E-journal for electrical and electronic engineers
AUTOMATYKA, ELEKTRYKA, ZAKLOCENIA
(AUTOMATICS, ELECTROTECHNICS, DISTURBANCES)
Vol. 8, nr 3 (29) 2017
Artificial Neural Network in Forecasting the Churn Phenomena Among Costumers of IT and Power Supply Services
Przemyslaw WOJDA, Krzysztof NOWICKI
Abstract
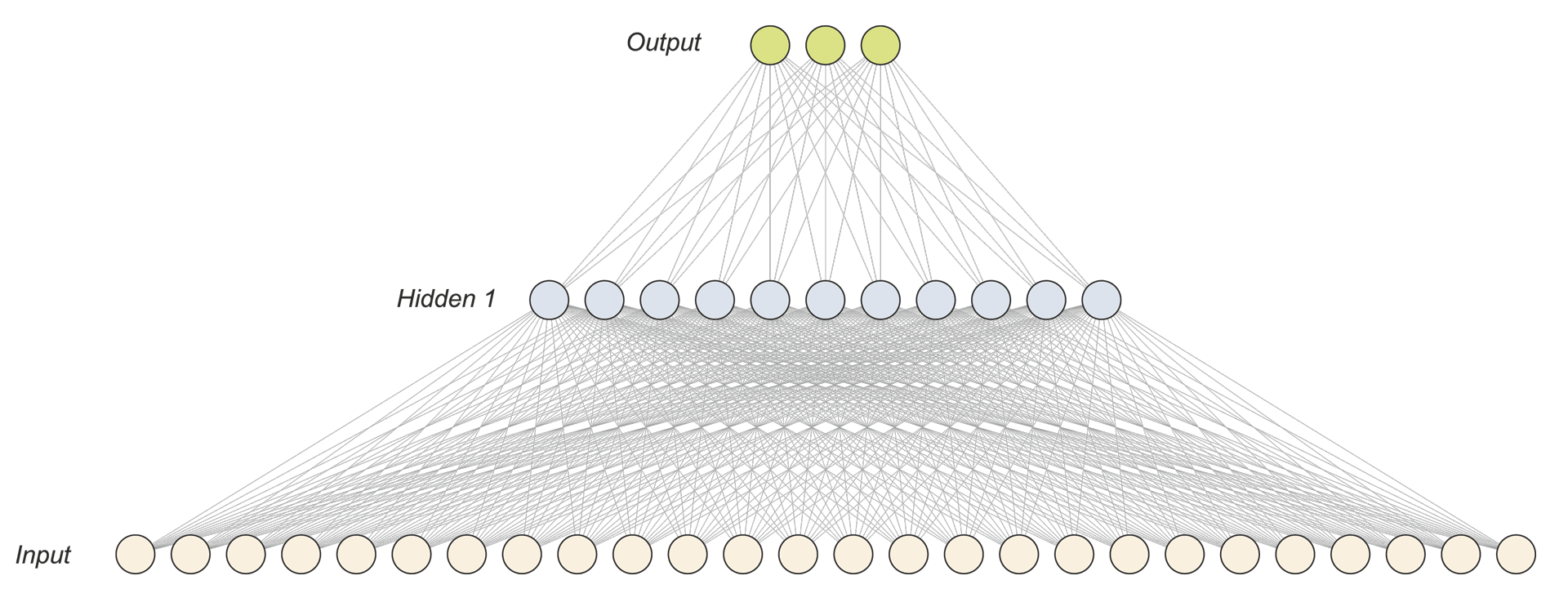
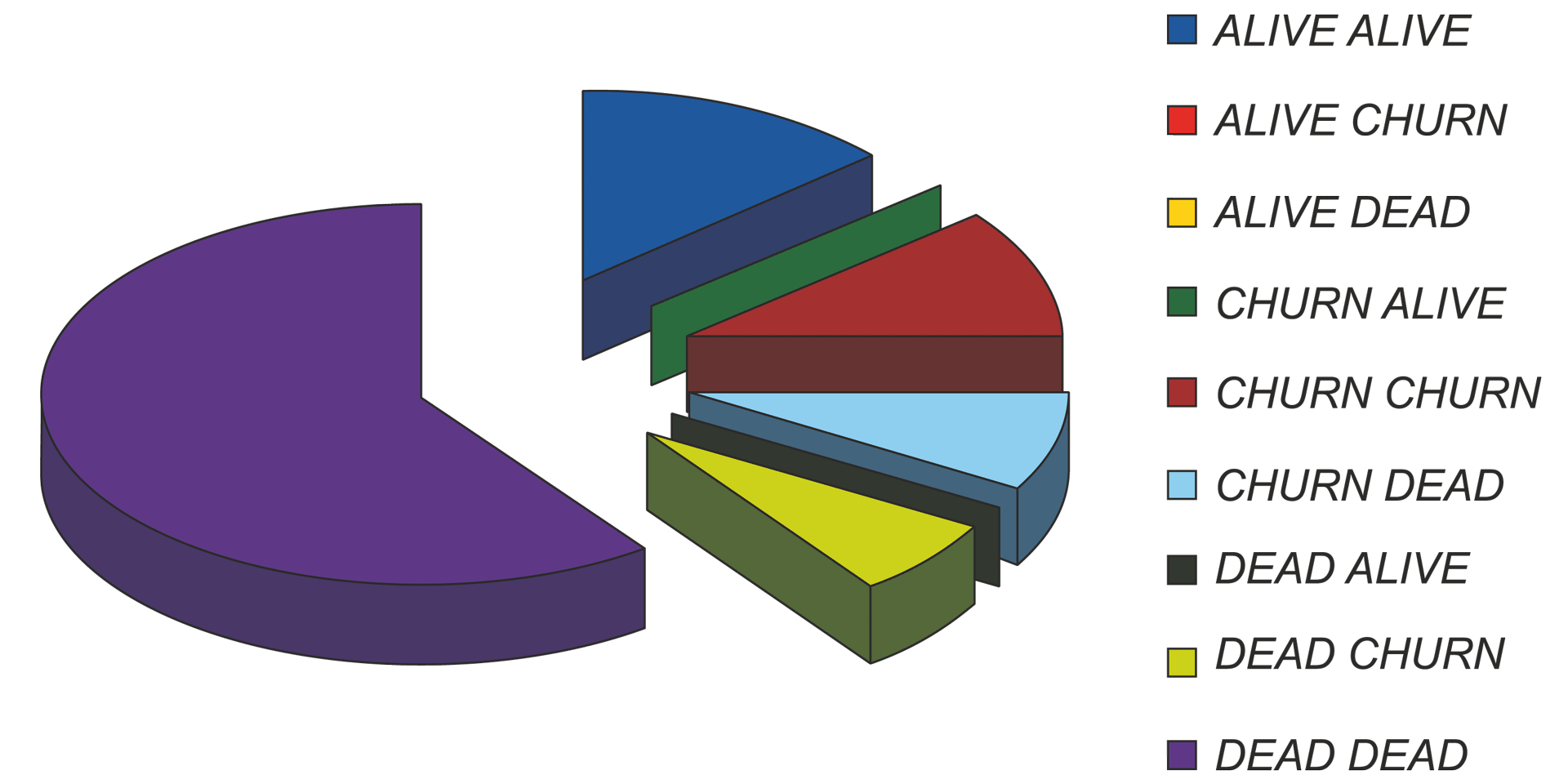
This paper presents an attempt to use an artificial neural network to investigate the churn phenomenon among the customers of a telecommunications operator. An attempt was made to create a data model based on the customer lifetime value (CLV) rather than on activity alone. A multilayered artificial neural network was used for the experiments. The results yielded a 99% successful identification rate for customers in no danger of leaving, while only 57% of those identified as in danger of leaving actually did so and stopped using the company's services.
Keywords
churn, ANN, CLV
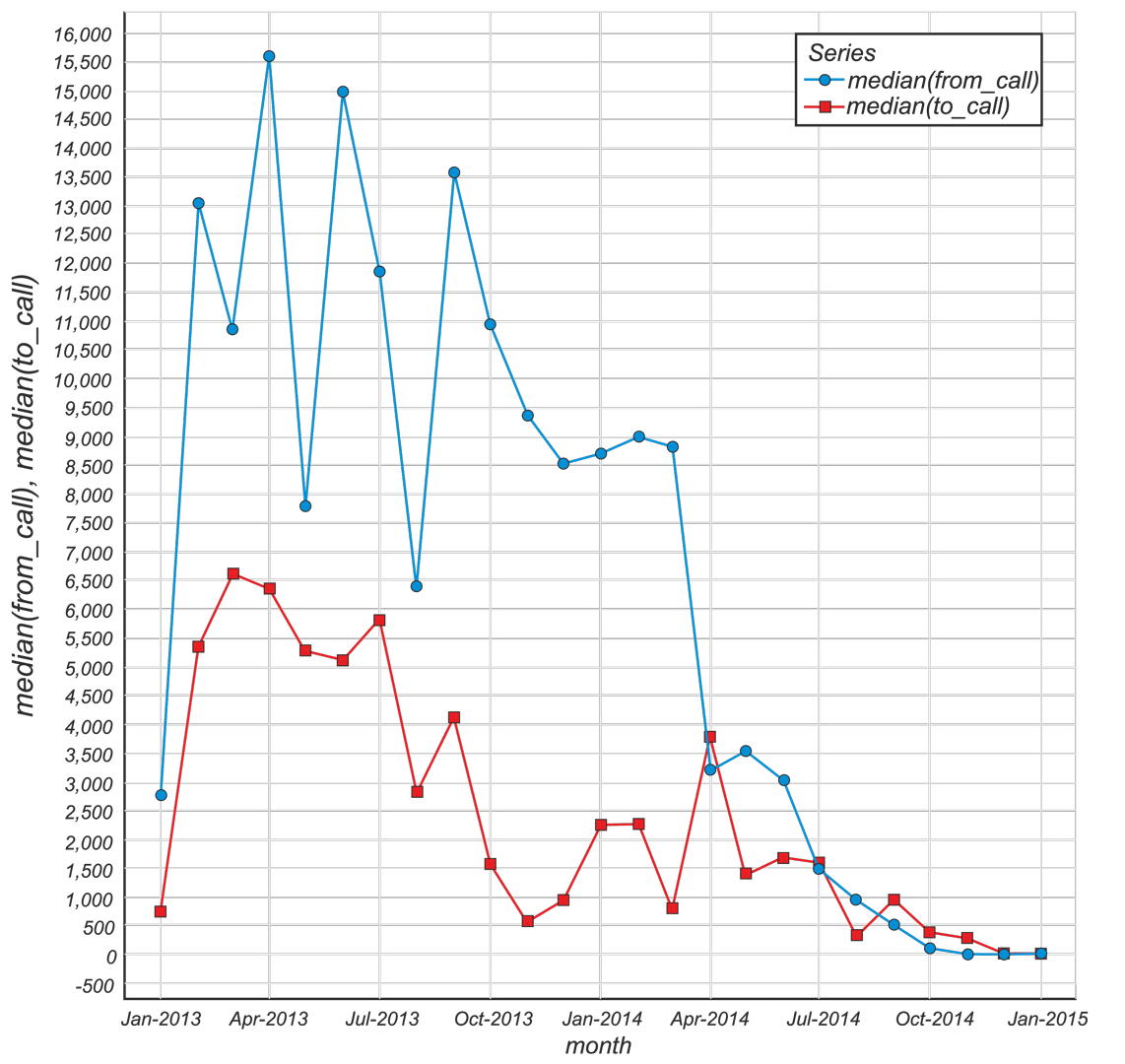
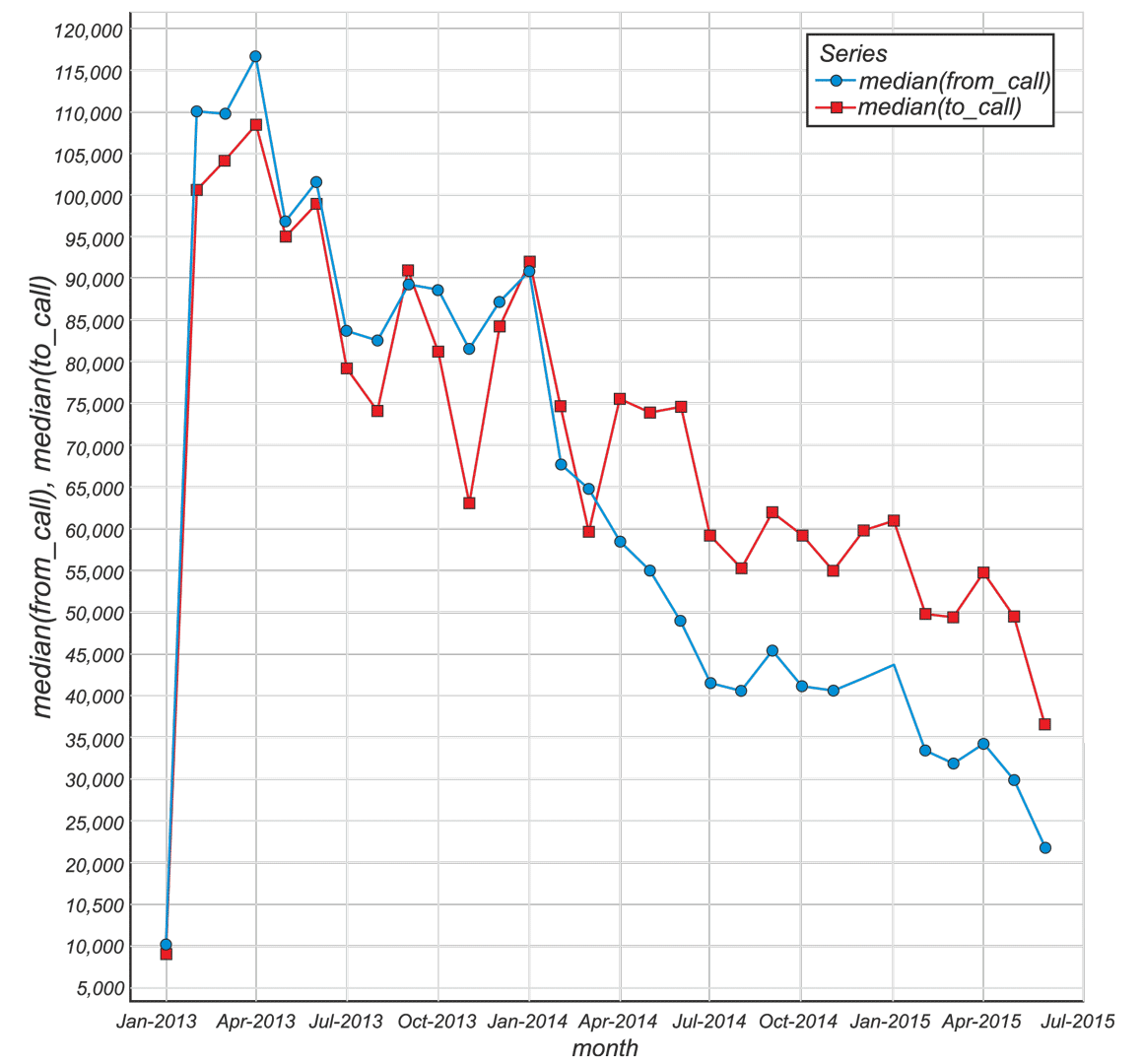
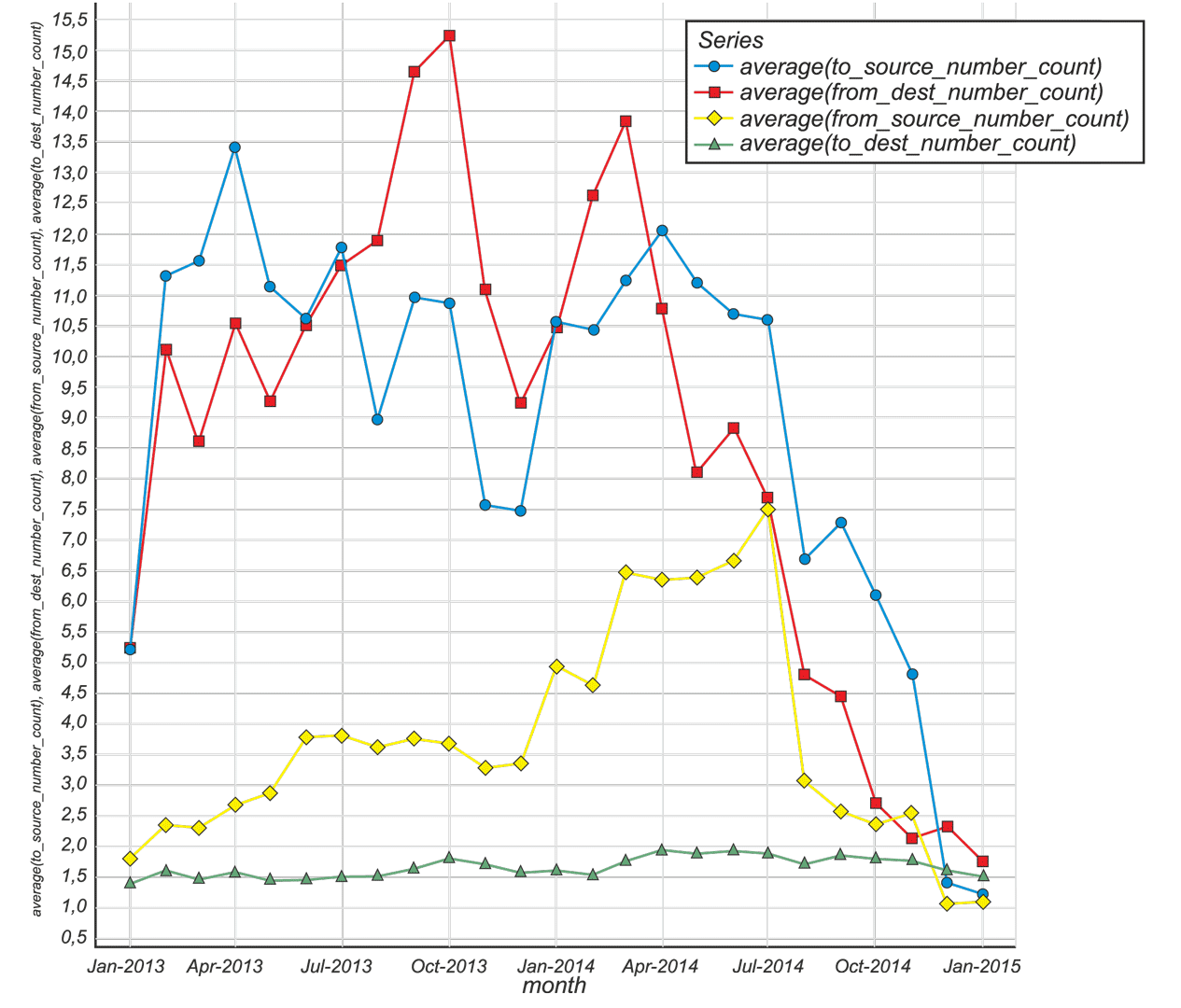
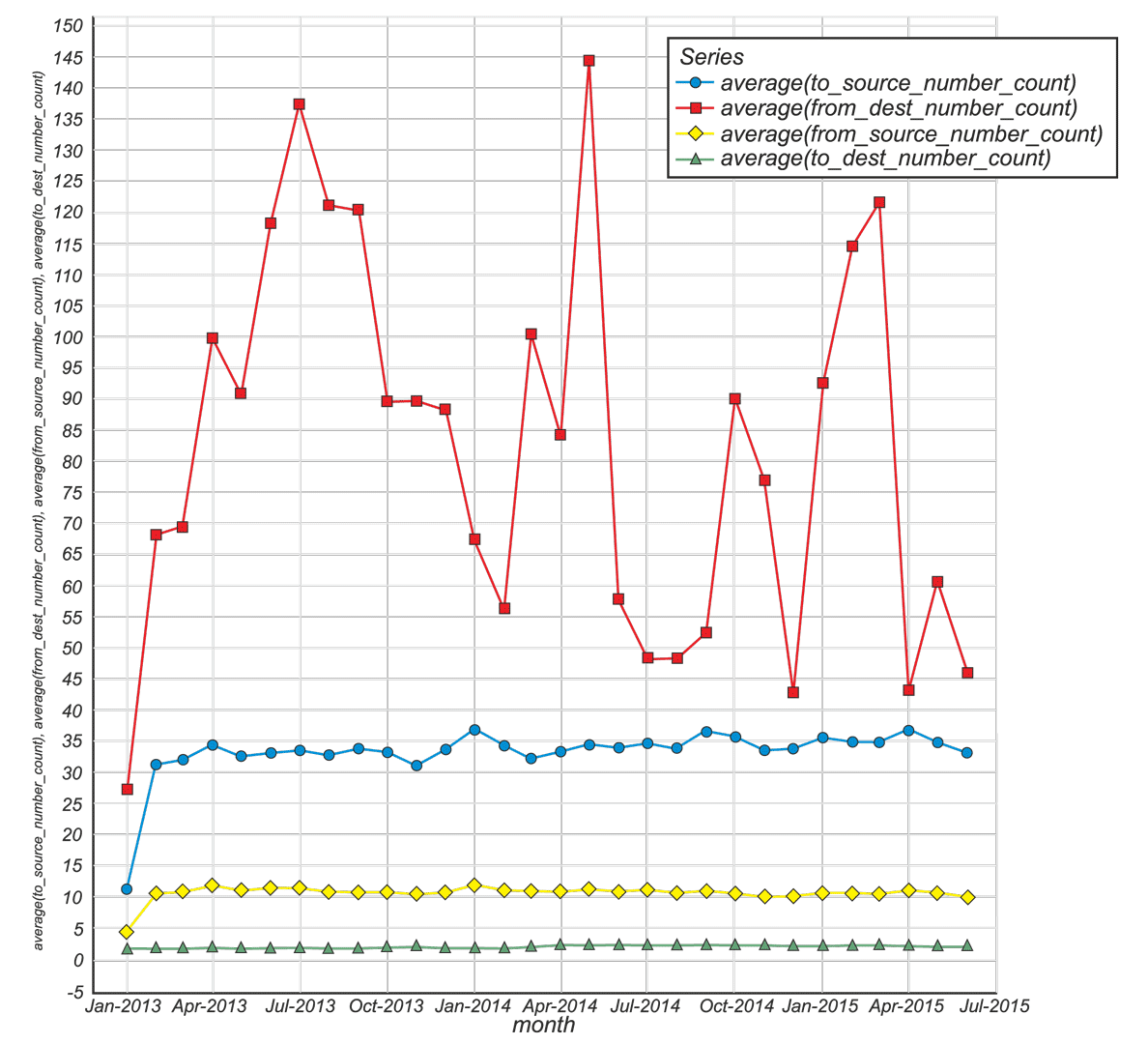
Fig.
Bilbiography
[1] J. Ljungehed (2017), “Predicting Customer Churn Using Recurrent Neural Networks”, Master in Computer Science, School of Computer Science and Communication, Stockholm, Sverige, 2017
[2] T. Vafeiadis, K.I. Diamantaras, G. Sarigiannidis, K.C. Chatzisavvas, “A comparison of machine learning techniques for customer churn prediction”, Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 55, pp. 1-9., 2015
[3] A. Ahmed, D.M. Linen, “A review and analysis of churn prediction methods for customer retention in telecom industries”, 4th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), IEEE Conference Publications, 2017
[4] Y. Zhang, J. Qi, H. Shu, Y. Li, “Predicting Churn Probability of Fixed-line Subscriber with Limited Information: A Data Mining Paradigm for Enterprise Computing”. In: A.M. Tjoa, L. Xu, S.S. Chaudhry (eds) “Research and Practical Issues of Enterprise Information Systems”. IFIP International Federation for Information Processing, vol 205. Springer, 2006
[5] M.B. Hosseni, M.J. Tarokh, “Customer Segmentation Using CLV Elements”, Journal of Service Science and Management, Vol.4, pp. 284-290, 2011
[6] K. Halicka, „Wykorzystanie sztucznych sieci neuronowych do prognozowania cen na giełdzie energii”, Rynek Energii, nr 1, 2010.
[7] R. Tadeusiewicz, „Sieci neuronowe”, Akademicka Oficyna Wydawnicza, Warszawa, 1993
[8] H. Abdi, “Coefficient of Variation”, Encyclopedia of Research Design, Thousand Oaks, CA, Sage, 2010
[9] J. Siderska, „Analiza możliwości zastosowania sieci neuronowych do modelowania wartości kapitału społecznego w firmach IT”, Economics and Management, no. 1, 2013.
[10] Y. Hifny, „Deep Learning Based on Manhattan Update Rule”, http://www.helwan.edu.eg/university/staff/~yhifny/publications/dnn_crf_MH.pdf, dostęp 7.12.2017
[11] Q. Liao, L.Z. Leibo, T. Poggio, „How Important Is Weight Symmetry in Backpropagation?”, https://arxiv.org/pdf/1510.05067.pdf,arXiv:1510.05067v4 [cs.LG] 4 Feb 2016,
[12] K. Gajowniczek, T. Ząbkowski, „Problemy modelowania rezygnacji klientów w telefonii komórkowej”, Metody Ilościowe w Badaniach Ekonomicznych, t. XIII/3, s. 65–78), 2012