E-journal for electrical and electronic engineers
AUTOMATYKA, ELEKTRYKA, ZAKLOCENIA
(AUTOMATICS, ELECTROTECHNICS, DISTURBANCES)
Vol. 5, Nr 4 (18) 2014
Multi-phase Cage Induction Motors – Advantages and Disadvantages
Abstract
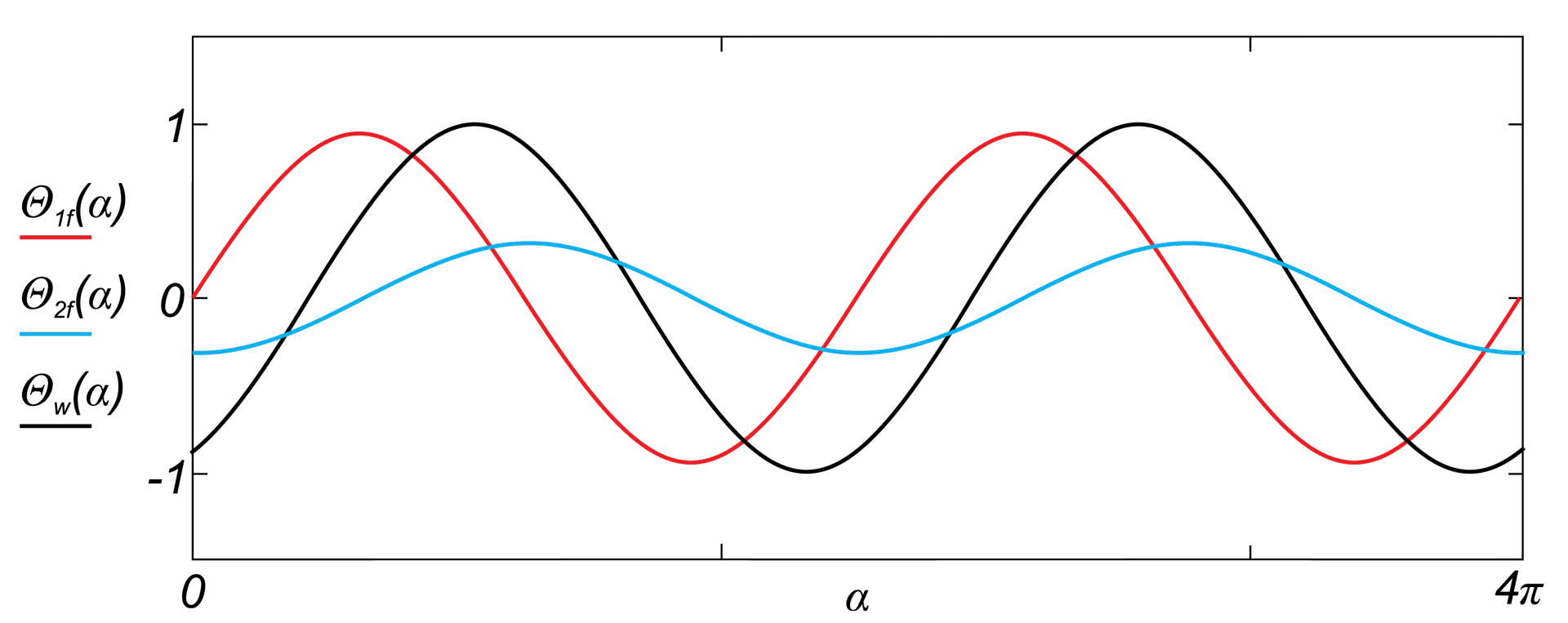
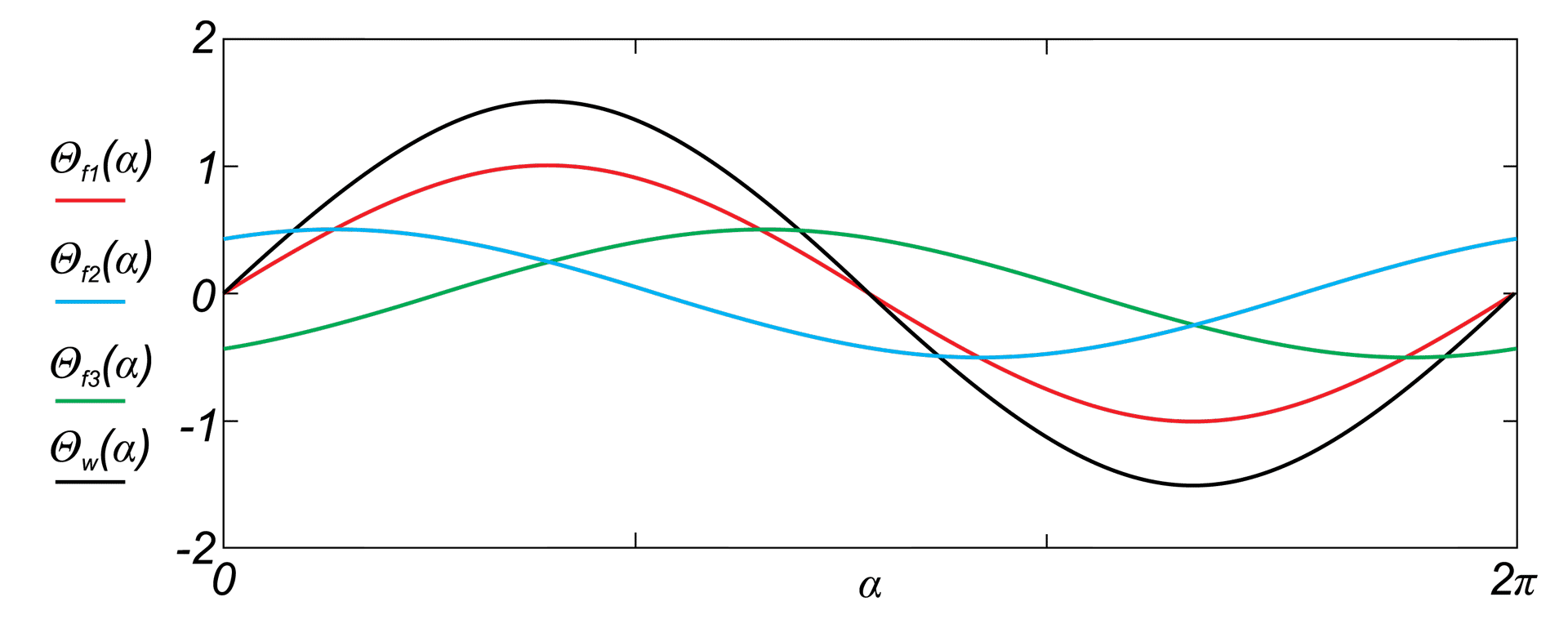
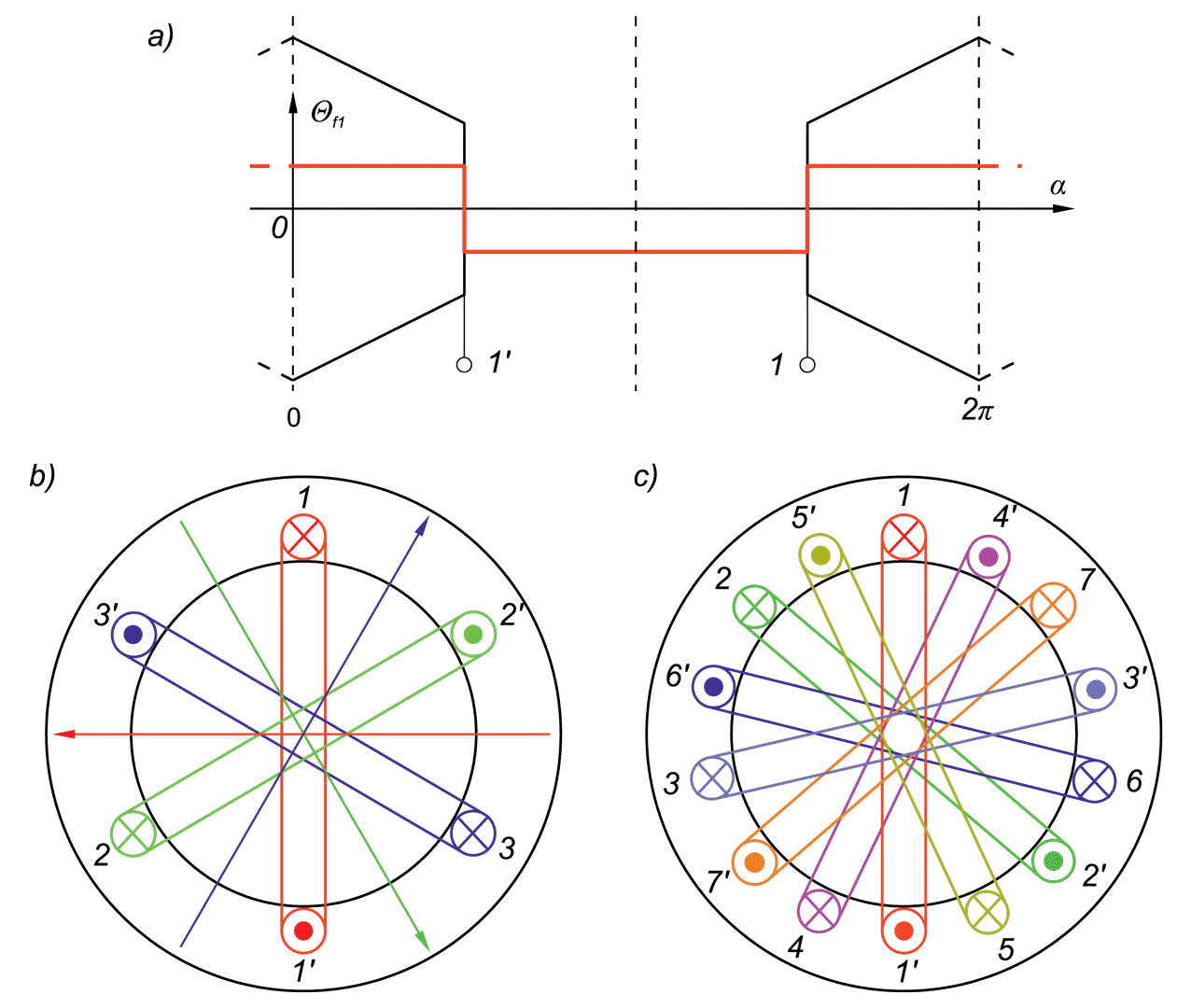
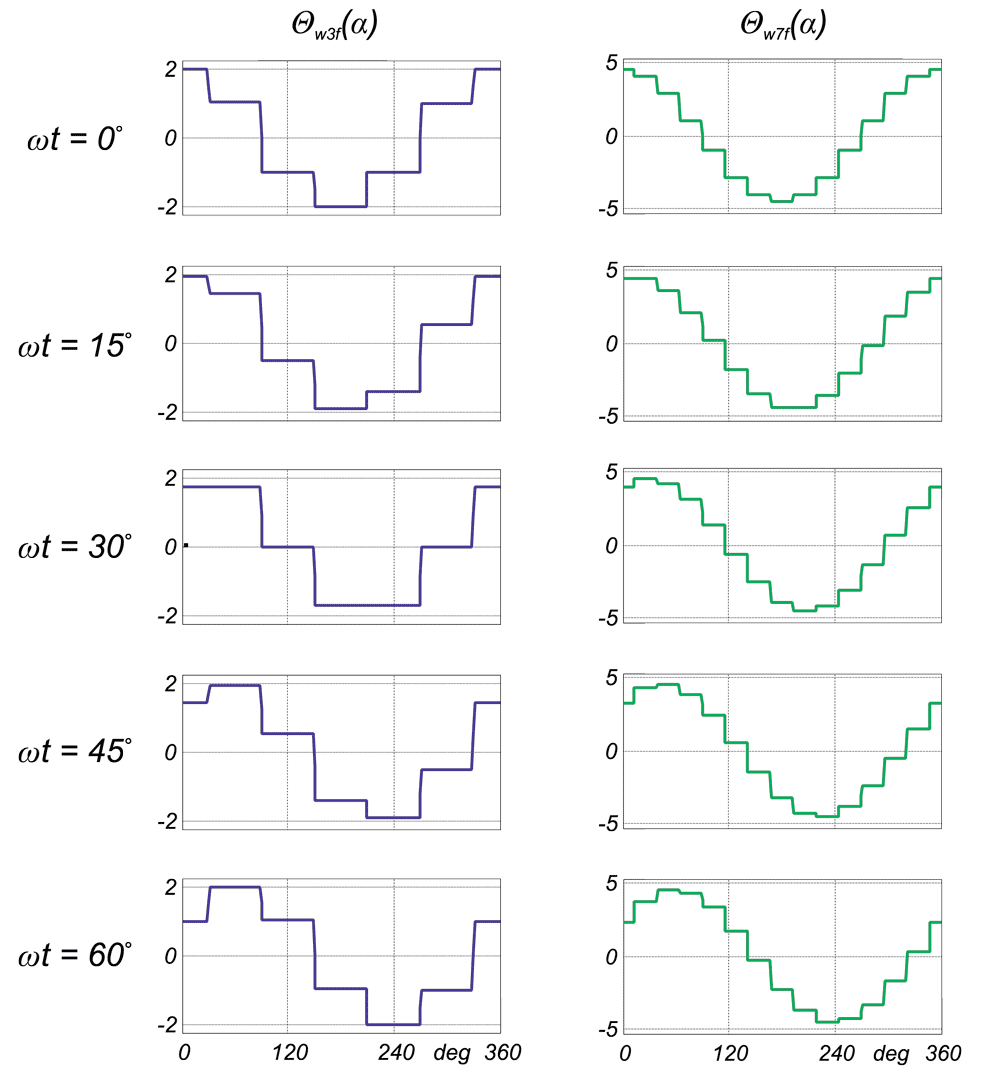
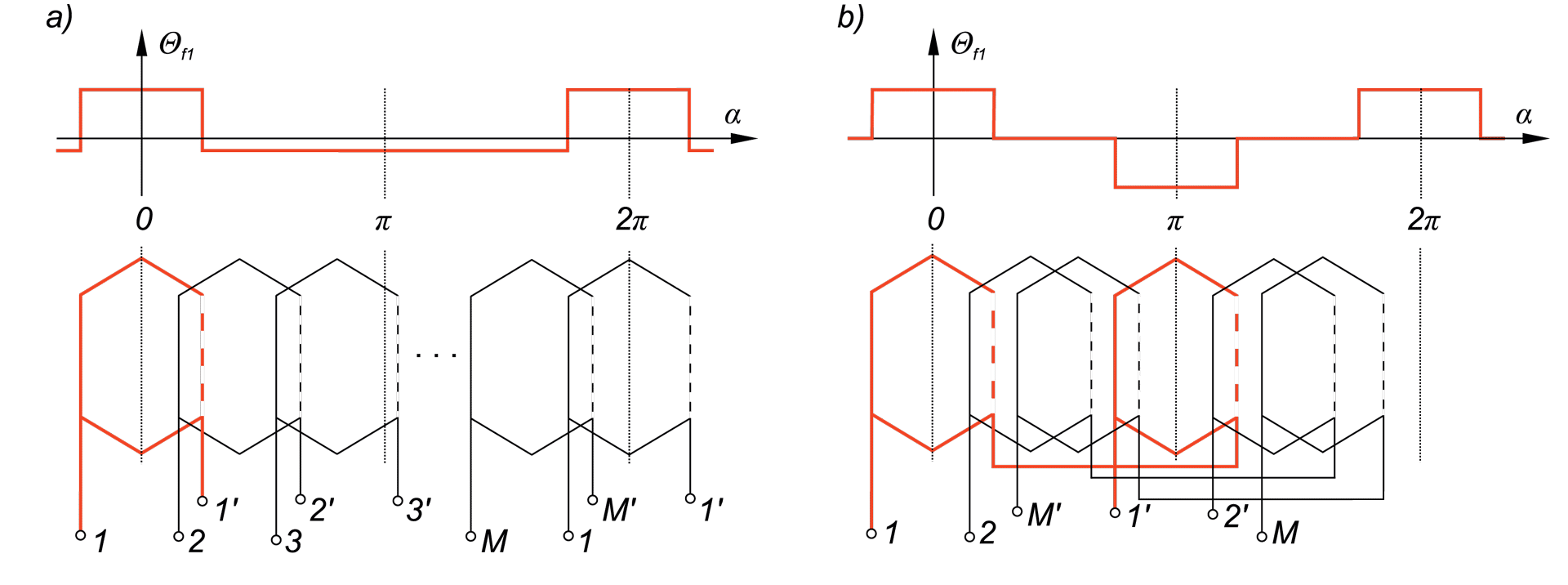
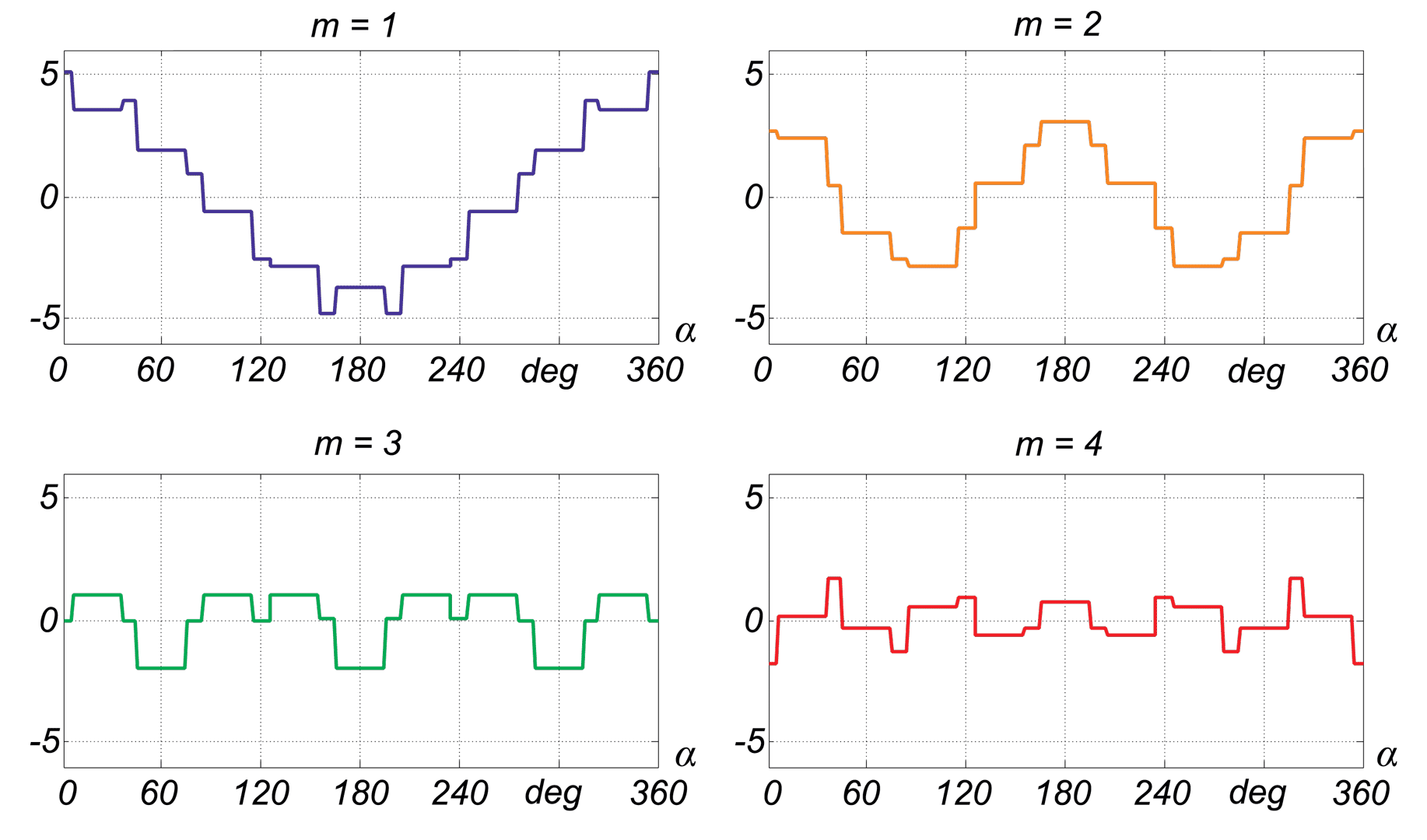
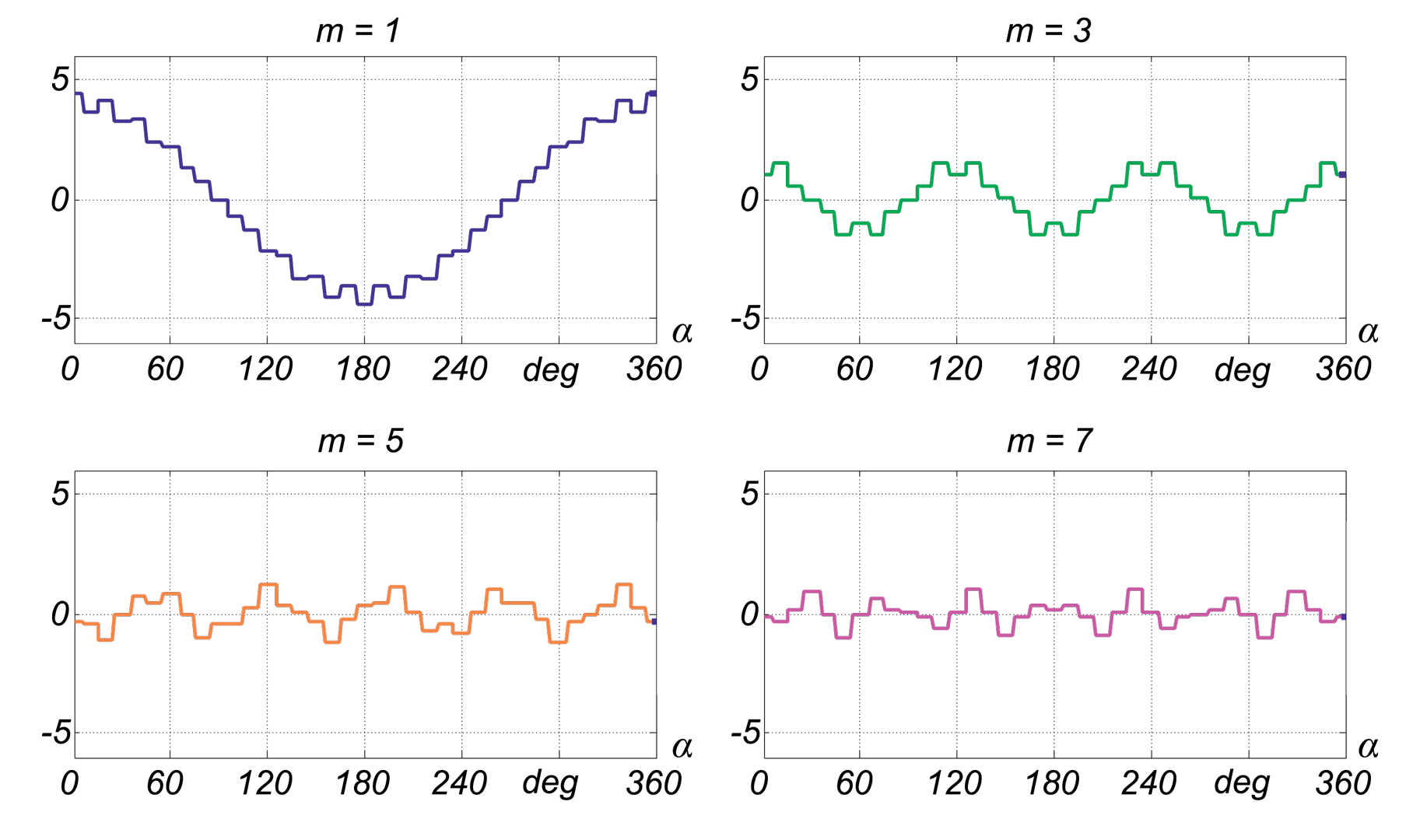
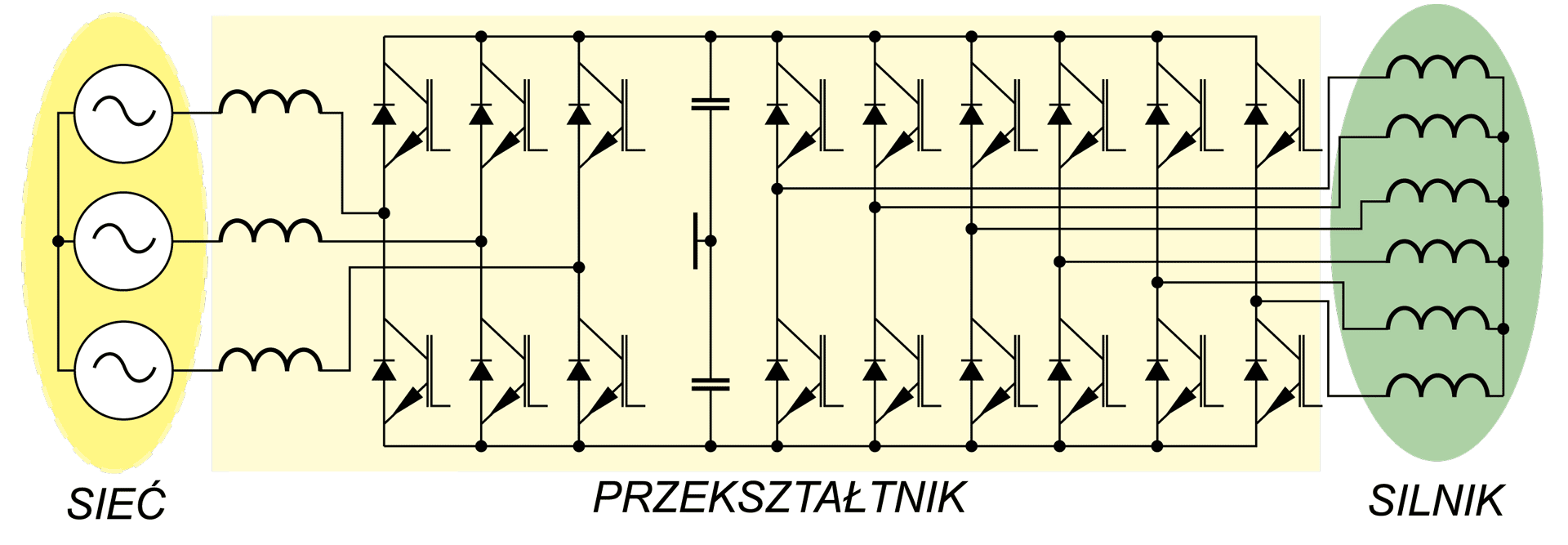
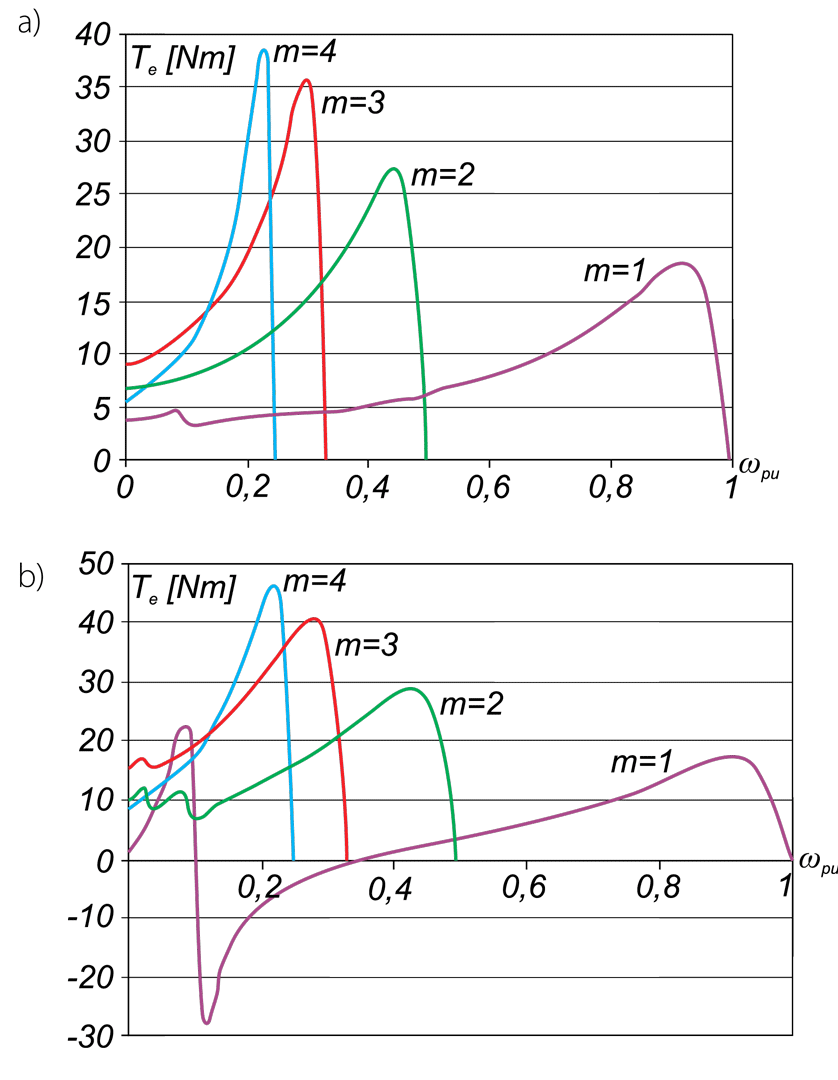
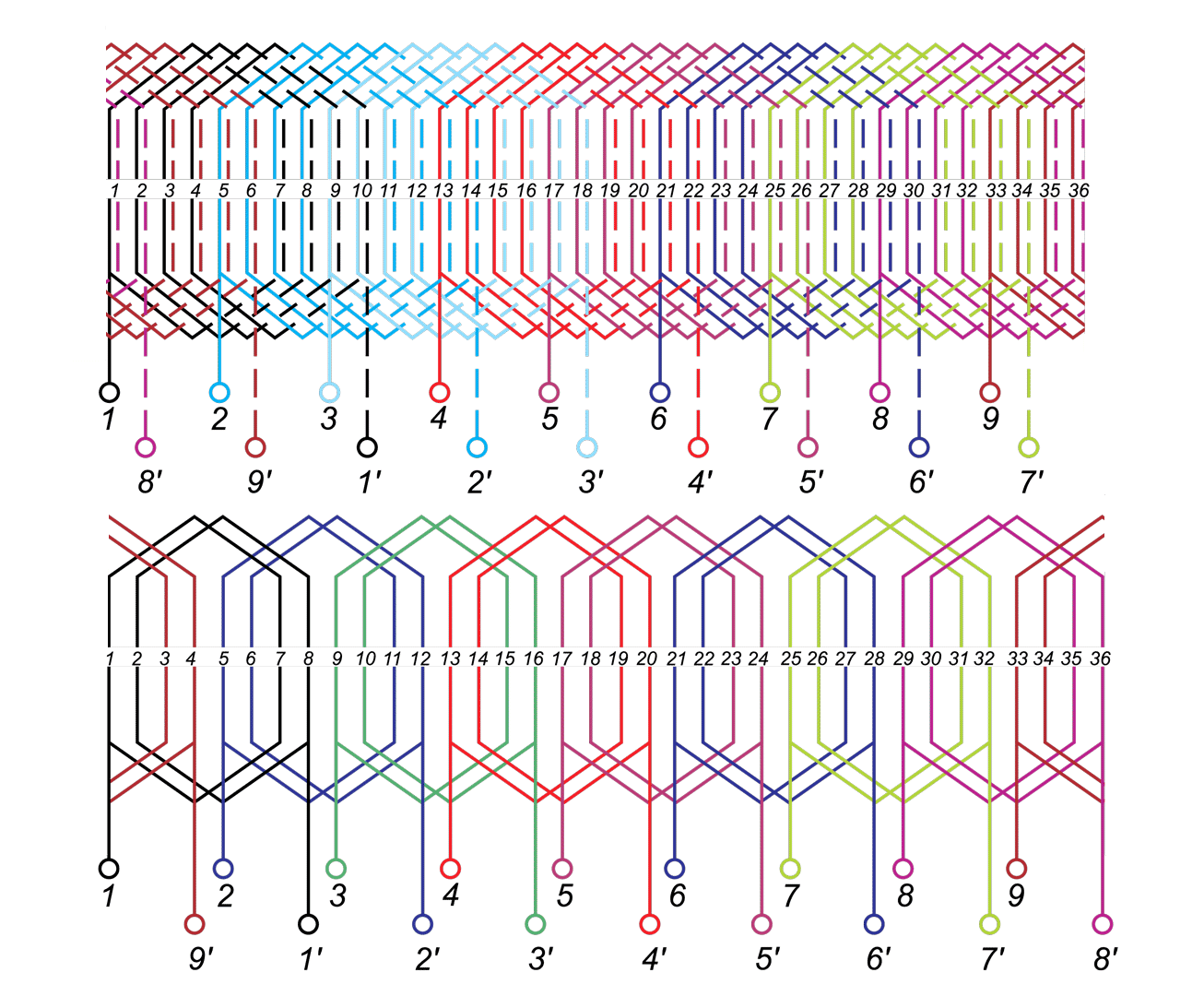
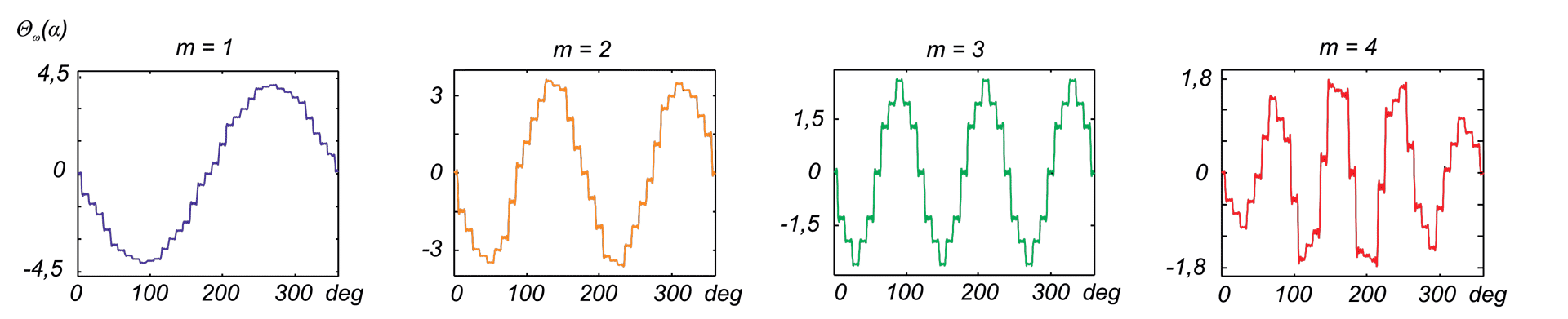
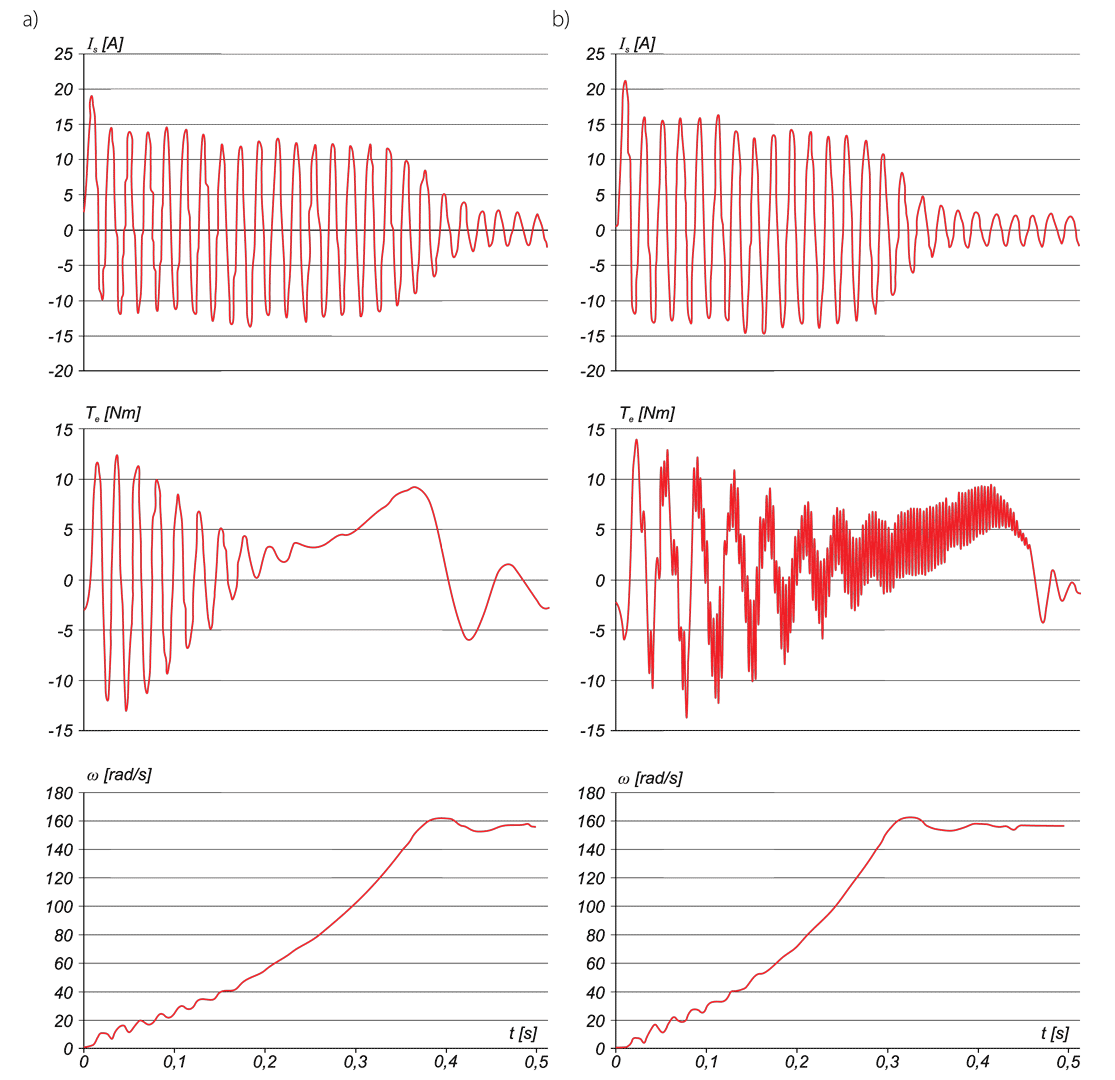
This paper describes advantages and disadvantages of induction motors with multi-phase windings. A comparison of possible developments of the air-gap flux density distribution using 3phase and multi-phase windings has been carried out. Moreover the possibility to shape performance characteristics of multi-phase induction motors has been shown. Multi-phase machines possess several advantages over conventional three-phase motors such as: reducing the amplitude and increasing the frequency of torque ripple , reducing the current per phase without increasing the voltage per phase, increasing efficiency, reliability and power within the same frame.
Keywords
induction motor, multi-phase winding, efficiency, electrical machine
Fig.
Bilbiography
[1] J. Bernatt, T. Glinka, "Electrical machines with 6-phase winding". Przegląd Elektrotechniczny, nr 12, 2008.
[2] J. Bernatt, T. Glinka, "Maszyny elektryczne z uzwojeniem 6-fazowym". Wiadomości Elektrotechniczne, nr 12, 2008.
[3] M. Dąbrowski, Projektowanie maszyn elektrycznych prądu przemiennego. WNT Warszawa 1988.
[4] P. Drozdowski, "Field oriented control of a 9-phase cage induction motor". Technical Transactions Z.4-E/1998 "Elektrotechnika", Wyd. Politechniki Krakowskiej ISSN 0011-4561, Kraków 1998.
[5] P. Drozdowski, "Parasitic effects of polyphase cage induction motors fed by a voltage source inverter". Prace Naukowe Instytutu Maszyn, Napędów i Pomiarów Elektrycznych Politechniki Wrocławskiej, nr 50, 2000.
[6] P. Drozdowski, Kształtowanie charakterystyk i własności ruchowych wielofazowych silników indukcyjnych klatkowych. Monografia 278. Wyd. Politechniki Krakowskiej, Kraków 2001. [7] P. Drozdowski, „Speed control of multiphase cage induction motors incorporating supply sequence”. Archives of Electrical Engineering. Volume 63, Issue 4, Pages 511–534, ISSN 1427-4221, Online 2300-2506, DOI: 10.2478/aee-2014-0035, December 2014.
[8] J. Gieras, Z. Piech, B. Tomczuk, Linear Synchronous Motors. Linear Synchronous Motors: Transportation and Automation Systems, Second Edition. CRC Press, 2011.
[9] C.B. Jacobina i inni, „Reduced Switch-Count Six-Phase AC Motor Drive Systems Without Input Reactor”. IEEE Trans. on Industrial Electronics, vol. 55, no. 5, 2008.
[10] A. Rogalski, A. Pochanke, K. Bieńkowski: Rozkład indukcji magnetycznej w szczelinie powietrznej silnika indukcyjnego wielofazowego. Proceedings of XL International Symposium on Electrical Machines SME'2004, 15 − 18 June, 2004, Hajnówka, Poland.
[11] A. Rogalski, A. Pochanke: „Silniki indukcyjne wielofazowe − układy napięć zasilających“. Zakład Maszyn Elektrycznych, Wydział Elektryczny Politechniki Warszawskiej, http://www.ime.pw.edu.pl/zme/pub/04/003rogalski.pdf (19.05.2014).
[12] M. Ronkowski, M. Michna, G. Kostro, F. Kutt, Maszyny wokół nas. Zastosowanie, budowa, modelowanie, charakterystyki, projektowanie. Wyd. Politechniki Gdańskiej, Gdańsk 2011.
[13] T. Sobczyk: Metodyczne aspekty modelowania matematycznego maszyn indukcyjnych. WNT, Warszawa 2004.
[14] J. Zawilak: Uzwojenia zmiennobiegunowe maszyn elektrycznych prądu przemiennego. Prace Naukowe Instytutu Układów Elektromaszynowych Politechniki Wrocławskiej, nr 37, seria M nr 7,1986.