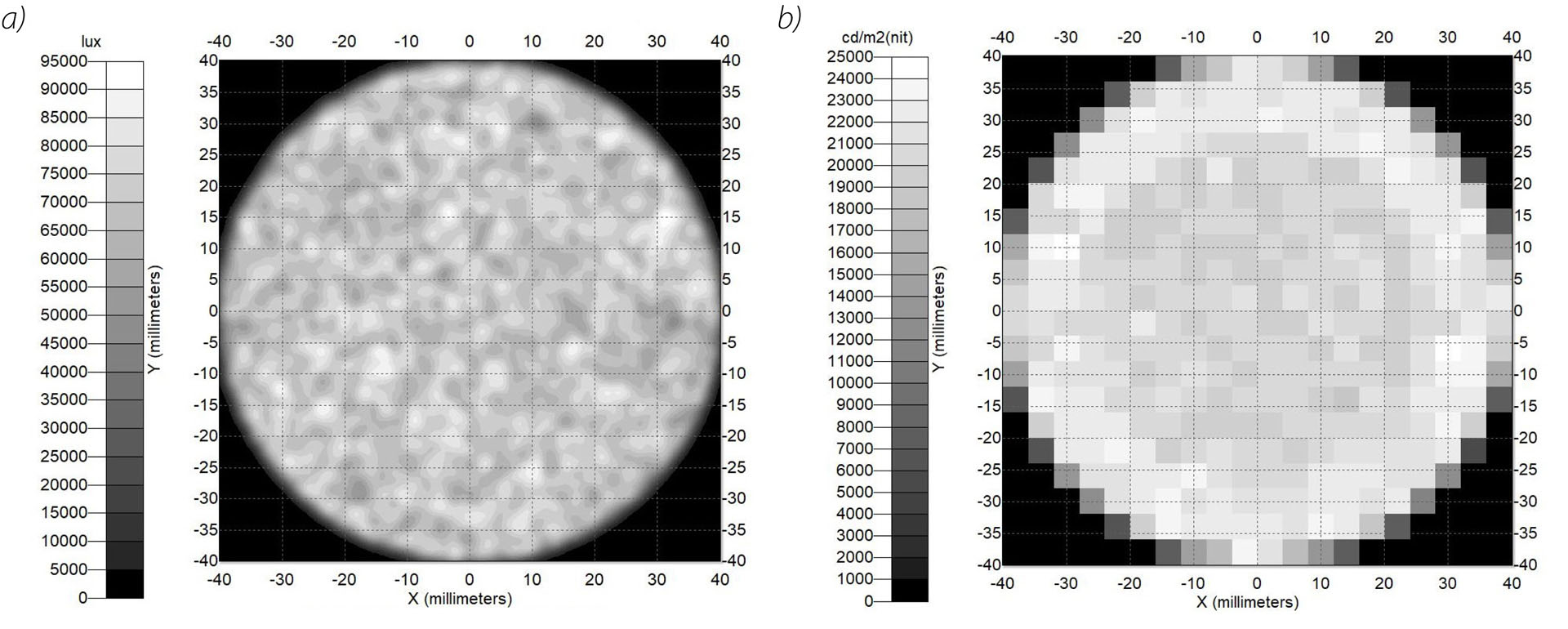
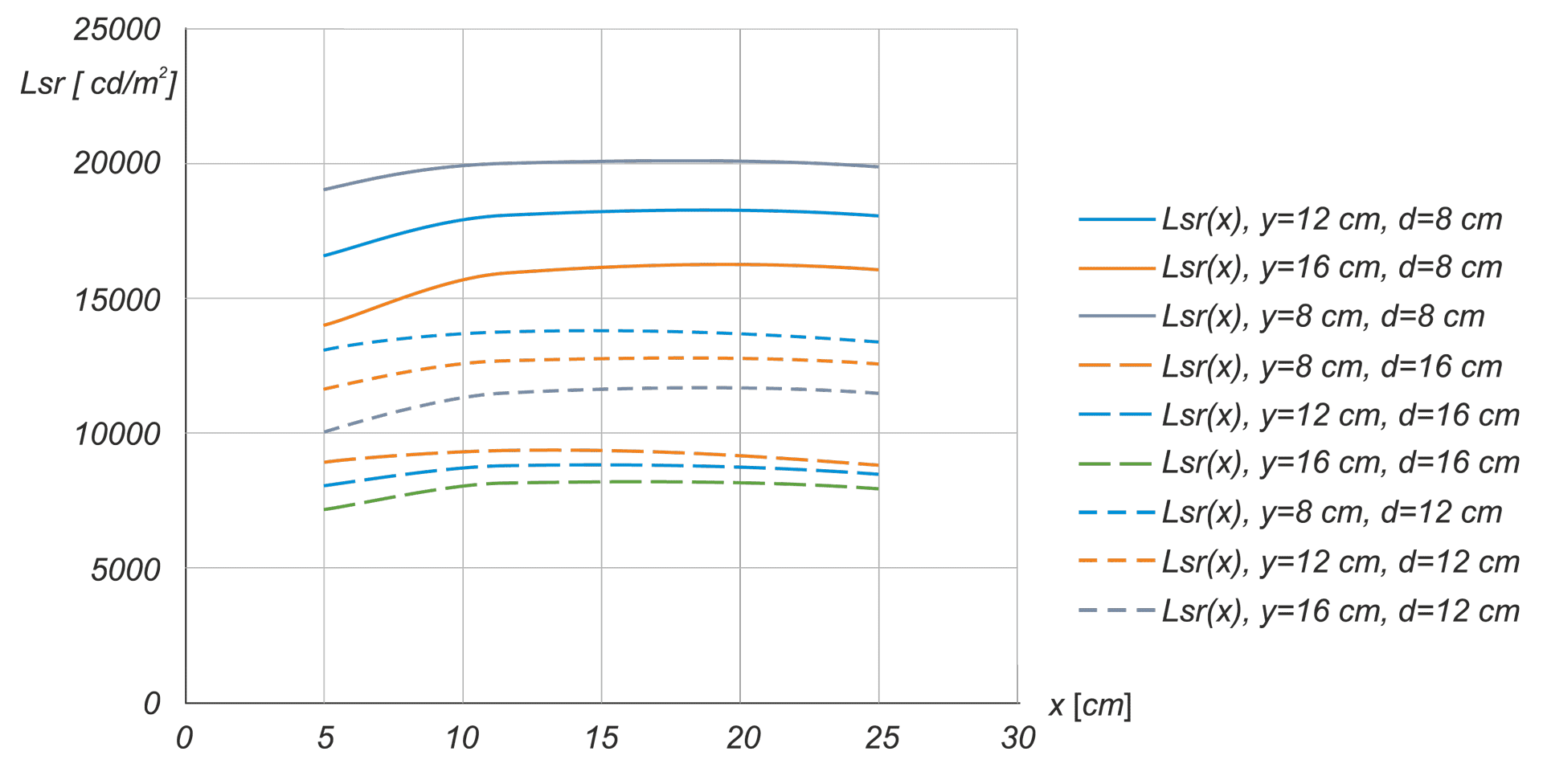
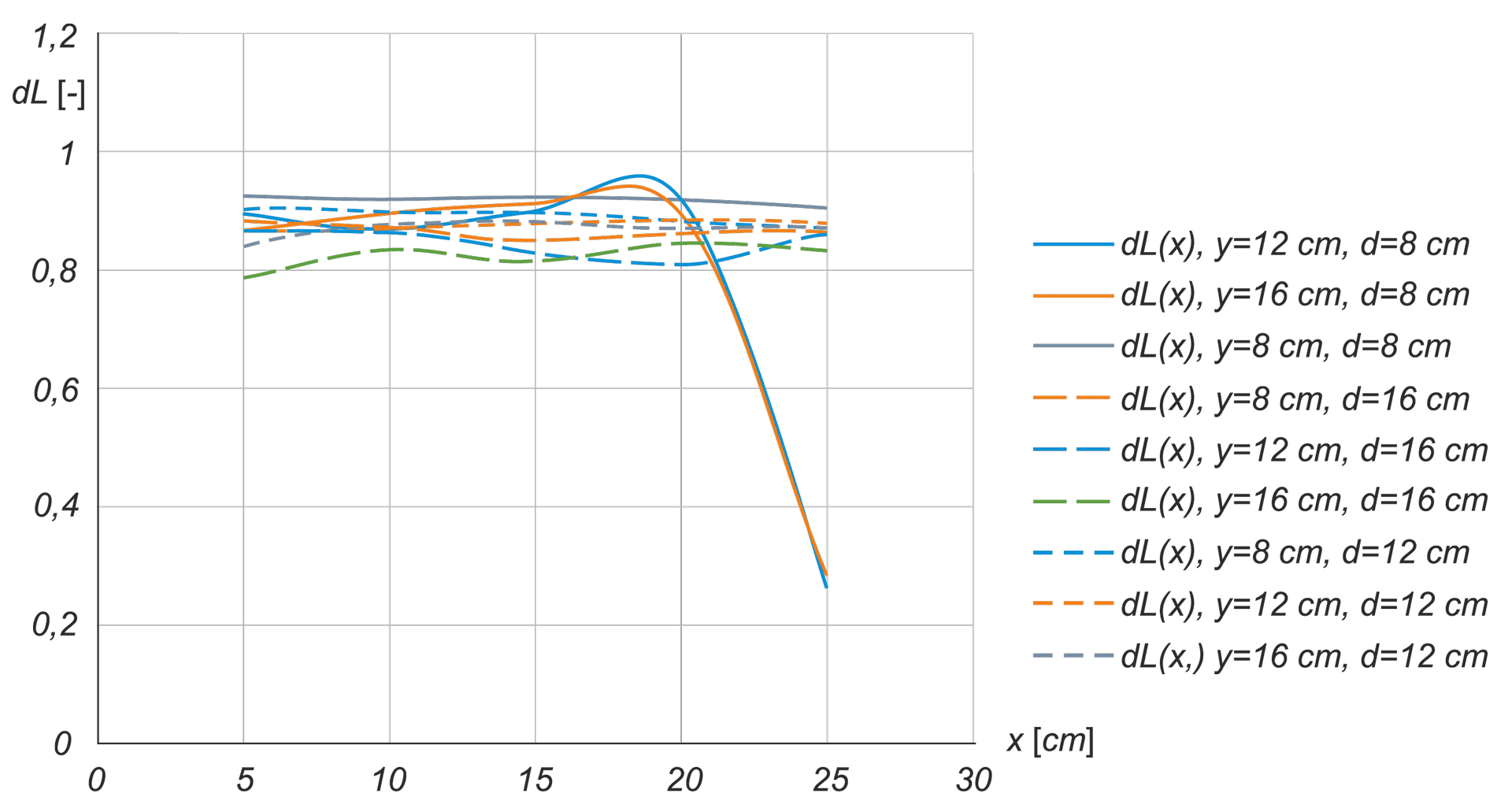
In the calibration procedure of luminance meters, it is crucial to establish a processing function specific to each meter. It is therefore necessary to develop a system that generates a standard luminance distribution with specific quantitative and geometric features. The article presents conclusions from analyses aimed at determining the initial requirements for the construction of a station for calibrating matrix luminance meters, as well as simulation results enabling the determination of the initial concept of the stations implementation.
Streszczenie
W procedurze wzorcowania mierników luminancji kluczowe jest ustalenie funkcji przetwarzania swoistej dla każdego egzemplarza miernika. Niezbędne jest zatem opracowanie systemu generującego wzorcowy rozkład luminancji o określonych cechach ilościowych i geometrycznych. W artykule zaprezentowano wnioski z analiz służących określeniu wymagań wstępnych do budowy stanowiska do wzorcowania matrycowych mierników luminancji oraz wyniki symulacji pozwalające na określenie wstępnej koncepcji realizacji stanowiska.
Keywords
luminance, matrix luminance meter, calibration
Słowa kluczowe
luminancja, matrycowy miernik luminancji, wzorcowanie
Rys. / Fig.
Bibliografia / Bilbiography
[1] ISO/CIE 19476:2014 “Characterization of the Performance of Illuminance Meters and Luminance Meters”, 2014.
[2] M.S. Rea., I.G. Jeffrey: “A new luminance and image analysis system for lighting and vision I. Equipment and calibration”, Journal of the Illuminating Engineering Society, 19(1), 64-72, 1990.
[3] CIE 244:2021 “Characterization of imaging luminance measurement devices (ILMDs)”, 2021.
[4] International Vocabulary of Metrology VIM BIPM, 2012.
[5] T. Moore I inni: “Approximate field measurement of surface luminance using a digital camera”, Lighting Research and Technology 32(1), 1-11, 2000.
[6] H. Cai. T.M. Chung.: ”Improving the quality of high dynamic range images”, Lighting Research and Technology, 43, 87-102, 2011.
[7] H. Cai: “High dynamic range photogrammetry for synchronous luminance and geometry measurement”, Lighting Research and Technology 45, 230-257, 2013.
[8] C. Pierson i inni: “Tutorial: Luminance maps for daylight studies from high dynamic range photohraphy”, LEUKOS, 17:2, 140-169, 2020.
[9] A. Borisuit i inni: “A new device for dynamic luminance mapping and glare risk assessment in buildings”, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 8485, Nonimaging Optics: Efficient Design for Illumination and Solar Concentration IX; 84850M, 2012.
[10] R.M. Poling., H. Cai: “Calculating luminous flux radiated to a camera lens via high dynamic range photogrammetry”, Lighting Research and Technology, 53, 119-145, 2021.
[11] ISO 11664-2/CIE S 014-2 (CIE 015:2018) Colorimetry, 3rd and 4th edition.
[12] CIE S 017/E:2020 “International lighting vocabulary”, 2020.
[13] U.J. Błaszczak i inni: „Characterization of multi-emitter tuneable LED source for endoscopic applications”, Metrology and Measurement Systems 26(1):153-169, 2019.
[14] Alireza Mahmoudi Nahavandi i inni: "LED primary selection algorithms for simulation of CIE standard illuminants," Optics Express 28, 34390-34405, 2020.
[15] A. Kokka i inni: “Development of white LED illuminants for colorimetry and recommendation of white LED reference spectrum for photometry“, Metrologia 55 526, 2018.
[16] F.J. Burgos I inni: „Spectral LED-Based Tuneable Light Source for the Reconstruction of CIE Standard Illuminants”. In: Elmoataz, A., Lezoray, O., Nouboud, F., Mammass, D. (eds) Image and Signal Processing. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 8509. Springer, 2014.