E-journal for electrical and electronic engineers
AUTOMATYKA, ELEKTRYKA, ZAKLOCENIA
(AUTOMATICS, ELECTROTECHNICS, DISTURBANCES)
Vol. 4, Nr 4 (14) 2013
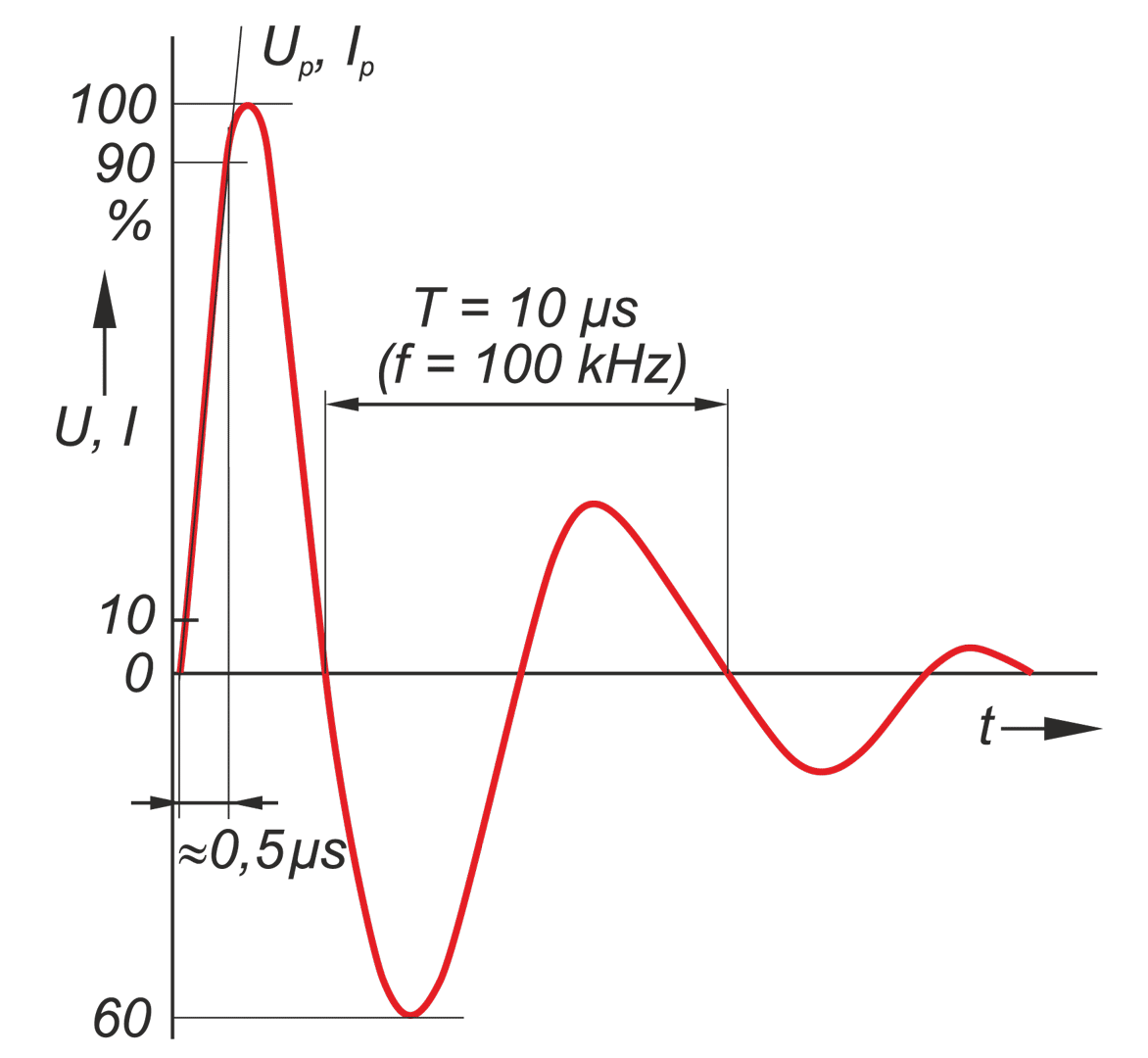
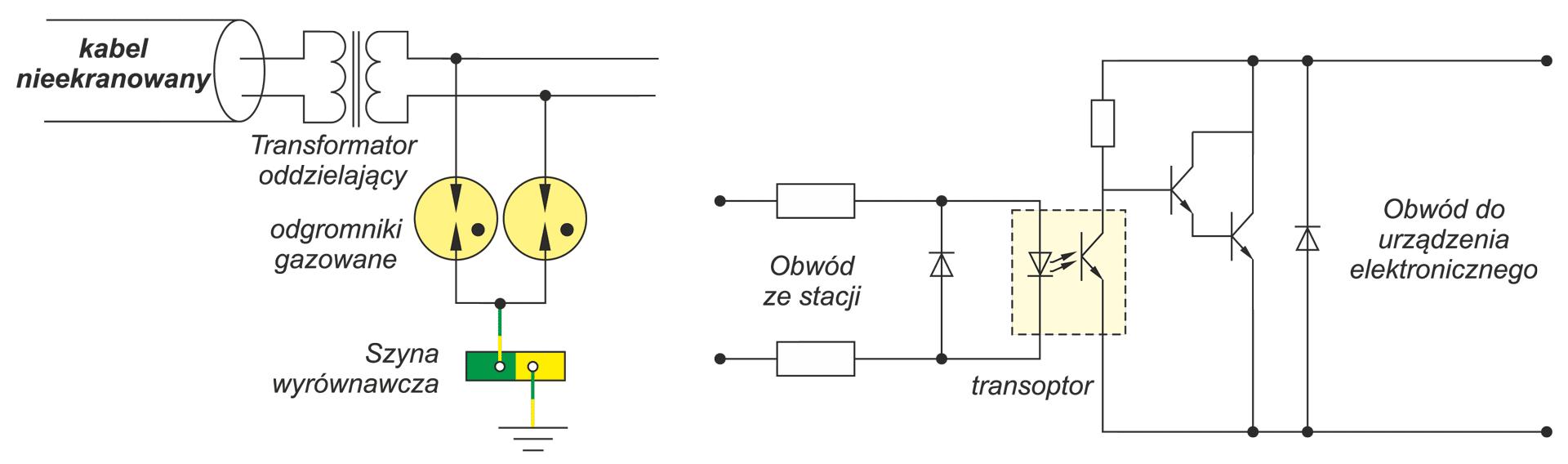
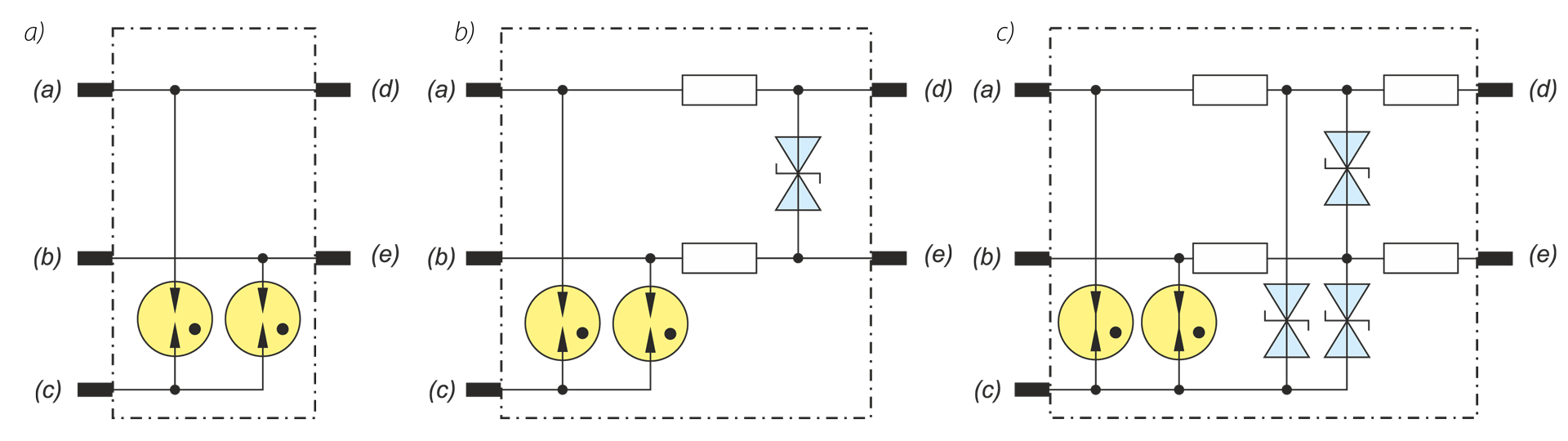
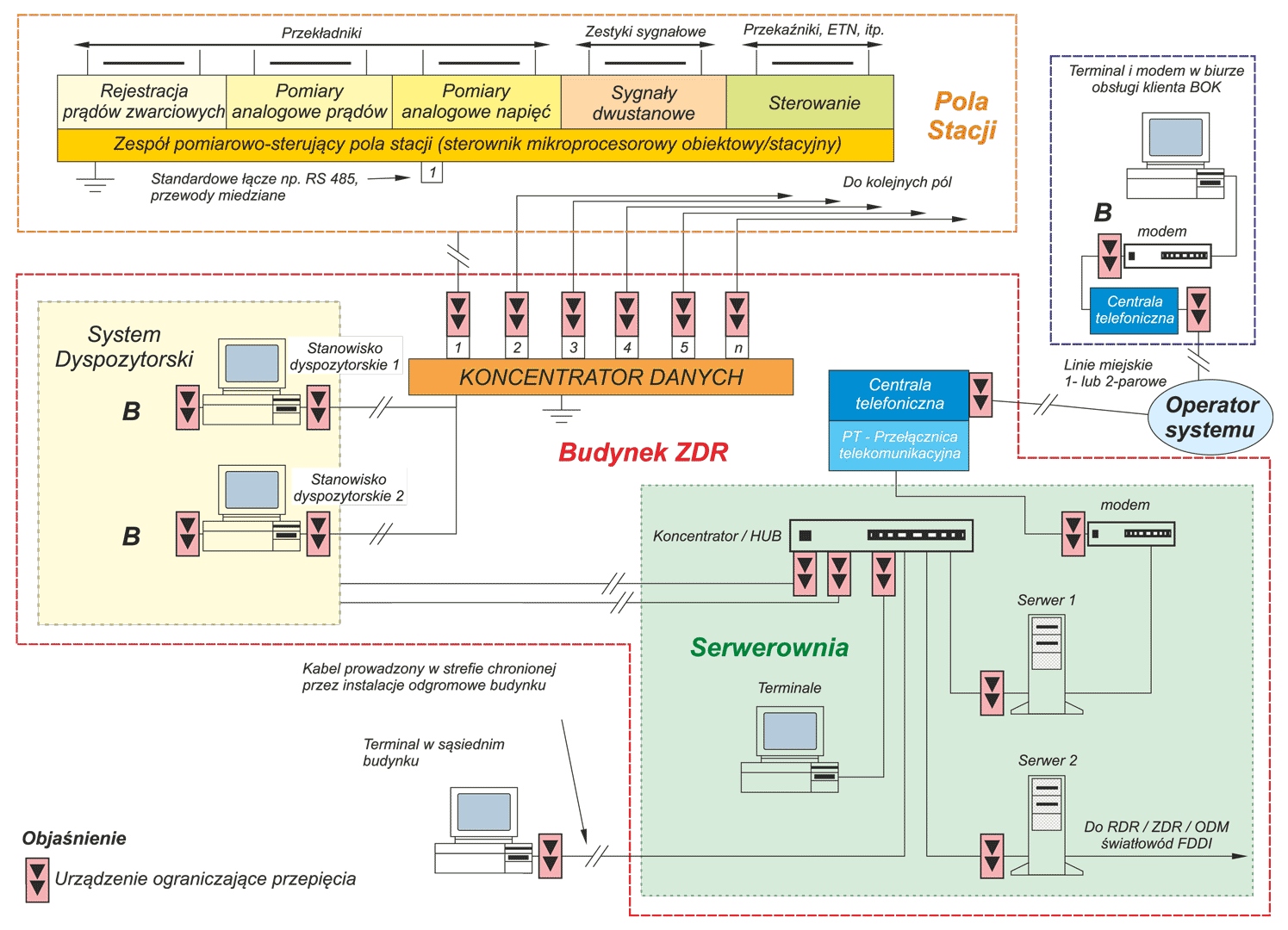
Creating the conditions for the safe and reliable operation of electronic equipment and systems requires the basic information about pulsed electromagnetic exposure in different places of signal circuits. This problem is particularly important in the case of signal lines which are on the premises of HV power station. Current and voltage surges are particularly dangerous for digital control and signaling systems. While designing protection systems against this type of risk, basic information about the levels of induced voltages in the signal transmission lines and the potential differences occurring within the station is required. Additionally the information about the levels of surge resistance of devices signal inputs are very important.. Keywordsovervoltage arresters, electromagnetic pulse, HV power station, current and voltage surges
Abstract
Creating the conditions for the safe and reliable operation of electronic equipment and systems requires the basic information about pulsed electromagnetic exposure in different places of signal circuits. This problem is particularly important in the case of signal lines which are on the premises of HV power station. Current and voltage surges are particularly dangerous for digital control and signaling systems. While designing protection systems against this type of risk, basic information about the levels of induced voltages in the signal transmission lines and the potential differences occurring within the station is required. Additionally the information about the levels of surge resistance of devices signal inputs are very important.
Keywords
overvoltage arresters, electromagnetic pulse, HV power station, current and voltage surges
Fig.
Bilbiography
*Artykuł był opublikowany w materiałach konferencyjnych AUTOMATYKA, ELEKTRYKA, ZAKŁÓCENIA − 2006
[1] PN -86/E-05003/01 Ochrona odgromowa obiektów budowlanych. Wymagania ogólne.
[2] PN -IEC 61024-1:2001 Ochrona odgromowa obiektów budowanych. Zasady ogólne
[3] PN -IEC 61312-1 Ochrona przed piorunowym impulsem elektromagnetycznym. Zasady ogólne.
[4] PN -IEC 61024-1-2:2002 Ochrona odgromowa obiektów budowlanych. Zasady ogólne. Przewodnik B – Projektowanie, montaż, konserwacja
i sprawdzanie urządzeń piorunochronnych.
[5] PN -EN 50174-3:2005 Technika informatyczna. Instalacje okablowania. Część 3: Planowanie i wykonawstwo instalacji na zewnątrz budynku.
[6] IEEE Std 4487-2000 IEEE, Recommended Practice for Protection of Wire-Line Communication Facilities Serving Electrical Supply Location.
[7] IEEE Std 1646TM − 2004, Standard Communication Delivery Time Performance Requirements for Electric Power Substation.
[8] NAMUR NE 21:1998, Elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit von Betriebsmitteln der Prozess- und Labortechnik.
[9] PN -EN 55024:2000 Kompatybilność elektromagnetyczna (EMC ). Urządzenia informatyczne. Charakterystyka odporności. Metodyka
pomiaru i dopuszczalne poziomy.
[10] PN -EN 61000-4-4:1998/A1:1999/A2:2003 Kompatybilność elektromagnetyczna (EMC). Metody badań i pomiarów. Badania odporności na
serie szybkich zakłóceń impulsowych.
[11] PN -EN 61000-4-5:1998/A1:2003 Kompatybilność elektromagnetyczna (EMC). Metody badań i pomiarów. Badania odporności na udary.
[12] PN -EN 61000-4-12:1999 Kompatybilność elektromagnetyczna (EMC ). Metody badań i pomiarów. Badania odporności na przebiegi
oscylacyjne. Podstawowa publikacja EMC.
[13] PN -EN 61010-1:2000 Wymagania bezpieczeństwa elektrycznych przyrządów pomiarowych, automatyki i urządzeń laboratoryjnych.
[14] PN -EN 61643-21:2004 Niskonapięciowe urządzenia ograniczające przepięcia – Część 21: Urządzenia do ograniczania przepięć w sieciach
telekomunikacyjnych i sygnalizacyjnych. Wymagania eksploatacyjne i metody badań.
[15] PN -EN 61643-311:2003E Elementy do niskonapięciowych urządzeń ograniczających przepięcia- Część 311: Wymagania dla iskierników
gazowych (GDT ).
[16] PN -EN 60255-22-4:2003E Przekaźniki energoelektryczne. Część 22-4: Badania odporności na zakłócenia elektryczne przekaźników
pomiarowych i urządzeń zabezpieczeniowych. Badanie odporności na szybkozmienne zakłócenia przejściowe.