E-journal for electrical and electronic engineers
AUTOMATYKA, ELEKTRYKA, ZAKLOCENIA
(AUTOMATICS, ELECTROTECHNICS, DISTURBANCES)
vol. 9, nr 4 (34) 2018
Diagnostic of Control Systems for Power Unit
Mariusz PAWLAK
Abstract
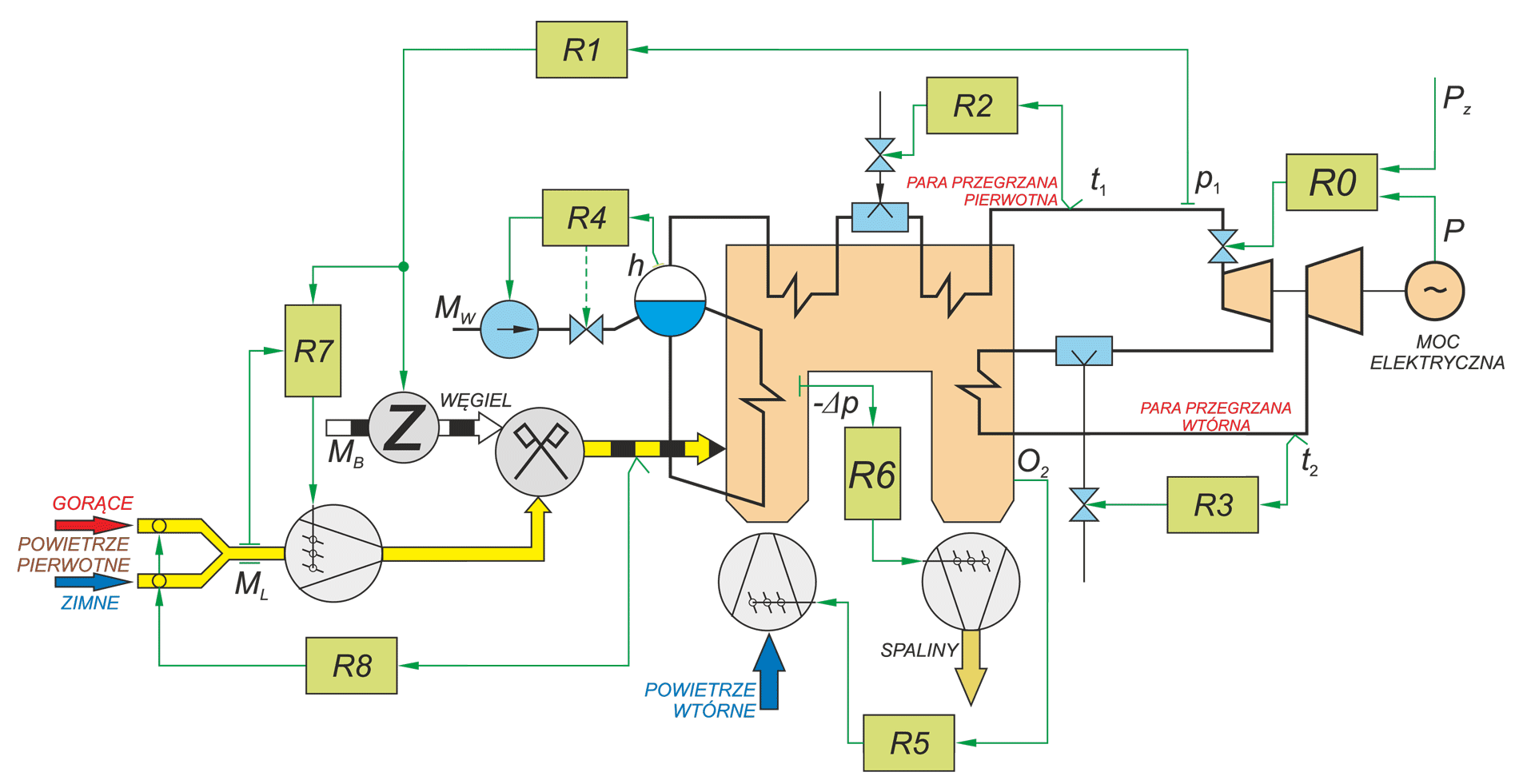
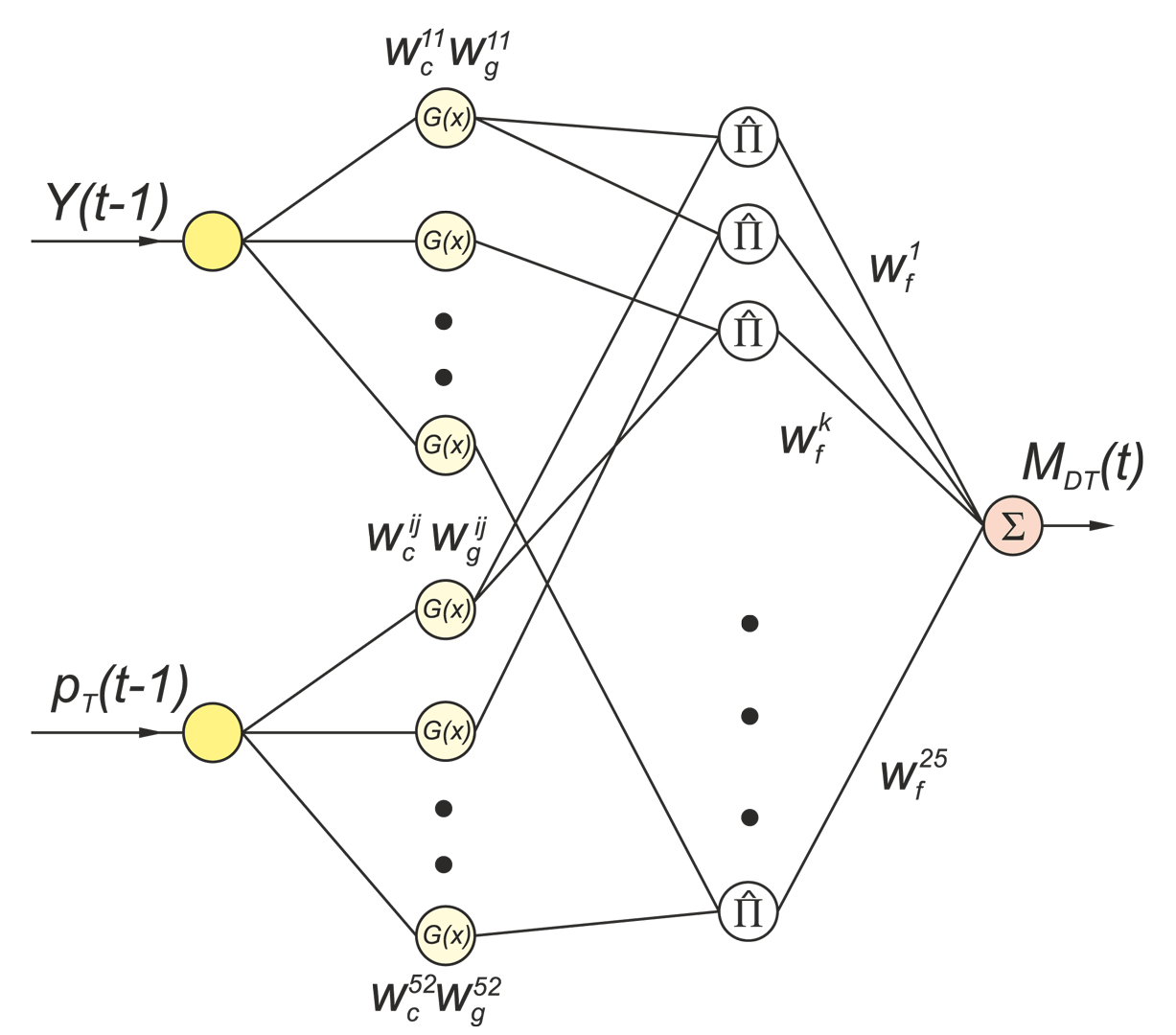
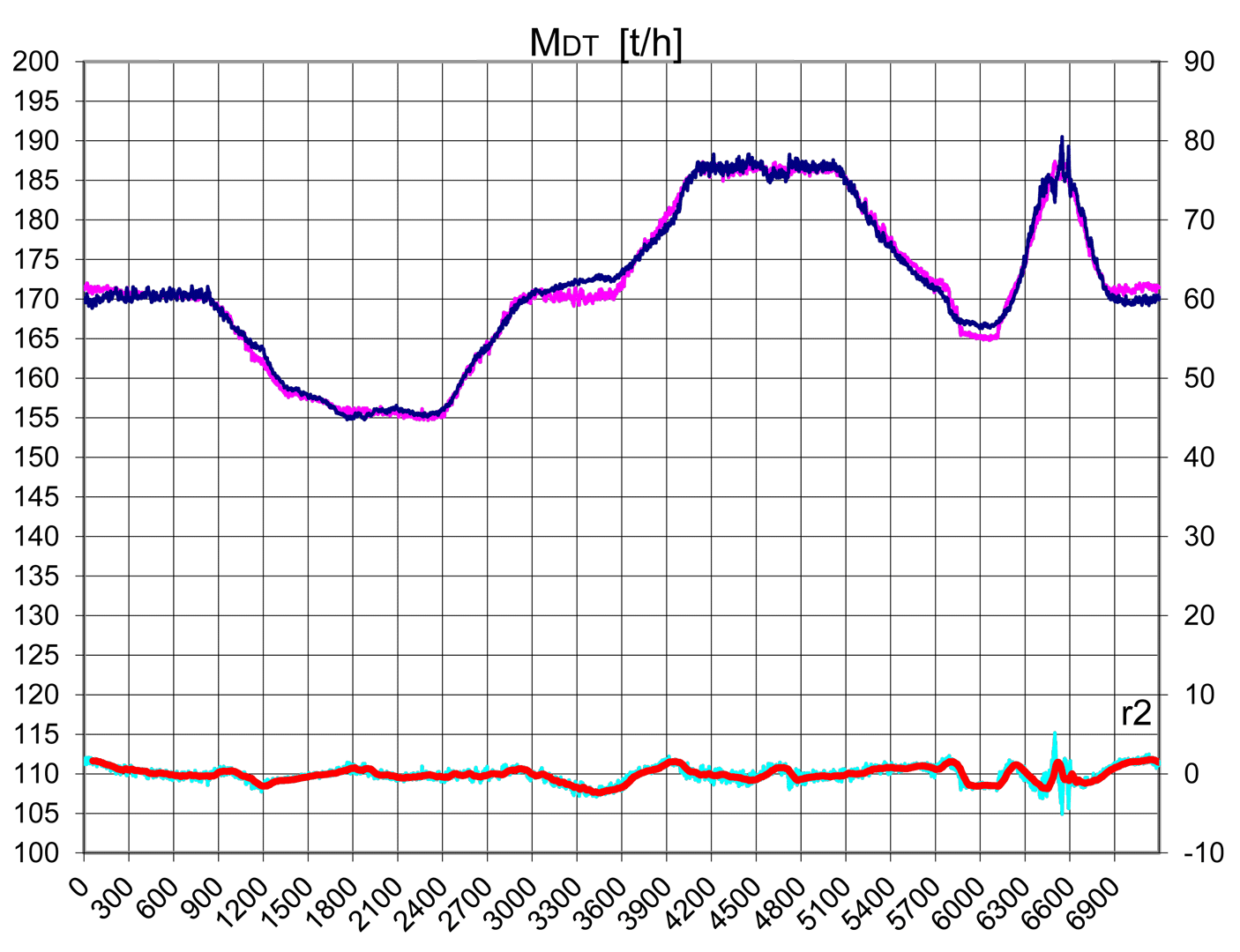
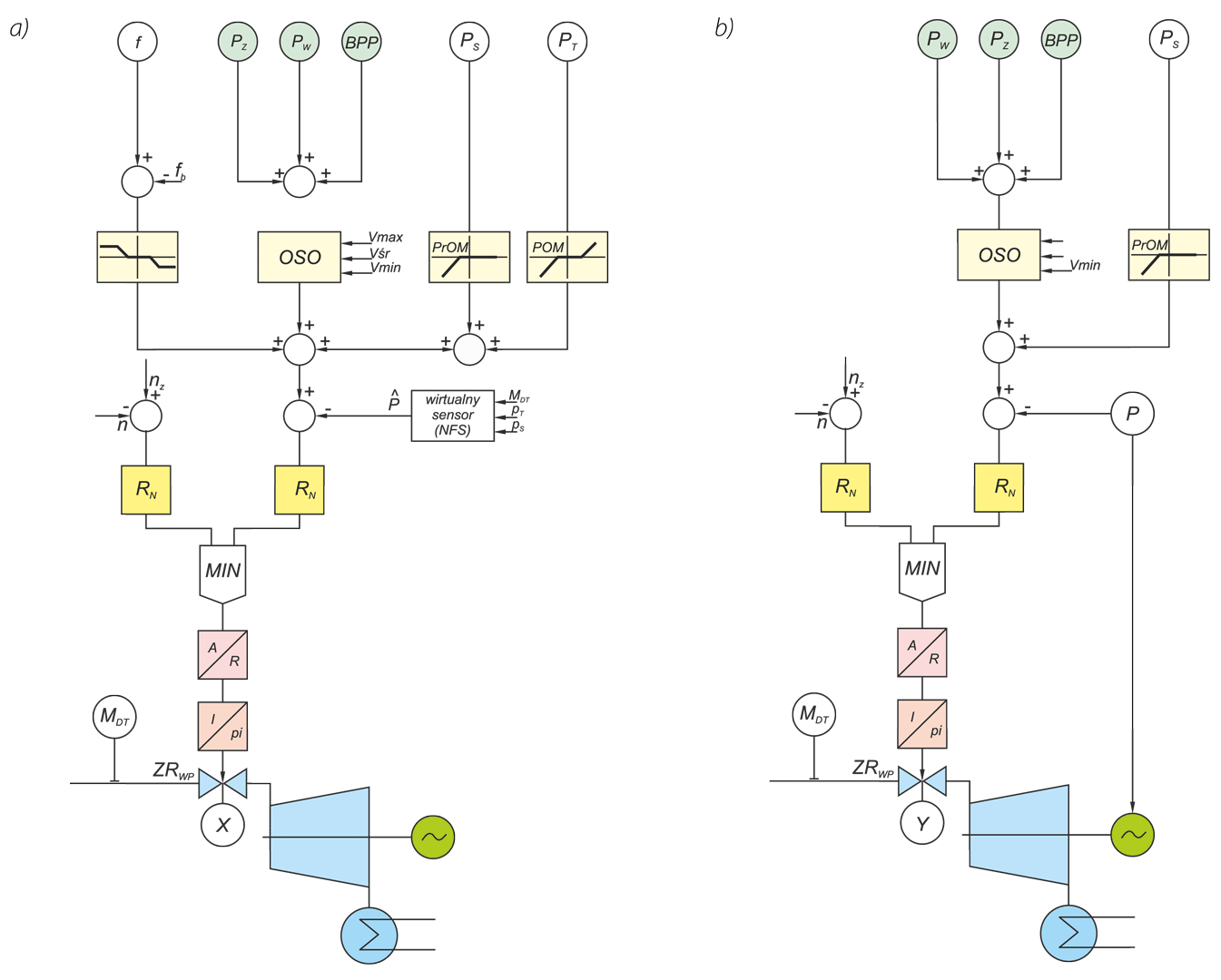
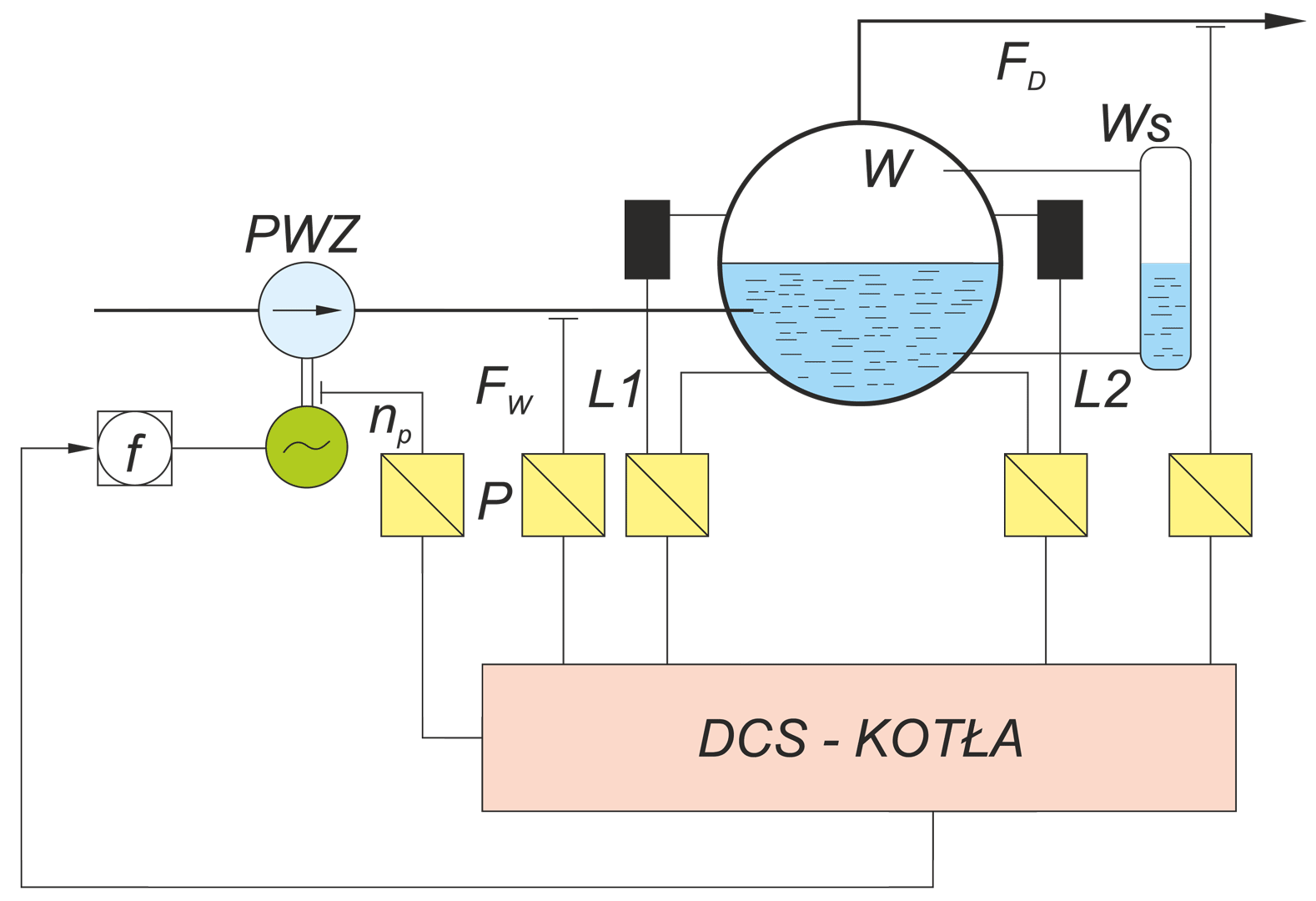
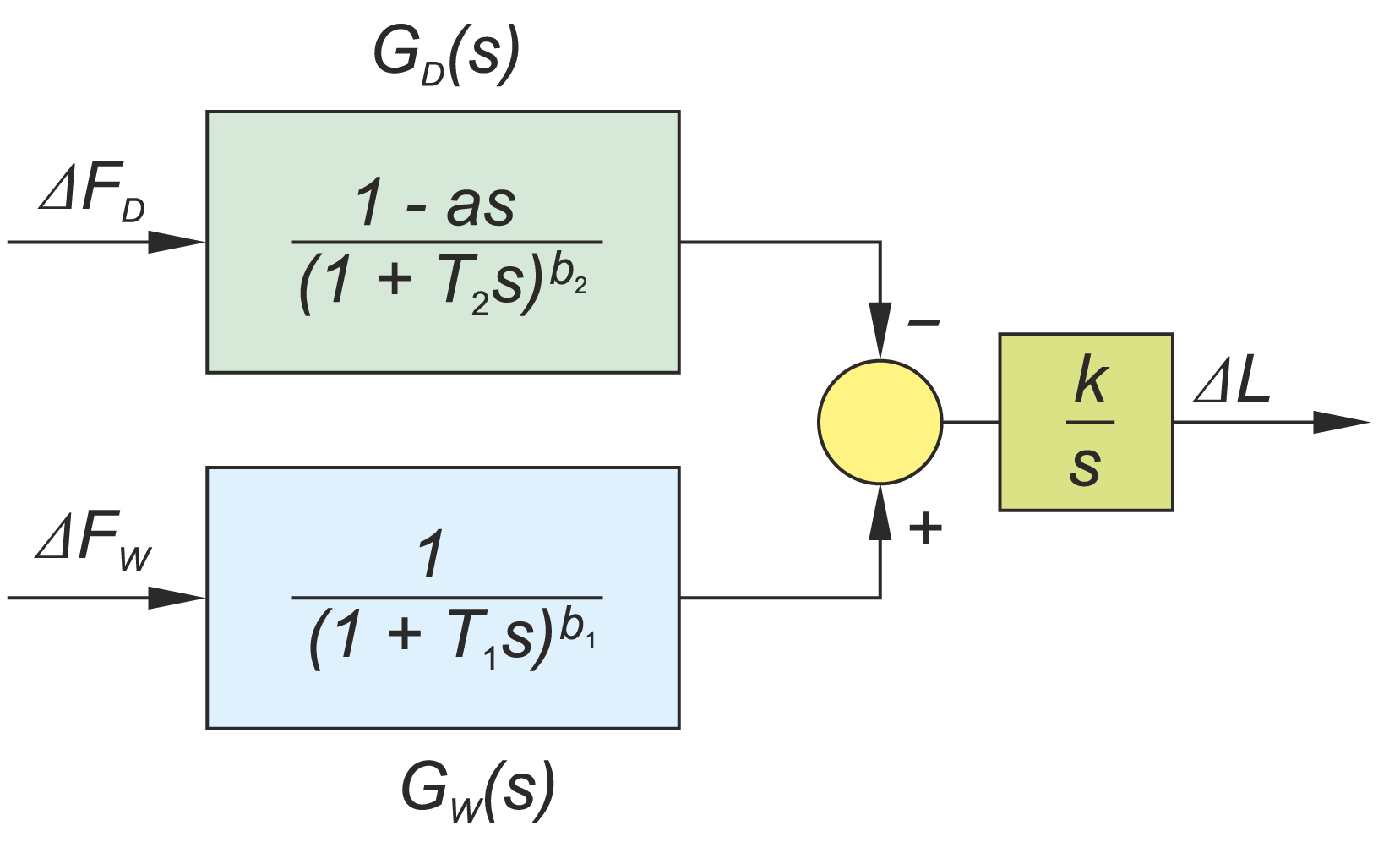
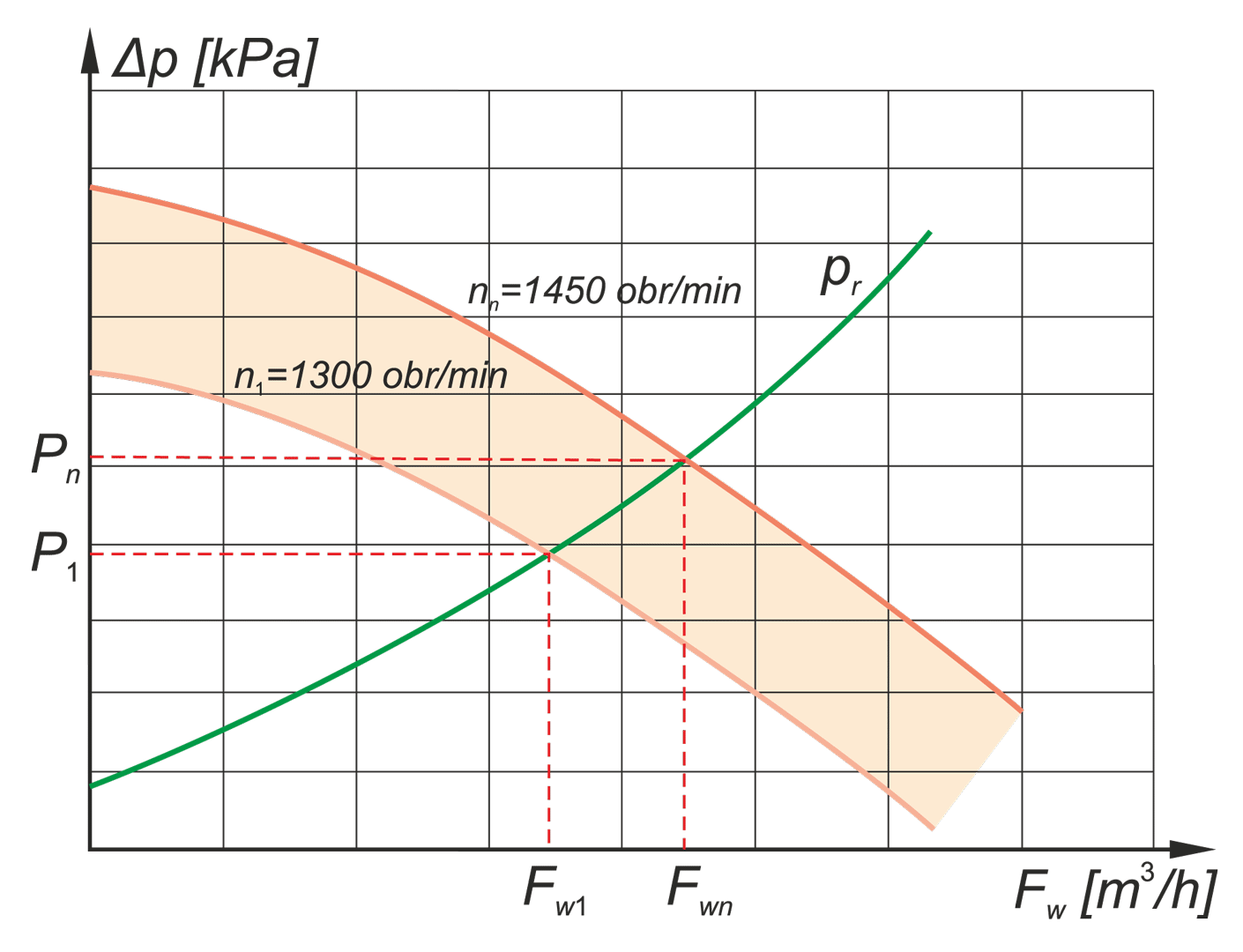
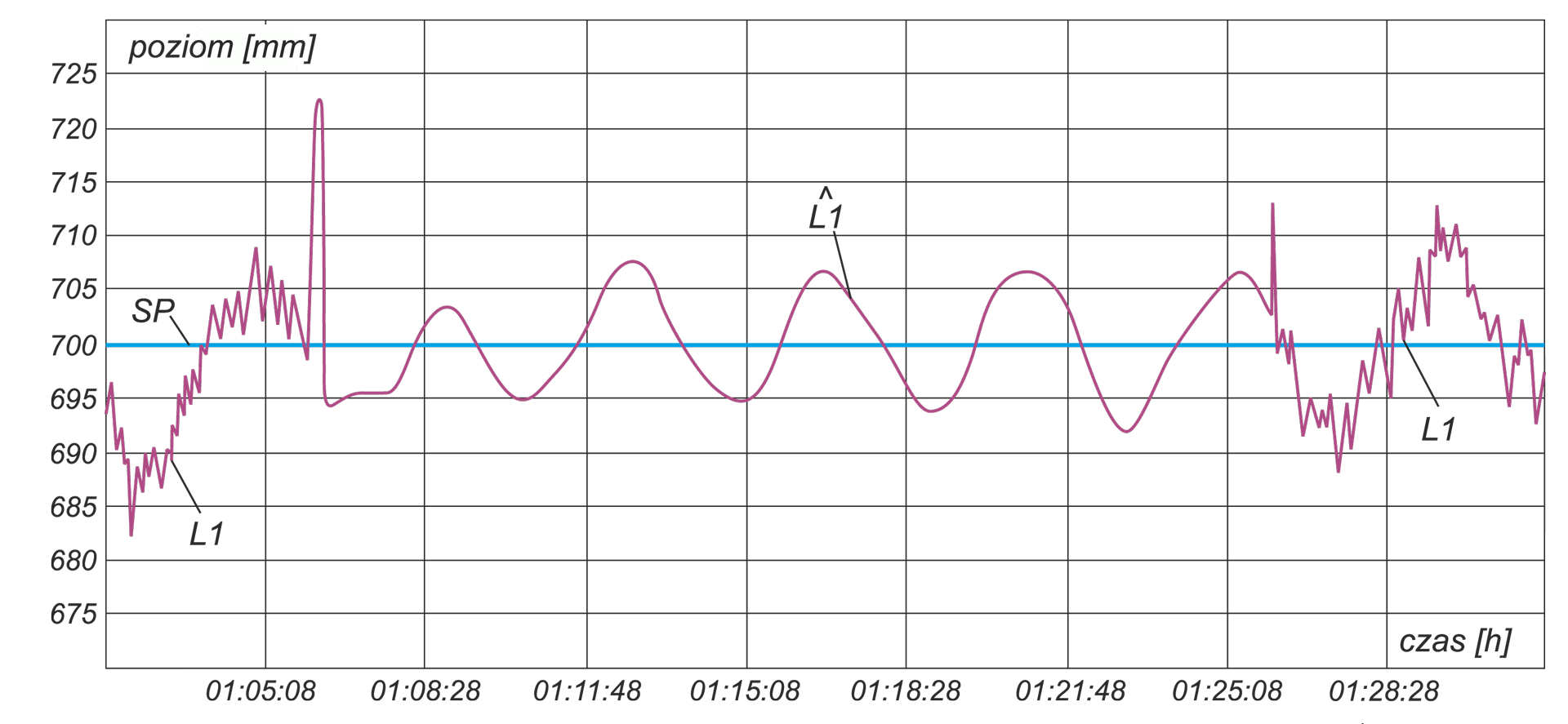
The paper describes operation of control systems in power unit. Particular attention has been paid to technical designs used in conventional power engineering and in renewable energy systems. A power unit has been characterised as multidimensional control system. Conception of diagnostic systems operating in on-line mode has been presented. Idea of fault tolerant control systems (tolerance related to failures in measurement circuits) has been illustrated by two examples: steam turbine control system and boiler drum water level control system.
Keywords
power unit, diagnostic, control systems
Fig.
Bilbiography
[1] R. Isermann (2006), “Fault Diagnosis Systems, An Introduction From Fault Detection to Fault Tolerance”, Springer-Verlag, New York.
[2] R.J. Patton, P.M. Frank, R.N. Clark (Red.) (200), “Issues of Fault Diagnosis for Dynamic Systems”, Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2000).
[3] M. Pawlak (2016), “Water Level Control System for a Boiler Drum of a Power Boiler Resistant to Measuring Track Damage.” Maintenance Problems, 2/2016 (101), str.135-144.
[4] Y. Yang, Y.Z. Lu (1991), “Sensor Fault Tolerant Control and its Application”, Symposium on Fault Detection Supervision and Safety for Technical Processes- SAFEPROCESS’91, Baden-Baden, Vol.1, 55-60.
[5] M. Pawlak, J.M. Koscielny, P. Wasiewicz (2015), ”Fault Tolerant Control Systems – Method of Increasing of Process Reliability and Safety”, Maintenance and Reliability 17 (3): 398–407.
[6] M. Pawlak (2016), “Performance Analysis of Power Boiler Drum Water Level Control Systems”, Acta Energetica 4/29 (2016) pp. 81–89.
[7] M. Pawlak (2015), ”Tolerowac uszkodzenia”, Chemia przemyslowa nr 3/2015 str.44-47.
[8] D. Lindsley (2005), “Power-plant control and instrumentation. The control of boilers and HRSG systems”, London: The Institution of Electrical Engineers.
[9] J. Rakowski (1976), ”Automatyka cieplnych urzadzen silowni”, Warszawa: Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne
[10]M. Blanke, M. Kinnaert, J. Lunze, M. Staroswiecki (2003), “Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Control”, Springer-Verlag, New York.
[11]M.J. Guerrero, T. Peng, W. Gui (2016), “Open-Switch Fault Diagnosis and Fault Tolerant for Matrix Converter With Finite Control Set-Model Predictive Control”, IEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, Vol. 63, No.9.
[12]P. Wasiewicz (2010), ”Sterowanie tolerujace uszkodzenia na bazie sterownikow PLC”, Pomiary Automatyka Robotyka, str.106 – 109.
[13]M. Witczak (2014), “Fault Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Control Strategies for Non-Linear Systems”. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
[14]J. Korbicz, J.M. Koscielny, Z. Kowalczuk, W. Cholewa (Red.) (2002), „Diagnostyka procesow. Modele, Metody sztucznej inteligencji, Zastosowania”, Wydawnictwo Naukowe Techniczne, Warszawa.
[15]J. Korbicz, J.M. Koscielny, Z. Kowalczuk, W. Cholewa (2004), “Fault, Diagnosis, Models, Artificial Intelligence, Applications”, Springer-Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg.
[16]J. M. Koscielny (2001),” Diagnostyka zautomatyzowanych procesow przemyslowych”, Akademicka Oficyna Wydawnicza EXIT, Warszawa.
[17]S. Won-Kee, K. Oh-Kyu, M.E. Lee (1997),” Fault Tolerant Model Based Predictive Control With Application to Boiler Systems”. IFAC Symposium on Fault Detection Supervision and Safety for Technical Processes- SAFEPROCESS’97, Kingston Upon Hull Vol.2. 1240-1245.
[18]A. Paoli, M. Sartini, S. Lafortuneb (2011),”Active Fault Tolerant Control of Discrete Event Systems Using Online Diagnostics”. Automatica, 47, 639-649.
[19]M. Pawlak (2018), “Diagnostics of Control Systems”, Automatyka Elektryka Zakłocenia, DOI: 10.17274/AEZ.2018.33.03, pp. 44-55, Vol.9 Nr 3 (33) 2018.